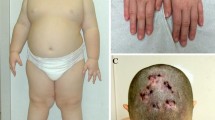
Abstract
Background
Obesity is a multifactorial chronic disease with a high, increasing worldwide prevalence. Genetic causes account for 7% of the cases in children with extreme obesity.
Data sources
This narrative review was conducted by searching for papers published in the PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase and SciELO databases and included 161 articles. The search used the following search terms: “obesity”, “obesity and genetics”, “leptin”, “Prader-Willi syndrome”, and “melanocortins”. The types of studies included were systematic reviews, clinical trials, prospective cohort studies, cross-sectional and prospective studies, narrative reviews, and case reports.
Results
The leptin-melanocortin pathway is primarily responsible for the regulation of appetite and body weight. However, several important aspects of the pathophysiology of obesity remain unknown. Genetic causes of obesity can be grouped into syndromic, monogenic, and polygenic causes and should be assessed in children with extreme obesity before the age of 5 years, hyperphagia, or a family history of extreme obesity. A microarray study, an analysis of the melanocortin type 4 receptor gene mutations and leptin levels should be performed for this purpose. There are three therapeutic levels: lifestyle modifications, pharmacological treatment, and bariatric surgery.
Conclusions
Genetic study technologies are in constant development; however, we are still far from having a personalized approach to genetic causes of obesity. A significant proportion of the affected individuals are associated with genetic causes; however, there are still barriers to its approach, as it continues to be underdiagnosed.
Video Abstract (MP4 1041807 KB)



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Singh RK, Kumar P, Mahalingam K. Molecular genetics of human obesity: a comprehensive review. C R Biol. 2017;340:87–108.
Kaur Y, de Souza RJ, Gibson WT, Meyre D. A systematic review of genetic syndromes with obesity. Obes Rev. 2017;18:603–34.
Engin A. The definition and prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:1–17.
Chooi YC, Ding C, Magkos F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism. 2019;92:6–10.
Concepción-Zavaleta M, Ramos-Yataco A, Alcalde-Loyola C, Moreno-Marreros D, Coronado-Arroyo J, Ildefonso-Najarro S, et al. Complications of obesity in children and adolescents during covid-19 pandemic: a narrative review. Rev Cuerpo Méd Hosp Nac Almanzor Aguinaga Asenjo. 2021;14:55–61.
Peinado Fabregat MI, Saynina O, Sanders LM. Obesity and overweight among children with medical complexity. Pediatrics. 2022;151:e2022058687.
Kumari S, Shukla S, Acharya S. Childhood obesity: prevalence and prevention in modern society. Cureus. 2022;14:e31640.
Centers for disease control and prevention. Childhood obesity facts. Overweight and obesity. 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/childhood.html. Accessed 30 Dec 2022.
World obesity. World obesity Atlas 2023. London: Global Obesity Federation; 2023. https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/?cat=19. Accessed 20 Mar 2023.
World Health Organization. WHO European Regional obesity report 2022. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe; 2022.
Boutari C, Mantzoros CS. A 2022 update on the epidemiology of obesity and a call to action: as its twin COVID-19 pandemic appears to be receding, the obesity and dysmetabolism pandemic continues to rage on. Metabolism. 2022;133:155217.
Wu FY, Yin RX. Recent progress in epigenetics of obesity. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022;14:171.
Mahmoud AM. An overview of epigenetics in obesity: the role of lifestyle and therapeutic interventions. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:1341.
Kahan LG, Mehrzad R. Chapter 10-environmental factors related to the obesity epidemic. In: Mehrzad R, editor. Obesity. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2020. p. 117–39.
Von Noorden C. Section VII. Diabetes mellitus. In: Clinical treatises on pathology and therapy of disorders of metabolism and nutrition. New York: E.B. Treat & Co; 1907. p. 211.
Malhotra S, Sivasubramanian R, Srivastava G. Evaluation and management of early onset genetic obesity in childhood. J Pediatr Genet. 2021;10:194–204.
