Abstract
Urban flooding has become a widespread issue across the world over the last few decades, making it crucial for cities to prioritise the flood risk mitigation. Kolkata has been selected as the study area as this city is densely urbanised and waterlogging situation is frequent here. The main goal of this paper is to apply the Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs-Urban Flood Risk Mitigation (InVEST-UFRM) model for the city Kolkata to understand the flood-like situation after consecutive rainfall for 2 h with different rainfall depths and find possible mitigation measures. The result finds Kolkata is covered up with 75% impervious surface where more than 80% of the rain water transforms into runoff after 2 h of rainfall and northern portion of Kolkata is extremely vulnerable to flooding. About 47% flood volume increases by 71% with a change in rainfall depth. Open green spaces have the highest potentiality to retain rainfall. Average runoff retention capacity of watersheds reduces about 10% with increase in 50% increase in rainfall. Economic damage costs about 10 lakh rupees for the most vulnerable area of 5.45 km2 from the study area with a rainfall depth of 47 mm in 2 h. Flood risk related mitigation measures that should be followed for the study area with three perspectives like precipitation parameter, excess runoff reduction and runoff retention measures. Application of this model for urban flood mitigation is comparatively easy to use and more approachable for any urban area.











Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 May 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11486-y
References
Al-Zahrani MA (2018) Assessing the impacts of rainfall intensity and urbanization on storm runoff in an arid catchment. Arab J Geosci 11:208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3569-4
Amoako C, Cobbinah PB, Mensah Darkwah R (2019) Complex twist of fate: the geopolitics of flood management regimes in Accra, Ghana. Cities 89:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CITIES.2019.02.006
Ansari TA, Katpatal YB, Vasudeo AD (2016) Spatial evaluation of impacts of increase in impervious surface area on SCS-CN and runoff in Nagpur urban watersheds. India Arab J Geosci 9:702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2702-5
Assumma V, Quagliolo C, Comino E, Mondini G (2022) Definition of an integrated theoretical framework to assess the NBS suitability in flood risk areas. In: Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics). Springer, Cham, pp 228–237
Bathrellos GD, Gaki-Papanastassiou K, Skilodimou HD et al (2012) Potential suitability for urban planning and industry development using natural hazard maps and geological–geomorphological parameters. Environ Earth Sci 66:537–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1263-x
Bathrellos GD, Karymbalis E, Skilodimou HD et al (2016) Urban flood hazard assessment in the basin of Athens Metropolitan city, Greece. Environ Earth Sci 75:319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5157-1
Bathrellos GD, Skilodimou HD, Chousianitis K et al (2017) Suitability estimation for urban development using multi-hazard assessment map. Sci Total Environ 575:119–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.025
Berndtsson R, Becker P, Persson A et al (2019) Drivers of changing urban flood risk: a framework for action. J Environ Manage 240:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.03.094
Chan FKS, Yang LE, Scheffran J et al (2021) Urban flood risks and emerging challenges in a Chinese delta: the case of the Pearl River Delta. Environ Sci Policy 122:101–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2021.04.009
Chang H, Pallathadka A, Sauer J et al (2021) Assessment of urban flood vulnerability using the social-ecological-technological systems framework in six US cities. Sustain Cities Soc 68:102786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.102786
Chen Y, Zhou H, Zhang H et al (2015) Urban flood risk warning under rapid urbanization. Environ Res 139:3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.02.028
Citakoglu H, Minarecioglu N (2021) Trend analysis and change point determination for hydro-meteorological and groundwater data of Kizilirmak basin. Theor Appl Climatol 145:1275–1292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03696-9
Dai X, Wang L, Tao M et al (2021) Assessing the ecological balance between supply and demand of blue-green infrastructure. J Environ Manage 288:112454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112454
