Abstract
Background
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a genetic disorder caused by inactivating mutations in the TSC1 and TSC2 genes, causing overactivation of the mechanistic (previously referred to as mammalian) target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway in fetal life. The mTOR pathway plays a crucial role in several brain processes leading to TSC-related epilepsy, intellectual disability, and autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Pre-natal or early post-natal diagnosis of TSC is now possible in a growing number of pre-symptomatic infants.
Data sources
We searched PubMed for peer-reviewed publications published between January 2010 and April 2023 with the terms “tuberous sclerosis”, “autism”, or “autism spectrum disorder”,” animal models”, “preclinical studies”, “neurobiology”, and “treatment”.
Results
Prospective studies have highlighted that developmental trajectories in TSC infants who were later diagnosed with ASD already show motor, visual and social communication skills in the first year of life delays. Reliable genetic, cellular, electroencephalography and magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers can identify pre-symptomatic TSC infants at high risk for having autism and epilepsy.
Conclusions
Preventing epilepsy or improving therapy for seizures associated with prompt and tailored treatment strategies for autism in a sensitive developmental time window could have the potential to mitigate autistic symptoms in infants with TSC.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Washington: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
Maenner MJ, Shaw KA, Bakian AV, Bilder DA, Durkin MS, Esler A, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years-autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2018. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2021;70:1–16.
Tarver J, Palmer M, Webb S, Scott S, Slonims V, Simonoff E, et al. Child and parent outcomes following parent interventions for child emotional and behavioral problems in autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Autism. 2019;23:1630–44.
Wang SH, Zhang HT, Zou YY, Cheng SM, Zou XB, Chen KY. Efficacy and moderating factors of the Early Start Denver Model in Chinese toddlers with autism spectrum disorder: a longitudinal study. World J Pediatr. 2023;19:741–52.
Aaronson B, Estes A, Rogers SJ, Dawson G, Bernier R. The early start Denver model intervention and mu rhythm attenuation in autism spectrum disorders. J Autism Dev Disord. 2022;52:3304–13.
Cheroni C, Caporale N, Testa G. Autism spectrum disorder at the crossroad between genes and environment: contributions, convergences, and interactions in ASD developmental pathophysiology. Mol Autism. 2020;11:69.
Fernandez BA, Scherer SW. Syndromic autism spectrum disorders: moving from a clinically defined to a molecularly defined approach. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2017;19:353–71.
Lim HK, Yoon JH, Song M. Autism Spectrum disorder genes: disease-related networks and compensatory strategies. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022;15:922840.
Emberti Gialloreti L, Enea R, Di Micco V, Di Giovanni D, Curatolo P. Clustering analysis supports the detection of biological processes related to autism spectrum disorder. Genes (Basel). 2020;11:1476.
Specchio N, Di Micco V, Trivisano M, Ferretti A, Curatolo P. The epilepsy-autism spectrum disorder phenotype in the era of molecular genetics and precision therapy. Epilepsia. 2022;63:6–21.
Di Giovanni D, Enea R, Di Micco V, Benvenuto A, Curatolo P, Emberti GL. Using machine learning to explore shared genetic pathways and possible endophenotypes in autism spectrum disorder. Genes (Basel). 2023;14:313.
Emberti Gialloreti L, Curatolo P. Autism spectrum disorder: why do we know so little? Front Neurol. 2018;9:670.
Hulbert SW, Jiang YH. Monogenic mouse models of autism spectrum disorders: common mechanisms and missing links. Neuroscience. 2016;321:3–23.
Benvenuto A, Moavero R, Alessandrelli R, Manzi B, Curatolo P. Syndromic autism: causes and pathogenetic pathways. World J Pediatr. 2009;5:169–76.
Curatolo P, Bombardieri R, Jozwiak S. Tuberous sclerosis. Lancet. 2008;372:657–68.
Curatolo P, Specchio N, Aronica E. Advances in the genetics and neuropathology of tuberous sclerosis complex: edging closer to targeted therapy. Lancet Neurol. 2022;21:843–56.
de Vries PJ, Wilde L, de Vries MC, Moavero R, Pearson DA, Curatolo P. A clinical update on tuberous sclerosis complex-associated neuropsychiatric disorders (TAND). Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2018;178:309–20.