Loos RJF, Yeo GSH. The genetics of obesity: from discovery to biology. Nat Rev Genet. 2022;23:120–33.
Podyma B, Parekh K, Güler AD, Deppmann CD. Metabolic homeostasis via BDNF and its receptors. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2021;32:488–99.
Tas A, Atabey M, Gokcen P, Ozel MI, Karagoz ZK, Ugur K, et al. Leptin/melanocortin pathway hormones in obese patients after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;26:1484–91.
Bathina S, Das UN. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its clinical implications. Arch Med Sci. 2015;11:1164–78.
Miranda M, Morici JF, Zanoni MB, Bekinschtein P. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a key molecule for memory in the healthy and the pathological brain. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:363.
Nakagomi A, Okada S, Yokoyama M, Yoshida Y, Shimizu I, Miki T, et al. Role of the central nervous system and adipose tissue BDNF/TrkB axes in metabolic regulation. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2015;1:15009.
Spetter MS, Feld GB, Thienel M, Preissl H, Hege MA, Hallschmid M. Oxytocin curbs calorie intake via food-specific increases in the activity of brain areas that process reward and establish cognitive control. Sci Rep. 2018;8:2736.
Prida E, Fernández-González S, Pena-León V, Pérez-Lois R, Fernø J, Seoane LM, et al. Crosstalk between melanin concentrating hormone and endocrine factors: implications for obesity. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:2436.
Dayton K, Miller J. Finding treatable genetic obesity: strategies for success. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2018;30:526–31.
Schalla MA, Taché Y, Stengel A. Neuroendocrine peptides of the gut and their role in the regulation of food intake. Compr Physiol. 2021;11:1679–730.
Rovella V, Rodia G, Di Daniele F, Cardillo C, Campia U, Noce A, et al. Association of gut hormones and microbiota with vascular dysfunction in obesity. Nutrients. 2021;13:613.
Psilopanagioti A, Nikou S, Logotheti S, Arbi M, Chartoumpekis DV, Papadaki H. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor in the human hypothalamus is associated with body mass index and colocalizes with the anorexigenic neuropeptide nucleobindin-2/nesfatin-1. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:14899.
Devesa J. The complex world of regulation of pituitary growth hormone secretion: the role of ghrelin, klotho, and nesfatins in it. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:636403.
Motta G, Allasia S, Ghigo E, Lanfranco F. Ghrelin actions on somatotropic and gonadotropic function in humans. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2016;138:3–25.
Witkamp RF. The role of fatty acids and their endocannabinoid-like derivatives in the molecular regulation of appetite. Mol Aspects Med. 2018;64:45–67.
Mishra AK, Dubey V, Ghosh AR. Obesity: an overview of possible role(s) of gut hormones, lipid sensing and gut microbiota. Metabolism. 2016;65:48–65.
Magne F, Gotteland M, Gauthier L, Zazueta A, Pesoa S, Navarrete P, et al. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio: a relevant marker of gut dysbiosis in obese patients? Nutrients. 2020;12:1474.
Duan M, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Zou R, Guo M, Zheng H. Characteristics of gut microbiota in people with obesity. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0255446.
de Wouters DA, Huwart SJP, Cani PD, Everard A. Gut microbes and food reward: from the gut to the brain. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:947240.
Clarke G, Stilling RM, Kennedy PJ, Stanton C, Cryan JF, Dinan TG. Minireview: gut microbiota: the neglected endocrine organ. Mol Endocrinol. 2014;28:1221–38.
Van Hul M, Cani PD. The gut microbiota in obesity and weight management: microbes as friends or foe? Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023;19:258–71.
Thaker VV. Genetic and epigenetic causes of obesity. Adolesc Med State Art Rev. 2017;28:379–405.
Pigeyre M, Yazdi FT, Kaur Y, Meyre D. Recent progress in genetics, epigenetics and metagenomics unveils the pathophysiology of human obesity. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016;130:943–86.