Dasgupta S, Gosain AK, Rao S et al (2013) A megacity in a changing climate: the case of Kolkata. Clim Change 116:747–766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-012-0516-3
Dawod GM, Mirza MN, Al-Ghamdi KA (2013) Assessment of several flood estimation methodologies in Makkah metropolitan area, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 6:985–993. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0405-5
De US, Singh GP, Rase DM (2013) Urban flooding in recent decades in four mega cities of India. J Indian Geophys Union 17:153–165
Directorate of Census Operations WB (2014) Census of India 2011 - West Bengal - Series 20 - Part XII A - District Census Handbook, Kolkata. India
Effati F, Karimi H, Yavari A (2021) Investigating effects of land use and land cover patterns on land surface temperature using landscape metrics in the city of Tehran, Iran. Arab J Geosci 14:1240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07433-4
Elouissi A, Habi M, Benaricha B, Boualem SA (2017) Climate change impact on rainfall spatio-temporal variability (Macta watershed case, Algeria). Arab J Geosci 10:496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3264-x
Elsebaie IH (2012) Developing rainfall intensity–duration–frequency relationship for two regions in Saudi Arabia. J King Saud Univ - Eng Sci 24:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2011.06.001
Farr TG, Rosen PA, Caro E et al (2007) The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev Geophys 45. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005RG000183
Foster SR (2006) The city as an ecological space: social capital and urban land use. Notre Dame Law Rev 82:527–582
Gitika T, Ranjan S (2014) Estimation of surface runoff using NRCS curve number procedure in Buriganga Watershed, Assam, India -a geospatial approach. Int Res J Earth Sci ISSN Int ResJ Earth Sci 2:2321–2527
Görkemli B, Citakoglu H, Haktanir T, Karaboga D (2022) A new method based on artificial bee colony programming for the regional standardized intensity–duration–frequency relationship. Arab J Geosci 15:272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09377-1
Guerreiro SB, Glenis V, Dawson RJ, Kilsby C (2017) Pluvial flooding in European cities-a continental approach to urban flood modelling. Water (Switzerland) 9:296. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9040296
Haktanir T, Citakoglu H (2015) Closure to “Trend, Independence, Stationarity, and Homogeneity Tests on Maximum Rainfall Series of Standard Durations Recorded in Turkey” by Tefaruk Haktanir and Hatice Citakoglu. J Hydrol Eng 20. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001246
Haktanir T, Citakoglu H (2014) Trend, independence, stationarity, and homogeneity tests on maximum rainfall series of standard durations recorded in Turkey. J Hydrol Eng 19. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000973
Haktanir T, Citakoglu H, Seckin N (2016) Regional frequency analyses of successive-duration annual maximum rainfalls by L-moments method. Hydrol Sci J 61:647–668. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2014.966722
Hamel P, Guerry AD, Polasky S et al (2021) Mapping the benefits of nature in cities with the InVEST software. NPJ Urban Sustain 1:25. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42949-021-00027-9
Hammami S, Zouhri L, Souissi D et al (2019) Application of the GIS based multi-criteria decision analysis and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) in the flood susceptibility mapping (Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4754-9
Haque I, Mehta S, Kumar A (2019) Towards sustainable and inclusive cities: the case of Kolkata
Houston D, Werrity A, Bassett D et al (2011) Pluvial (rain-related) flooding in urban areas: the invisible hazard. Joseph Rowntree Foundation
Kadaverugu A, Nageshwar Rao C, Viswanadh GK (2021) Quantification of flood mitigation services by urban green spaces using InVEST model: a case study of Hyderabad city, India. Model Earth Syst Environ 7:589–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-00937-0
Khan A, Atta-ur-Rahman S, Ayub M (2022) Impact of soil sealing on the genesis of pluvial flood in Peshawar, Pakistan. Arab J Geosci 15:575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09816-7
KMC (2020) City Disaster Management Plan of Kolkata. Kolkata
Kumar N, Liu X, Narayanasamydamodaran S, Pandey KK (2021) A systematic review comparing urban flood management practices in India to China’s sponge city program. Sustain. 13:6346
Leonard T (2012) United Nations Conference on Environment and Development, Rio de Janeiro, 1992. In: Encyclopedia of U.S.-Latin American Relations. CQ Press, 2300 N Street, NW, Suite 800, Washington DC 20037 United States