Northrup H, Aronow ME, Bebin EM, Bissler J, Darling TN, de Vries PJ, et al. Updated international tuberous sclerosis complex diagnostic criteria and surveillance and management recommendations. Pediatr Neurol. 2021;123:50–66.
Canevini MP, Kotulska-Jozwiak K, Curatolo P, La Briola F, Peron A, Słowińska M, et al. Current concepts on epilepsy management in tuberous sclerosis complex. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2018;178:299–308.
Dragoumi P, O’Callaghan F, Zafeiriou DI. Diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis complex in the fetus. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2018;22:1027–34.
Davis PE, Filip-Dhima R, Sideridis G, Peters JM, Au KS, Northrup H, et al. Presentation and diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis complex in infants. Pediatrics. 2017;140:e20164040.
Numis AL, Major P, Montenegro MA, Muzykewicz DA, Pulsifer MB, Thiele EA. Identification of risk factors for autism spectrum disorders in tuberous sclerosis complex. Neurology. 2011;76:981–7.
Kingswood JC, D’Augères GB, Belousova E, Ferreira JC, Carter T, Castellana R, et al. TuberOus SClerosis registry to increase disease Awareness (TOSCA)–baseline data on 2093 patients. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017;12:2.
Curatolo P, Moavero R, de Vries PJ. Neurological and neuropsychiatric aspects of tuberous sclerosis complex. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14:733–45.
Chu-Shore CJ, Major P, Camposano S, Muzykewicz D, Thiele EA. The natural history of epilepsy in tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsia. 2010;51:1236–41.
Mitchell RA, Mitchell M, Williams K. The autism spectrum disorder phenotype in children with tuberous sclerosis complex: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2022;64:1214–29.
Ebert DH, Greenberg ME. Activity-dependent neuronal signalling and autism spectrum disorder. Nature. 2013;493:327–37.
Jiang CC, Lin LS, Long S, Ke XY, Fukunaga K, Lu YM, et al. Signalling pathways in autism spectrum disorder: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7:229.
Capal JK, Bernardino-Cuesta B, Horn PS, Murray D, Byars AW, Bing NM, et al. Influence of seizures on early development in tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsy Behav. 2017;70:245–52.
Nabbout R, Belousova E, Benedik MP, Carter T, Cottin V, Curatolo P, et al. Epilepsy in tuberous sclerosis complex: findings from the TOSCA study. Epilepsia Open. 2019;4:73–84.
Specchio N, Pietrafusa N, Trivisano M, Moavero R, De Palma L, Ferretti A, et al. Autism and epilepsy in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex. Front Neurol. 2020;11:639.
Critchley M, Earl C. Tuberose sclerosis and allied conditions. Brain. 1932;55:311–46.
Kanner L. Autistic disturbances of affective contact. Nerv Child. 1943;2:217–50.
Moss J, Howlin P. Autism spectrum disorders in genetic syndromes: implications for diagnosis, intervention and understanding the wider autism spectrum disorder population. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2009;53:852–73.
Waltereit R, Japs B, Schneider M, de Vries PJ, Bartsch D. Epilepsy and Tsc2 haploinsufficiency lead to autistic-like social deficit behaviors in rats. Behav Genet. 2011;41:364–72.
Nguyen LH, Mahadeo T, Bordey A. mTOR hyperactivity levels influence the severity of epilepsy and associated neuropathology in an experimental model of tuberous sclerosis complex and focal cortical dysplasia. J Neurosci. 2019;39:2762–73.
Aronica E, Specchio N, Luinenburg MJ, Curatolo P. Epileptogenesis in tuberous sclerosis complex-related developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. Brain. 2023;146:2694–710.
Chaudry S, Vasudevan N. mTOR-dependent spine dynamics in autism. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022;15:877609.
Czapski GA, Babiec L, Jęśko H, Gąssowska-Dobrowolska M, Cieślik M, Matuszewska M, et al. Synaptic alterations in a transgenic model of tuberous sclerosis complex: relevance to autism spectrum disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:10058.
Pagani M, Barsotti N, Bertero A, Trakoshis S, Ulysse L, Locarno A, et al. mTOR-related synaptic pathology causes autism spectrum disorder-associated functional hyperconnectivity. Nat Commun. 2021;12:6084.
Rosina E, Battan B, Siracusano M, Di Criscio L, Hollis F, Pacini L, et al. Disruption of mTOR and MAPK pathways correlates with severity in idiopathic autism. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9:50.