Choquet H, Meyre D. Genomic insights into early-onset obesity. Genome Med. 2010;2:36.
Locke AE, Kahali B, Berndt SI, Justice AE, Pers TH, Day FR, et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature. 2015;518:197–206.
Vourdoumpa A, Paltoglou G, Charmandari E. The genetic basis of childhood obesity: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2023;15:1416.
Butler MG, Miller JL, Forster JL. Prader-Willi syndrome-clinical genetics, diagnosis and treatment approaches: an update. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2019;15:207–44.
Muscogiuri G, Barrea L, Faggiano F, Maiorino MI, Parrillo M, Pugliese G, et al. Obesity in Prader-Willi syndrome: physiopathological mechanisms, nutritional and pharmacological approaches. J Endocrinol Invest. 2021;44:2057–70.
Kim SJ, Cho SY, Jin DK. Prader-Willi syndrome: an update on obesity and endocrine problems. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2021;26:227–36.
Angulo MA, Butler MG, Cataletto ME. Prader-Willi syndrome: a review of clinical, genetic, and endocrine findings. J Endocrinol Invest. 2015;38:1249–63.
Iughetti L, Vivi G, Balsamo A, Corrias A, Crinò A, Delvecchio M, et al. Thyroid function in patients with Prader-Willi syndrome: an Italian multicenter study of 339 patients. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019;32:159–65.
Noordam C, Höybye C, Eiholzer U. Prader-Willi syndrome and hypogonadism: a review article. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:2705.
Basak S, Basak A. Proteins and proteases of Prader-Willi syndrome: a comprehensive review and perspectives. Biosci Rep. 2022;42:BSR20220610.
Napolitano L, Barone B, Morra S, Celentano G, La Rocca R, Capece M, et al. Hypogonadism in patients with Prader Willi syndrome: a narrative review. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:1993.
Baldini L, Robert A, Charpentier B, Labialle S. Phylogenetic and molecular analyses identify SNORD116 targets involved in the Prader-Willi syndrome. Mol Biol Evol. 2022;39:msa348.
Qi Y, Purtell L, Fu M, Lee NJ, Aepler J, Zhang L, et al. Snord116 is critical in the regulation of food intake and body weight. Sci Rep. 2016;6:18614.
Engle SE, Bansal R, Antonellis PJ, Berbari NF. Cilia signaling and obesity. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021;110:43–50.
Melluso A, Secondulfo F, Capolongo G, Capasso G, Zacchia M. Bardet-Biedl syndrome: current perspectives and clinical outlook. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2023;19:115–32.
Tsang SH, Aycinena ARP, Sharma T. Ciliopathy: Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1085:171–4.
Weihbrecht K, Goar WA, Pak T, Garrison JE, DeLuca AP, Stone EM, et al. Keeping an eye on Bardet-Biedl syndrome: a comprehensive review of the role of Bardet-Biedl syndrome genes in the eye. Med Res Arch. 2017. https://doi.org/10.18103/mra.v5i9.1526.
Zhong F, Tan M, Gao Y. Novel multiallelic variants, two BBS2 and one PKD1 variant, of renal ciliopathies: a case report and literature review. Eur J Med Genet. 2023;66:104753.
Geets E, Meuwissen MEC, Van Hul W. Clinical, molecular genetics and therapeutic aspects of syndromic obesity. Clin Genet. 2019;95:23–40.
Kang S. Adipose tissue malfunction drives metabolic dysfunction in Alström syndrome. Diabetes. 2021;70:323–5.
Bettini S, Bombonato G, Dassie F, Favaretto F, Piffer L, Bizzotto P, et al. Liver fibrosis and steatosis in Alström syndrome: a genetic model for metabolic syndrome. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11:797.
Rodrigues JM, Fernandes HD, Caruthers C, Braddock SR, Knutsen AP. Cohen syndrome: review of the literature. Cureus. 2018;10:e3330.