Mahdi ES, Mohamedmeki MZ (2020) Analysis of rainfall intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) curves of Baghdad city. In: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, p 012066
Malik S, Pal SC, Sattar A et al (2020) Trend of extreme rainfall events using suitable global circulation model to combat the water logging condition in Kolkata Metropolitan Area. Urban Clim 32:100599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2020.100599
Mercado JMR, Kawamura A, Amaguchi H (2020) Interrelationships of the barriers to integrated flood risk management adaptation in Metro Manila, Philippines. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 49:101683. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJDRR.2020.101683
Mignot E, Li X, Dewals B (2019) Experimental modelling of urban flooding: a review. J Hydrol 568:334–342
Mukherjee AB, Bardhan S (2021) Flood vulnerability and slum concentration mapping in Indian city of Kolkata: a post Amphan analysis. Water Sci 35:109–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/23570008.2021.1957641
Mukherjee S, Sikdar PK, Pal S, Schütt B (2021) Assessment of environmental water security of an Asian deltaic megacity and its peri-urban wetland areas. Sustainability 13:2772. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052772
Mukhopadhyay AK, Deb AK, Chowdhury G et al (2019) Post-monsoon waterlogging-associated upsurge of cholera cases in and around Kolkata metropolis, 2015. Epidemiol Infect 147:e167. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268819000529
Natarajan S, Radhakrishnan N (2020) An integrated hydrologic and hydraulic flood modeling study for a medium-sized ungauged urban catchment area: a case study of Tiruchirappalli City using HEC-HMS and HEC-RAS. J Inst Eng Ser A 101:381–398
Pal I, Ghosh S, Tuladhar N (2022) Risk governance perspectives for compounding hazards: a case study in Megacity Kolkata. In: Pandemic, Risk, Response, and Resilience. Elsevier, pp 335–347
Pallathadka A, Sauer J, Chang H, Grimm NB (2022) Full title: urban flood risk and green infrastructure: who is exposed to risk and who benefits from investment? A case study of three U.S. Cities Landsc Urban Plan 223:104417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2022.104417
Qi W, Ma C, Xu H et al (2021) A review on applications of urban flood models in flood mitigation strategies. Springer Netherlands
Quagliolo C, Comino E, Pezzoli A (2021) Nature-based simulation to address climate change-related flooding. preliminary insights on a small-sized Italian city. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics). Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH, pp 544–553
Rafiq F, Ahmed S, Ahmad S, Ali Khan A (2016) Urban floods in India. Int J Sci Eng Res 7:721–734
Rangari VA, Sridhar V, Umamahesh NV, Patel AK (2020) Rainfall runoff modelling of urban area using HEC-HMS: a case study of Hyderabad City. In: Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering. Springer, pp 113–125
Ross CW, Prihodko L, Anchang J et al (2018) HYSOGs250m, global gridded hydrologic soil groups for curve-number-based runoff modeling. Sci data 5:180091. https://doi.org/10.1038/SDATA.2018.91
Row S (1976) Appendix I : USDA / SCS curve number method for estimating daily runoff, pp 88–90
Rumbach A (2017) At the roots of urban disasters: planning and uneven geographies of risk in Kolkata, India. J Urban Aff 39:783–799. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352166.2017.1282771
Saha S, Saha A, Das M et al (2021) Analyzing spatial relationship between land use/land cover (LULC) and land surface temperature (LST) of three urban agglomerations (UAs) of Eastern India. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 22:100507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2021.100507
Sakieh Y (2017) Understanding the effect of spatial patterns on the vulnerability of urban areas to flooding. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 25:125–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2017.09.004
Salman AM, Li Y (2018) Flood risk assessment, future trend modeling, and risk communication: a review of ongoing research. Nat Hazards Rev 19:04018011. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)NH.1527-6996.0000294
Shahid M, Rahman KU, Balkhair KS, Nabi A (2020) Impact assessment of land use and climate changes on the variation of runoff in Margalla Hills watersheds, Pakistan. Arab J Geosci 13:239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5231-1