Mühlebner A, Bongaarts A, Sarnat HB, Scholl T, Aronica E. New insights into a spectrum of developmental malformations related to mTOR dysregulations: challenges and perspectives. J Anat. 2019;235:521–42.
Curatolo P, Moavero R, van Scheppingen J, Aronica E. mTOR dysregulation and tuberous sclerosis-related epilepsy. Expert Rev Neurother. 2018;18:185–201.
Bassetti D, Luhmann HJ, Kirischuk S. Effects of mutations in TSC genes on neurodevelopment and synaptic transmission. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:7273.
Bozzi Y, Provenzano G, Casarosa S. Neurobiological bases of autism-epilepsy comorbidity: a focus on excitation/inhibition imbalance. Eur J Neurosci. 2018;47:534–48.
Gąssowska-Dobrowolska M, Czapski GA, Cieślik M, Zajdel K, Frontczak-Baniewicz M, Babiec L, et al. Microtubule cytoskeletal network alterations in a transgenic model of tuberous sclerosis complex: relevance to autism spectrum disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:7303.
Ebrahimi-Fakhari D, Saffari A, Wahlster L, Di Nardo A, Turner D, Lewis TL, et al. Impaired mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy in neuronal models of tuberous sclerosis complex. Cell Rep. 2016;17:1053–70.
Fu C, Cawthon B, Clinkscales W, Bruce A, Winzenburger P, Ess KC. GABAergic interneuron development and function is modulated by the Tsc1 gene. Cereb Cortex. 2012;22:2111–9.
Ka M, Smith AL, Kim WY. MTOR controls genesis and autophagy of GABAergic interneurons during brain development. Autophagy. 2017;13:1348–63.
Amegandjin CA, Choudhury M, Jadhav V, Carriço JN, Quintal A, Berryer M, et al. Sensitive period for rescuing parvalbumin interneurons connectivity and social behavior deficits caused by TSC1 loss. Nat Commun. 2021;12:3653.
Yang J, Yang X, Tang K. Interneuron development and dysfunction. FEBS J. 2022;289:2318–36.
Iannone AF, De Marco García NV. The emergence of network activity patterns in the somatosensory cortex-an early window to autism spectrum disorders. Neuroscience. 2021;466:298–309.
Eichmüller OL, Corsini NS, Vértesy Á, Morassut I, Scholl T, Gruber VE, et al. Amplification of human interneuron progenitors promotes brain tumors and neurological defects. Science. 2022;375:eabf5546.
Katsarou AM, Moshé SL, Galanopoulou AS. Interneuronopathies and their role in early life epilepsies and neurodevelopmental disorders. Epilepsia Open. 2017;2:284–306.
Cherubini E, Di Cristo G, Avoli M. Dysregulation of GABAergic signaling in neurodevelomental disorders: targeting cation-chloride co-transporters to re-establish a proper E/I balance. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:813441.
Powell EM. Interneuron development and epilepsy: early genetic defects cause long-term consequences in seizures and susceptibility. Epilepsy Curr. 2013;13:172–6.
Milovanovic M, Grujicic R. Electroencephalography in assessment of autism spectrum disorders: a review. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:686021.
Powell EM, Campbell DB, Stanwood GD, Davis C, Noebels JL, Levitt P. Genetic disruption of cortical interneuron development causes region- and GABA cell type-specific deficits, epilepsy, and behavioral dysfunction. J Neurosci. 2003;23:622–31.
Dufour BD, McBride E, Bartley T, Juarez P, Martínez-Cerdeño V. Distinct patterns of GABAergic interneuron pathology in autism are associated with intellectual impairment and stereotypic behaviors. Autism. 2023;27:1730–45.
Righes Marafiga J, Vendramin Pasquetti M, Calcagnotto ME. GABAergic interneurons in epilepsy: more than a simple change in inhibition. Epilepsy Behav. 2021;121:106935.
Ruffolo G, Iyer A, Cifelli P, Roseti C, Mühlebner A, van Scheppingen J, et al. Functional aspects of early brain development are preserved in tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) epileptogenic lesions. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;95:93–101.
Vezzani A, Aronica E, Mazarati A, Pittman QJ. Epilepsy and brain inflammation. Exp Neurol. 2013;244:11–21.
Vezzani A, Ravizza T, Bedner P, Aronica E, Steinhäuser C, Boison D. Astrocytes in the initiation and progression of epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022;18:707–22.