Gong J, Zhang L, Long Y, Xiao B, Long H. Cohen syndrome in two patients from China. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022;10:e2053.
Wang H, Falk MJ, Wensel C, Traboulsi EI. Cohen syndrome. In: Adam MP, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJ, Gripp KW, et al., editors. GeneReviews®. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 2016. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1482/. Accessed 5 Apr 2023.
Sarathi V, Wadhwa R. Albright hereditary osteodystrophy. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559141/. Accessed 2 Feb 2023.
Ucciferro P, Anastasopoulou C. Pseudohypoparathyroidism. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547709/. Accessed 5 Apr 2023.
Salcedo-Arellano MJ, Hagerman RJ, Martínez-Cerdeño V. Fragile X syndrome: clinical presentation, pathology and treatment. Gac Med Mex. 2020;156:60–6.
Hunter J, Rivero-Arias O, Angelov A, Kim E, Fotheringham I, Leal J. Epidemiology of fragile X syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med Genet A. 2014;164A:1648–58.
Hagerman RJ, Berry-Kravis E, Hazlett HC, Bailey DB Jr, Moine H, Kooy RF, et al. Fragile X syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primer. 2017;3:17065.
Mahmoud R, Kimonis V, Butler MG. Genetics of obesity in humans: a clinical review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:11005.
Lazea C, Sur L, Florea M. ROHHAD (rapid-onset obesity with hypoventilation, hypothalamic dysfunction, autonomic dysregulation) syndrome—what every pediatrician should know about the etiopathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment: a review. Int J Gen Med. 2021;14:319–26.
Lee JM, Shin J, Kim S, Gee HY, Lee JS, Cha DH, et al. Rapid-onset obesity with hypoventilation, hypothalamic, autonomic dysregulation, and neuroendocrine tumors (ROHHADNET) syndrome: a systematic review. BioMed Res Int. 2018;2018:1250721.
Harvengt J, Gernay C, Mastouri M, Farhat N, Lebrethon MC, Seghaye MC, et al. ROHHAD(NET) syndrome: systematic review of the clinical timeline and recommendations for diagnosis and prognosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:dgaa247.
Bellad A, Bandari AK, Pandey A, Girimaji SC, Muthusamy B. A novel missense variant in PHF6 gene causing Börjeson-Forssman-Lehman syndrome. J Mol Neurosci. 2020;70:1403–9.
Khairat R, Elhossini R, Sobreira N, Wohler E, Otaify G, Mohamed AM, et al. Expansion of the phenotypic and mutational spectrum of Carpenter syndrome. Eur J Med Genet. 2022;65:104377.
Cascella M, Muzio MR. Cornelia de Lange syndrome. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554584/. Accessed 5 Apr 2023.
Milani D, Manzoni FMP, Pezzani L, Ajmone P, Gervasini C, Menni F, et al. Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: clinical features, genetic basis, diagnosis, and management. Ital J Pediatr. 2015;41:4.
Nordang GBN, Busk ØL, Tveten K, Hanevik HI, Fell AKM, Hjelmesæth J, et al. Next-generation sequencing of the monogenic obesity genes LEP, LEPR, MC4R, PCSK1 and POMC in a Norwegian cohort of patients with morbid obesity and normal weight controls. Mol Genet Metab. 2017;121:51–6.
Wasim M, Awan FR, Najam SS, Khan AR, Khan HN. Role of leptin deficiency, inefficiency, and leptin receptors in obesity. Biochem Genet. 2016;54:565–72.
Maurya R, Bhattacharya P, Dey R, Nakhasi HL. Leptin functions in infectious diseases. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2741.
Gruzdeva O, Borodkina D, Uchasova E, Dyleva Y, Barbarash O. Leptin resistance: underlying mechanisms and diagnosis. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019;12:191–8.
Kleinendorst L, Abawi O, van der Kamp HJ, Alders M, Meijers-Heijboer HEJ, van Rossum EFC, et al. Leptin receptor deficiency: a systematic literature review and prevalence estimation based on population genetics. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020;182:47–56.
Huvenne H, Dubern B, Clément K, Poitou C. Rare genetic forms of obesity: clinical approach and current treatments in 2016. Obes Facts. 2016;9:158–73.
Doulla M, McIntyre AD, Hegele RA, Gallego PH. A novel MC4R mutation associated with childhood-onset obesity: a case report. Paediatr Child Health. 2014;19:515–8.
Aykut A, Özen S, Gökşen D, Ata A, Onay H, Atik T, et al. Melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) gene variants in children and adolescents having familial early-onset obesity: genetic and clinical characteristics. Eur J Pediatr. 2020;179:1445–52.
Styne DM, Arslanian SA, Connor EL, Farooqi IS, Murad MH, Silverstein JH, et al. Pediatric obesity—assessment, treatment, and prevention: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102:709–57.
Gregoric N, Groselj U, Bratina N, Debeljak M, Zerjav Tansek M, Suput Omladic J, et al. Two cases with an early presented proopiomelanocortin deficiency—a long-term follow-up and systematic literature review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:689387.
van der Valk ES, Kleinendorst L, Delhanty PJD, van der Voorn B, Visser JA, van Haelst MM, et al. Obesity and hyperphagia with increased defective ACTH: a novel POMC variant. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107:e3699–704.
Farooqi IS, Drop S, Clements A, Keogh JM, Biernacka J, Lowenbein S, et al. Heterozygosity for a POMC-null mutation and increased obesity risk in humans. Diabetes. 2006;55:2549–53.
Ramos-Molina B, Martin MG, Lindberg I. PCSK1 variants and human obesity. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2016;140:47–74.
Ramos-Molina B, Lindberg I, Peinado JR. Regulated proteolysis of signaling molecules: the proprotein convertases. In: Bradshaw RA, Stahl PD, editors. Encyclopedia of cell biology. Waltham: Academic Press; 2016. p. 555–567. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123944474100677. Accessed 30 Jan 2023.
Aerts L, Terry NA, Sainath NN, Torres C, Martín MG, Ramos-Molina B, et al. Novel homozygous inactivating mutation in the PCSK1 gene in an infant with congenital malabsorptive diarrhea. Genes (Basel). 2021;12:710.
Stijnen P, Ramos-Molina B, O’Rahilly S, Creemers JWM. PCSK1 mutations and human endocrinopathies: from obesity to gastrointestinal disorders. Endocr Rev. 2016;37:347–71.
Stijnen P, Tuand K, Varga TV, Franks PW, Aertgeerts B, Creemers JWM. The association of common variants in PCSK1 with obesity: a HuGE review and meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol. 2014;180:1051–65.
da Fonseca ACP, Abreu GM, Palhinha L, Zembrzuski VM, Campos Junior M, Carneiro JRI, et al. A rare potential pathogenic variant in the BDNF gene is found in a Brazilian patient with severe childhood-onset obesity. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021;14:11–22.
Sandrini L, Di Minno A, Amadio P, Ieraci A, Tremoli E, Barbieri SS. Association between obesity and circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels: systematic review of literature and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:2281.
Han JC, Liu QR, Jones M, Levinn RL, Menzie CM, Jefferson-George KS, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and obesity in the WAGR syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:918–27.
Lindberg I, Fricker LD. Obesity, POMC, and POMC-processing enzymes: surprising results from animal models. Endocrinology. 2021;162:bqab155.
Vivoli M, Lindberg I. Chapter 246-Prohormone convertase 2. In: Kastin AJ, editor. Handbook of biologically active peptides (second edition). Boston: Academic Press; 2013. p. 1797–1802. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123850959002463. Accessed 30 Jan 2023.
Littleton SH, Berkowitz RI, Grant SFA. Genetic determinants of childhood obesity. Mol Diagn Ther. 2020;24:653–63.