Matta SM, Hill-Yardin EL, Crack PJ. The influence of neuroinflammation in autism spectrum disorder. Brain Behav Immun. 2019;79:75–90.
Robinson-Agramonte MLA, Noris García E, Fraga Guerra J, Vega Hurtado Y, Antonucci N, Semprún-Hernández N, et al. Immune dysregulation in autism spectrum disorder: what do we know about It? Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:3033.
Zahra A, Wang Y, Wang Q, Wu J. Shared etiology in autism spectrum disorder and epilepsy with functional disability. Behav Neurol. 2022;2022:5893519.
Weichhart T, Hengstschläger M, Linke M. Regulation of innate immune cell function by mTOR. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15:599–614.
Jones RG, Pearce EJ. MenTORing immunity: mTOR signaling in the development and function of tissue-resident immune cells. Immunity. 2017;46:730–42.
Boer K, Crino PB, Gorter JA, Nellist M, Jansen FE, Spliet WGM, et al. Gene expression analysis of tuberous sclerosis complex cortical tubers reveals increased expression of adhesion and inflammatory factors. Brain Pathol. 2010;20:704–19.
Mills JD, Iyer AM, van Scheppingen J, Bongaarts A, Anink JJ, Janssen B, et al. Coding and small non-coding transcriptional landscape of tuberous sclerosis complex cortical tubers: implications for pathophysiology and treatment. Sci Rep. 2017;7:8089.
Gruber VE, Luinenburg MJ, Colleselli K, Endmayr V, Anink JJ, Zimmer TS, et al. Increased expression of complement components in tuberous sclerosis complex and focal cortical dysplasia type 2B brain lesions. Epilepsia. 2022;63:364–74.
Zimmer TS, Korotkov A, Zwakenberg S, Jansen FE, Zwartkruis FJT, Rensing NR, et al. Upregulation of the pathogenic transcription factor SPI1/PU.1 in tuberous sclerosis complex and focal cortical dysplasia by oxidative stress. Brain Pathol. 2021;31:e12949.
Arena A, Zimmer TS, van Scheppingen J, Korotkov A, Anink JJ, Mühlebner A, et al. Oxidative stress and inflammation in a spectrum of epileptogenic cortical malformations: molecular insights into their interdependence. Brain Pathol. 2019;29:351–65.
Fuso A, Iyer AM, van Scheppingen J, Maccarrone M, Scholl T, Hainfellner JA, et al. Promoter-specific hypomethylation correlates with IL-1β overexpression in tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC). J Mol Neurosci. 2016;59:464–70.
Prabowo AS, Anink JJ, Lammens M, Nellist M, van den Ouweland AMW, Adle-Biassette H, et al. Fetal brain lesions in tuberous sclerosis complex: TORC1 activation and inflammation. Brain Pathol. 2013;23:45–59.
Alfano V, Romagnolo A, Mills JD, Cifelli P, Gaeta A, Morano A, et al. Unexpected effect of IL-1β on the function of GABAA receptors in pediatric focal cortical dysplasia. Brain Sci Brain Sci. 2022;12:807.
Ruffolo G, Alfano V, Romagnolo A, Zimmer T, Mills JD, Cifelli P, et al. GABAA receptor function is enhanced by Interleukin-10 in human epileptogenic gangliogliomas and its effect is counteracted by Interleukin-1β. Sci Rep. 2022;12:17956.
Palma E, Ruffolo G, Cifelli P, Roseti C, van Vliet EA, Aronica E. Modulation of GABAA receptors in the treatment of epilepsy. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23:5563–8.
Usui N, Kobayashi H, Shimada S. Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of autism spectrum disorder. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:5487.
Terrone G, Balosso S, Pauletti A, Ravizza T, Vezzani A. Inflammation and reactive oxygen species as disease modifiers in epilepsy. Neuropharmacology. 2020;167:107742.
Zimmer TS, Ciriminna G, Arena A, Anink JJ, Korotkov A, Jansen FE, et al. Chronic activation of anti-oxidant pathways and iron accumulation in epileptogenic malformations. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2020;46:546–63.
Walma DAC, Yamada KM. The extracellular matrix in development. Development. 2020;147:dev175596.
Lu P, Takai K, Weaver VM, Werb Z. Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011;3:a005058.
Dityatev A, Fellin T. Extracellular matrix in plasticity and epileptogenesis. Neuron Glia Biol. 2008;4:235–47.
Leifeld J, Förster E, Reiss G, Hamad MIK. Considering the role of extracellular matrix molecules, in particular reelin, in granule cell dispersion related to temporal lobe epilepsy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:917575.
Korotkov A, Luinenburg MJ, Romagnolo A, Zimmer TS, van Scheppingen J, Bongaarts A, et al. Down-regulation of the brain-specific cell-adhesion molecule contactin-3 in tuberous sclerosis complex during the early postnatal period. J Neurodev Disord. 2022;14:8.
Broekaart DWM, Scheppingen J, Anink JJ, Wierts L, Hof B, Jansen FE, et al. Increased matrix metalloproteinases expression in tuberous sclerosis complex: modulation by microRNA 146a and 147b in vitro. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2020;46:142–59.
Broekaart DW, Bertran A, Jia S, Korotkov A, Senkov O, Bongaarts A, et al. The matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor IPR-179 has antiseizure and antiepileptogenic effects. J Clin Invest. 2021;131:e138332.
Rogers SL, Rankin-Gee E, Risbud RM, Porter BE, Marsh ED. Normal development of the perineuronal net in humans; in patients with and without epilepsy. Neuroscience. 2018;384:350–60.
Chaunsali L, Tewari BP, Sontheimer H. Perineuronal net dynamics in the pathophysiology of epilepsy. Epilepsy Curr. 2021;21:273–81.
Prohl AK, Scherrer B, Tomas-Fernandez X, Davis PE, Filip-Dhima R, Prabhu SP, et al. Early white matter development is abnormal in tuberous sclerosis complex patients who develop autism spectrum disorder. J Neurodev Disord. 2019;11:36.
Gruber VE, Lang J, Endmayr V, Diehm R, Pimpel B, Glatter S, et al. Impaired myelin production due to an intrinsic failure of oligodendrocytes in mTORpathies. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2021;47:812–25.
Mühlebner A, van Scheppingen J, de Neef A, Bongaarts A, Zimmer TS, Mills JD, et al. Myelin pathology beyond white matter in tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) cortical tubers. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2020;79:1054–64.
Zonouzi M, Berger D, Jokhi V, Kedaigle A, Lichtman J, Arlotta P. Individual oligodendrocytes show bias for inhibitory axons in the neocortex. Cell Rep. 2019;27:2799–808.e3.
Fang LP, Zhao N, Caudal LC, Chang HF, Zhao R, Lin CH, et al. Impaired bidirectional communication between interneurons and oligodendrocyte precursor cells affects social cognitive behavior. Nat Commun. 2022;13:1394.
Galvez-Contreras AY, Zarate-Lopez D, Torres-Chavez AL, Gonzalez-Perez O. Role of oligodendrocytes and myelin in the pathophysiology of autism spectrum disorder. Brain Sci. 2020;10:951.
Bromfield EB, Cavazos JE, Sirven JI. An introduction to epilepsy. London: Routledge; 2006.
Specchio N, Curatolo P. Developmental and epileptic encephalopathies: what we do and do not know. Brain. 2021;144:32–43.
Scheffer IE, Liao J. Deciphering the concepts behind “Epileptic encephalopathy” and “Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy”. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2020;24:11–4.
Specchio N, Wirrell EC, Scheffer IE, Nabbout R, Riney K, Samia P, et al. International league against epilepsy classification and definition of epilepsy syndromes with onset in childhood: position paper by the ILAE task force on nosology and definitions. Epilepsia. 2022;63:1398–442.
Moavero R, Mühlebner A, Luinenburg MJ, Craiu D, Aronica E, Curatolo P. Genetic pathogenesis of the epileptogenic lesions in tuberous sclerosis complex: therapeutic targeting of the mTOR pathway. Epilepsy Behav. 2022;131:107713.
Ehninger D, Han S, Shilyansky C, Zhou Y, Li W, Kwiatkowski DJ, et al. Reversal of learning deficits in a Tsc2+/- mouse model of tuberous sclerosis. Nat Med. 2008;14:843–8.
Talos DM, Sun H, Kosaras B, Joseph A, Folkerth RD, Poduri A, et al. Altered inhibition in tuberous sclerosis and type IIb cortical dysplasia. Ann Neurol. 2012;71:539–51.