Pinto RM, Steinmetz LS, Barbosa JMG, Mendes AFCS, Curado MP, da Cruz AD. The role of genetics in the pathophysiology of obesity: a systematic review. Obes Res. 2019;6:11–7.
Hinney A, Giuranna J. Polygenic obesity. In: Freemark MS, editor. Pediatric obesity: etiology, pathogenesis and treatment. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2018. p. 183–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68192-4_10.
Prakash J, Mittal B, Srivastava A, Awasthi S, Srivastava P, Srivastava N. Common genetic variant of INSIG2 gene rs7566605 polymorphism is associated with severe obesity in North India. Iran Biomed J. 2017;21:261–9.
Malzahn D, Müller-Nurasyid M, Heid IM, Wichmann HE, Bickeböller H, KORA study group. Controversial association results for INSIG2 on body mass index may be explained by interactions with age and with MC4R. Eur J Hum Genet. 2014;22:1217–24.
Harbron J, Van der Merwe L, Zaahl MG, Kotze MJ, Senekal M. Fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) gene polymorphisms are associated with physical activity, food intake, eating behaviors, psychological health, and modeled change in body mass index in overweight/obese Caucasian adults. Nutrients. 2014;6:3130–52.
Hess ME, Brüning JC. The fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) gene: obesity and beyond? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1842:2039–47.
Loos RJF. Genetic determinants of common obesity and their value in prediction. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;26:211–26.
Melmed S, Koenig R, Rosen C, Auchus R, Goldfine A. Williams textbook of endocrinology. 14th ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2019.
Arroyo-Johnson C, Mincey KD. Obesity epidemiology worldwide. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2016;45:571–9.
Forsythe E, Beales PL. Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013;21:8–13.
Gunay-Aygun M, Schwartz S, Heeger S, O’Riordan MA, Cassidy SB. The changing purpose of Prader-Willi syndrome clinical diagnostic criteria and proposed revised criteria. Pediatrics. 2001;108:E92.
Dai YL, Luo FH, Zhang HW, Ma MS, Luo XP, Liu L, et al. Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of childhood Prader-Willi syndrome in China. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022;17:221.
Priya S, Nampoothiri S, Sen P, Sripriya S. Bardet-Biedl syndrome: genetics, molecular pathophysiology, and disease management. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016;64:620–7.
Butler MG. Prader-Willi syndrome: obesity due to genomic imprinting. Curr Genomics. 2011;12:204–15.
Koves IH, Roth C. Genetic and syndromic causes of obesity and its management. Indian J Pediatr. 2018;85:478–85.
Larder R, Lim CT, Coll AP. Genetic aspects of human obesity. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;124:93–106.
Alves C, Franco RR. Prader-Willi syndrome: endocrine manifestations and management. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2020;64:223–34.
Crinò A, Fintini D, Bocchini S, Grugni G. Obesity management in Prader-Willi syndrome: current perspectives. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2018;11:579–93.
Yang Q, Xiao T, Guo J, Su Z. Complex relationship between obesity and the fat mass and obesity locus. Int J Biol Sci. 2017;13:615–29.
Sehgal K, Khanna S. Gut microbiota: a target for intervention in obesity. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;15:1169–79.
Santos-Paulo S, Costello SP, Forster SC, Travis SP, Bryant RV. The gut microbiota as a therapeutic target for obesity: a scoping review. Nutr Res Rev. 2022;35:207–20.
Gill VJS, Soni S, Shringarpure M, Anusheel, Bhardwaj S, Yadav NK, et al. Gut microbiota interventions for the management of obesity: a literature review. Cureus. 2022;14:e29317.
Diene G, Angulo M, Hale PM, Jepsen CH, Hofman PL, Hokken-Koelega A, et al. Liraglutide for weight management in children and adolescents with Prader-Willi syndrome and obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;108:4–12.