Sato A, Kasai S, Kobayashi T, Takamatsu Y, Hino O, Ikeda K, et al. Rapamycin reverses impaired social interaction in mouse models of tuberous sclerosis complex. Nat Commun. 2012;3:1292.
Way SW, Rozas NS, Wu HC, McKenna J, Reith RM, Hashmi SS, et al. The differential effects of prenatal and/or postnatal rapamycin on neurodevelopmental defects and cognition in a neuroglial mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:3226–36.
Tsai PT, Hull C, Chu Y, Greene-Colozzi E, Sadowski AR, Leech JM, et al. Autistic-like behaviour and cerebellar dysfunction in Purkinje cell Tsc1 mutant mice. Nature. 2012;488:647–51.
Schneider M, de Vries PJ, Schönig K, Rößner V, Waltereit R. mTOR inhibitor reverses autistic-like social deficit behaviours in adult rats with both Tsc2 haploinsufficiency and developmental status epilepticus. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017;267:455–63.
Petrasek T, Vojtechova I, Klovrza O, Tuckova K, Vejmola C, Rak J, et al. mTOR inhibitor improves autistic-like behaviors related to Tsc2 haploinsufficiency but not following developmental status epilepticus. J Neurodev Disord. 2021;13:14.
Koike-Kumagai M, Fujimoto M, Wataya-Kaneda M. Sirolimus relieves seizures and neuropsychiatric symptoms via changes of microglial polarity in tuberous sclerosis complex model mice. Neuropharmacology. 2022;218:109203.
Kashii H, Kasai S, Sato A, Hagino Y, Nishito Y, Kobayashi T, et al. Tsc2 mutation rather than Tsc1 mutation dominantly causes a social deficit in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Hum Genomics. 2023;17:4.
McMahon JJ, Yu W, Yang J, Feng H, Helm M, McMahon E, et al. Seizure-dependent mTOR activation in 5-HT neurons promotes autism-like behaviors in mice. Neurobiol Dis. 2015;73:296–306.
Ruffolo G, Gaeta A, Cannata B, Pinzaglia C, Aronica E, Morano A, et al. GABAergic neurotransmission in human tissues is modulated by cannabidiol. Life (Basel). 2022;12:2042.
Farach LS, Richard MA, Lupo PJ, Sahin M, Krueger DA, Wu JY, et al. Epilepsy risk prediction model for patients with tuberous sclerosis complex. Pediatr Neurol. 2020;113:46–50.
Ogórek B, Hamieh L, Hulshof HM, Lasseter K, Klonowska K, Kuijf H, et al. TSC2 pathogenic variants are predictive of severe clinical manifestations in TSC infants: results of the EPISTOP study. Genet Med. 2020;22:1489–97.
Hulshof HM, Kuijf HJ, Kotulska K, Curatolo P, Weschke B, Riney K, et al. Association of early MRI characteristics with subsequent epilepsy and neurodevelopmental outcomes in children with tuberous sclerosis complex. Neurology. 2022;98:e1216–25.
Ruppe V, Dilsiz P, Reiss CS, Carlson C, Devinsky O, Zagzag D, et al. Developmental brain abnormalities in tuberous sclerosis complex: a comparative tissue analysis of cortical tubers and perituberal cortex. Epilepsia. 2014;55:539–50.
Scherrer B, Prohl AK, Taquet M, Kapur K, Peters JM, Tomas-Fernandez X, et al. The connectivity fingerprint of the fusiform gyrus captures the risk of developing autism in infants with tuberous sclerosis complex. Cereb Cortex. 2020;30:2199–214.
Cohen AL, Kroeck MR, Wall J, McManus P, Ovchinnikova A, Sahin M, et al. Tubers affecting the fusiform face area are associated with autism diagnosis. Ann Neurol. 2023;93:577–90.
Sato A, Tominaga K, Iwatani Y, Kato Y, Wataya-Kaneda M, Makita K, et al. Abnormal white matter microstructure in the limbic system is associated with tuberous sclerosis complex-associated neuropsychiatric disorders. Front Neurol. 2022;13:782479.
Vanes LD, Tye C, Tournier JD, Combes AJE, Shephard E, Liang H, et al. White matter disruptions related to inattention and autism spectrum symptoms in tuberous sclerosis complex. NeuroImage Clin. 2022;36:103163.
Peters JM, Prohl A, Kapur K, Nath A, Scherrer B, Clancy S, et al. Longitudinal effects of everolimus on white matter diffusion in tuberous sclerosis complex. Pediatr Neurol. 2019;90:24–30.
Srivastava S, Prohl AK, Scherrer B, Kapur K, Krueger DA, Warfield SK, et al. Cerebellar volume as an imaging marker of development in infants with tuberous sclerosis complex. Neurology. 2018;90:e1493–500.
Moavero R, Napolitano A, Cusmai R, Vigevano F, Figà-Talamanca L, Calbi G, et al. White matter disruption is associated with persistent seizures in tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsy Behav. 2016;60:63–7.
Cook IA, Wilson AC, Peters JM, Goyal MN, Bebin EM, Northrup H, et al. EEG spectral features in sleep of autism spectrum disorders in children with tuberous sclerosis complex. J Autism Dev Disord. 2020;50:916–23.
Zhang B, Guo D, Han L, Rensing N, Satoh A, Wong M. Hypothalamic orexin and mechanistic target of rapamycin activation mediate sleep dysfunction in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Neurobiol Dis. 2020;134:104615.
Elkhatib Smidt SD, Ghorai A, Taylor SC, Gehringer BN, Dow HC, Langer A, et al. The relationship between autism spectrum and sleep-wake traits. Autism Res. 2022;15:641–52.
Schoenberger A, Capal JK, Ondracek A, Horn PS, Murray D, Byars AW, et al. Language predictors of autism spectrum disorder in young children with tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsy Behav. 2020;103:106844.
Scheper M, Romagnolo A, Besharat ZM, Iyer AM, Moavero R, Hertzberg C, et al. MiRNAs and isomiRs: serum-based biomarkers for the development of intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder in tuberous sclerosis complex. Biomedicines. 2022;10:1838.
Moavero R, Kotulska K, Lagae L, Benvenuto A, Emberti Gialloreti L, Weschke B, et al. Is autism driven by epilepsy in infants with tuberous sclerosis complex? Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020;7:1371–81.
Talbott MR, Miller MR. Future directions for infant identification and intervention for autism spectrum disorder from a transdiagnostic perspective. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2020;49:688–700.
Randall M, Egberts KJ, Samtani A, Scholten RJ, Hooft L, Livingstone N, et al. Diagnostic tests for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in preschool children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;2018:CD009044.
Capal JK, Horn PS, Murray DS, Byars AW, Bing NM, Kent B, et al. Utility of the autism observation scale for infants in early identification of autism in tuberous sclerosis complex. Pediatr Neurol. 2017;75:80–6.
Moavero R, Benvenuto A, Emberti Gialloreti L, Siracusano M, Kotulska K, Weschke B, et al. Early clinical predictors of autism spectrum disorder in infants with tuberous sclerosis complex: results from the EPISTOP Study. J Clin Med. 2019;8:788.
Jeste SS, Sahin M, Bolton P, Ploubidis GB, Humphrey A. Characterization of autism in young children with tuberous sclerosis complex. J Child Neurol. 2008;23:520–5.
Zachor DA, Curatolo P. Recommendations for early diagnosis and intervention in autism spectrum disorders: an Italian-Israeli consensus conference. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2014;18:107–18.
Wu JY, Goyal M, Peters JM, Krueger D, Sahin M, Northrup H, et al. Scalp EEG spikes predict impending epilepsy in TSC infants: a longitudinal observational study. Epilepsia. 2019;60:2428–36.
Nabbout R, Kuchenbuch M, Chiron C, Curatolo P. Pharmacotherapy for seizures in tuberous sclerosis complex. CNS Drugs. 2021;35:965–83.
Curatolo P, Verdecchia M, Bombardieri R. Vigabatrin for tuberous sclerosis complex. Brain Dev. 2001;23:649–53.
van der Poest CE, Jansen FE, Braun KPJ, Peters JM. Update on drug management of refractory epilepsy in tuberous sclerosis complex. Pediatr Drugs. 2020;22:73–84.
Bombardieri R, Pinci M, Moavero R, Cerminara C, Curatolo P. Early control of seizures improves long-term outcome in children with tuberous sclerosis complex. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2010;14:146–9.
Kotulska K, Kwiatkowski DJ, Curatolo P, Weschke B, Riney K, Jansen F, et al. Prevention of epilepsy in infants with tuberous sclerosis complex in the EPISTOP trial. Ann Neurol. 2021;89:304–14.