Haqq AM, Chung WK, Dollfus H, Haws RM, Martos-Moreno GÁ, Poitou C, et al. Efficacy and safety of setmelanotide, a melanocortin-4 receptor agonist, in patients with Bardet-Biedl syndrome and Alström syndrome: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial with an open-label period. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10:859–68.
Mahmoud R, Kimonis V, Butler MG. Clinical trials in Prader-Willi syndrome: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:2150.
Salum KCR, Rolando JM, Zembrzuski VM, Carneiro JRI, Mello CB, Maya-Monteiro CM, et al. When leptin is not there: a review of what nonsyndromic monogenic obesity cases tell us and the benefits of exogenous leptin. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:722441.
Chakhtoura M, Haber R, Ghezzawi M, Rhayem C, Tcheroyan R, Mantzoros CS. Pharmacotherapy of obesity: an update on the available medications and drugs under investigation. EClinicalMedicine. 2023;58:101882.
Besci Ö, Fırat SN, Özen S, Çetinkaya S, Akın L, Kör Y, et al. A national multicenter study of leptin (LEP) and leptin receptor (LEPR) deficiency and systematic review. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgad099.
Farooqi IS, Wangensteen T, Collins S, Kimber W, Matarese G, Keogh JM, et al. Clinical and molecular genetic spectrum of congenital deficiency of the leptin receptor. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:237–47.
Niu J, Tong J, Blevins JE. Oxytocin as an anti-obesity treatment. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:743546.
Liu CM, Spaulding MO, Rea JJ, Noble EE, Kanoski SE. Oxytocin and food intake control: neural, behavioral, and signaling mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:10859.
Taha MA, Al-Maqati TN, Alnaam YA, Alharbi SS, Khaneen R, Almutairi H, et al. The association between brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein level and body mass index. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;59:99.
Ferraguti G, Terracina S, Micangeli G, Lucarelli M, Tarani L, Ceccanti M, et al. NGF and BDNF in pediatrics syndromes. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022;145:105015.
Wu SW, Xu B. Rapid and lasting effects of activating BDNF-expressing PVH neurons on energy balance. eNeuro. 2022;9:ENEURO.0009-22.2022.
Bumb JM, Bach P, Grosshans M, Wagner X, Koopmann A, Vollstädt-Klein S, et al. BDNF influences neural cue-reactivity to food stimuli and food craving in obesity. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2021;271:963–74.
Matheson J, Zhou XMM, Bourgault Z, Le Foll B. Potential of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), and diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL) enzymes as targets for obesity treatment: a narrative review. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14:1316.
André A, Gonthier MP. The endocannabinoid system: its roles in energy balance and potential as a target for obesity treatment. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42:1788–801.
Jastreboff AM, Kaplan LM, Frías JP, Wu Q, Du Y, Gurbuz S, et al. Triple–hormone-receptor agonist retatrutide for obesity—a phase 2 trial. N Engl J Med. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2301972.
Thenappan A, Nadler E. Bariatric surgery in children: indications, types, and outcomes. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019;21:24.
Hofmann B. Bariatric surgery for obese children and adolescents: a review of the moral challenges. BMC Med Ethics. 2013;14:18.
Kumar S, Kelly AS. Review of childhood obesity: from epidemiology, etiology, and comorbidities to clinical assessment and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017;92:251–65.
Bolling CF, Armstrong SC, Reichard KW, Michalsky MP. Metabolic and bariatric surgery for pediatric patients with severe obesity. Pediatrics. 2019;144:e20193224.
Gonzalez DO, Michalsky MP. Update on pediatric metabolic and bariatric surgery. Pediatr Obes. 2021;16:e12794.
Holéczy P, Pekař M, Bužga M, Evinová E. Current bariatric-metabolic surgery. Cas Lek Cesk. 2022;161:100–6.
Steinhart A, Tsao D, Pratt JSA. Pediatric metabolic and bariatric surgery. Surg Clin North Am. 2021;101:199–212.