Zhang L, Huang CC, Dai Y, Luo Q, Ji Y, Wang K, et al. Correction: Symptom improvement in children with autism spectrum disorder following bumetanide administration is associated with decreased GABA/glutamate ratios. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10:63.
van Andel DM, Sprengers JJ, Oranje B, Scheepers FE, Jansen FE, Bruining H. Effects of bumetanide on neurodevelopmental impairments in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex: an open-label pilot study. Mol Autism. 2020;11:30.
Juarez-Martinez EL, Sprengers JJ, Cristian G, Oranje B, van Andel DM, Avramiea AE, et al. Prediction of behavioral improvement through resting-state electroencephalography and clinical severity in a randomized controlled trial testing bumetanide in autism spectrum disorder. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2023;8:251–61.
Overwater IE, Rietman AB, Mous SE, Bindels-de Heus K, Rizopoulos D, ten Hoopen LW, et al. A randomized controlled trial with everolimus for IQ and autism in tuberous sclerosis complex. Neurology. 2019;93:e200–9.
Krueger DA, Sadhwani A, Byars AW, de Vries PJ, Franz DN, Whittemore VH, et al. Everolimus for treatment of tuberous sclerosis complex-associated neuropsychiatric disorders. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2017;4:877–87.
Krueger DA, Capal JK, Curatolo P, Devinsky O, Ess K, Tzadok M, et al. Short-term safety of mTOR inhibitors in infants and very young children with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC): multicentre clinical experience. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2018;22:1066–73.
Gelot AB, Represa A. Progression of fetal brain lesions in tuberous sclerosis complex. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:899.
Cavalheiro S, da Costa MDS, Richtmann R. Everolimus as a possible prenatal treatment of in utero diagnosed subependymal lesions in tuberous sclerosis complex: a case report. Childs Nerv Syst. 2021;37:3897–9.
Nithianantharajah J, Hannan AJ. Enriched environments, experience-dependent plasticity and disorders of the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:697–709.
McDonald NM, Hyde C, Choi AB, Gulsrud AC, Kasari C, Nelson CA, et al. Improving developmental abilities in infants with tuberous sclerosis complex: a pilot behavioral intervention study. Infants Young Child. 2020;33:108–18.
Kasari C. Update on behavioral interventions for autism and developmental disabilities. Curr Opin Neurol. 2015;28:124–9.
Bruni O, Cortesi F, Giannotti F, Curatolo P. Sleep disorders in tuberous sclerosis: a polysomnographic study. Brain Dev. 1995;17:52–6.
Bruni O, Alonso-Alconada D, Besag F, Biran V, Braam W, Cortese S, et al. Current role of melatonin in pediatric neurology: clinical recommendations. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2015;19:122–33.
Jansen FE, Van Huffelen AC, Algra A, Van Nieuwenhuizen O. Epilepsy surgery in tuberous sclerosis: a systematic review. Epilepsia. 2007;48:1477–84.
Specchio N, Pepi C, de Palma L, Moavero R, De Benedictis A, Marras CE, et al. Surgery for drug-resistant tuberous sclerosis complex-associated epilepsy: who, when, and what. Epileptic Disord. 2021;23:53–73.
Acknowledgements
SN was supported by Next-Generation EU (NGEU) and funded by the Ministry of University and Research (MUR), National Recovery and Resilience Plan (NRRP), under project No. MNESYS (PE0000006)–a multiscale integrated approach to the study of the nervous system in health and disease (DN. 1553 11.10.2022).
Funding
AE and SM were supported by Healthcare Research and Medical Sciences (ZonMw; No. 09120012010007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
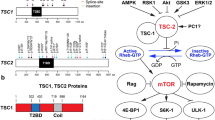
CP conceived the review. SM and AE contributed particularly to “Molecular and cellular mechanisms” and “Pre-clinical studies evaluating the efficacy of mTOR inhibitors in epilepsy and autism” and the preparation of Fig. 1. All authors drafted and prepared the manuscript. All authors read, revised, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not required.
Conflict of interest
No financial or non-financial benefits have been received or will be received from any party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Curatolo, P., Scheper, M., Emberti Gialloreti, L. et al. Is tuberous sclerosis complex-associated autism a preventable and treatable disorder?. World J Pediatr 20, 40–53 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-023-00762-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-023-00762-2