Thomas-Eapen N. Childhood obesity. Prim Care. 2021;48:505–15.
Alqahtani AR, Elahmedi M, Alqahtani YA. Bariatric surgery in monogenic and syndromic forms of obesity. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014;23:37–42.
Armstrong SC, Bolling CF, Michalsky MP, Reichard KW. Pediatric metabolic and bariatric surgery: evidence, barriers, and best practices. Pediatrics. 2019;144:e20193223.
Greydanus DE, Agana M, Kamboj MK, Shebrain S, Soares N, Eke R, et al. Pediatric obesity: current concepts. Dis Month. 2018;64:98–156.
Poitou C, Puder L, Dubern B, Krabusch P, Genser L, Wiegand S, et al. Long-term outcomes of bariatric surgery in patients with bi-allelic mutations in the POMC, LEPR, and MC4R genes. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2021;17:1449–56.
Satoh H, Mori S. Subregional assignment of the proopiomelanocortin gene (POMC) to human chromosome band 2p23.3 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1997;76:221–2.
Wolfe G, Salehi V, Browne A, Riddle R, Hall E, Fam J, et al. Metabolic and bariatric surgery for obesity in Prader Willi syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soard.2023.01.017.
Roth L, Ordnung M, Forkmann K, Mehl N, Horstmann A. A randomized-controlled trial to evaluate the app-based multimodal weight loss program zanadio for patients with obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2023;31:1300–10.
Ibrahim Abdalla MM. Ghrelin–physiological functions and regulation. Eur Endocrinol. 2015;11:90–5.
Fong AKW, Wong SKH, Lam CCH, Ng EKW. Ghrelin level and weight loss after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and gastric mini-bypass for Prader-Willi syndrome in Chinese. Obes Surg. 2012;22:1742–5.
Gantz MG, Driscoll DJ, Miller JL, Duis JB, Butler MG, Gourash L, et al. Critical review of bariatric surgical outcomes in patients with Prader-Willi syndrome and other hyperphagic disorders. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022;30:973–81.
Liu SYW, Wong SKH, Lam CCH, Ng EKW. Bariatric surgery for Prader-Willi syndrome was ineffective in producing sustainable weight loss: long term results for up to 10 years. Pediatr Obes. 2020;15:e12575.
Pratt JSA, Browne A, Browne NT, Bruzoni M, Cohen M, Desai A, et al. ASMBS pediatric metabolic and bariatric surgery guidelines, 2018. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2018;14:882–901.
Cooiman MI, Kleinendorst L, Aarts EO, Janssen IMC, van Amstel HKP, Blakemore AI, et al. Genetic obesity and bariatric surgery outcome in 1014 patients with morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2020;30:470–7.
Cifuentes L, Hurtado AMD, Eckel-Passow J, Acosta A. Precision medicine for obesity. Dig Dis Interv. 2021;5:239–48.
Campbell Am LV. Genetics of obesity. Aust Fam Physician. 2017;46:456–9.
Rohde K, Keller M, la Cour PL, Blüher M, Kovacs P, Böttcher Y. Genetics and epigenetics in obesity. Metabolism. 2019;92:37–50.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CZMJ contributed to conceptualization, methodology, reviewing and editing, and project administration. QAJE contributed to conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing of the original draft, and project administration. DVMdC, VdlCJdC, BCCM, and PLSL contributed to investigation and writing of the original draft. GOER contributed to investigation, reviewing and editing. ALEdJ, LCF, ZGFE, and CULA contributed to reviewing and editing. PIJ contributed to conceptualization, methodology, reviewing and editing. All authors approve the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not needed.
Conflict of interest
No financial or non-financial benefits have been received or will be received from any party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Concepción-Zavaleta, M.J., Quiroz-Aldave, J.E., Durand-Vásquez, M.d. et al. A comprehensive review of genetic causes of obesity. World J Pediatr 20, 26–39 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-023-00757-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-023-00757-z