Sharp R, Douglass J, Wolny S et al (2020) InVEST User Guide — InVEST documentation. In: InVEST 3.10.2.post21+ug.gb784d7e.d20220301 User’s Guid. Nat. Cap. Proj. Stanford Univ. Univ. Minnesota, Nat. Conserv. World Wildl. Fund https://invest-userguide.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html. Accessed 3 Mar 2022
Sikdar PK (2000) Geology of the Quaternary aquifers of the twin city of Calcutta - Howrah. J Geol Soc India 56:169–181
Simonovic SP, Schardong A, Sandink D, Srivastav R (2016) A web-based tool for the development of intensity duration frequency curves under changing climate. Environ Model Software 81:136–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2016.03.016
Smith DI (1994) Flood damage estimation - a review of urban stage-damage curves and loss functions. Water SA 20:231–238. https://doi.org/10.10520/aja03784738_1124
Soomro AG, Babar MM, Memon AH et al (2019) Sensitivity of direct runoff to curve number using the SCS-CN method. Civ Eng J 5:2738–2746. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-2019-03091445
Sparks A (2018) nasapower: a NASA POWER Global Meteorology, Surface Solar Energy and Climatology Data Client for R. J Open Source Softw 3:1035. https://doi.org/10.21105/JOSS.01035
Subyani AM, Al-Amri NS (2015) IDF curves and daily rainfall generation for Al-Madinah city, western Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 8:11107–11119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1999-9
Sušnik J, Strehl C, Postmes LA et al (2014) Assessment of the effectiveness of a risk-reduction measure on pluvial flooding and economic loss in Eindhoven, the Netherlands. In: Procedia Engineering. No longer published by Elsevier, pp 1619–1628
Tang S, Jiang J, Zheng Y et al (2021) Robustness analysis of storm water quality modelling with LID infrastructures from natural event-based field monitoring. Sci Total Environ 753. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.142007
Tessema SM, Lyon SW, Setegn SG, Mörtberg U (2014) Effects of different retention parameter estimation methods on the prediction of surface runoff using the SCS curve number method. Water Resour Manag 28:3241–3254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0674-3
Vermote E, Justice C, Claverie M, Franch B (2016) Preliminary analysis of the performance of the Landsat 8/OLI land surface reflectance product. Remote Sens Environ 185:46–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.04.008
Weinstein L, Rumbach A, Sinha S (2019) Resilient growth: fantasy plans and unplanned developments in India’s flood-prone coastal cities. Int J Urban Reg Res 43:273–291. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-2427.12743
Wu X, Guo J (2021) A new economic loss assessment system for urban severe rainfall and flooding disasters based on big data fusion. In: Economic Impacts and Emergency Management of Disasters in China. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 259–287
Wu X, Zhou L, Gao G et al (2016) Urban flood depth-economic loss curves and their amendment based on resilience: evidence from Lizhong Town in Lixia River and Houbai Town in Jurong River of China. Nat Hazards 82:1981–2000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2281-5
Zhou Q, Leng G, Su J, Ren Y (2019) Comparison of urbanization and climate change impacts on urban flood volumes: importance of urban planning and drainage adaptation. Sci Total Environ 658:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.184
Zope PE, Eldho TI, Jothiprakash V (2016) Development of rainfall intensity duration frequency curves for Mumbai City, India. J Water Resour Prot 8:756–765. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2016.87061
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This paper is the authors’ own original work, which has not been previously published elsewhere.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants and agencies involved in the study.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that the entire work is original. We did not publish any other manuscript on this research area. We did not publish this work to any other journal or conference.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Amjad Kallel
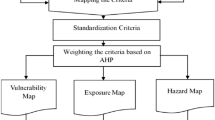
The original online version of this article was revised: In this article the wrong figure appeared as Fig. 1.; the figure should have appeared as shown below.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bose, S., Mazumdar, A. Urban flood risk assessment and mitigation with InVEST-UFRM model: a case study on Kolkata city, West Bengal state (India). Arab J Geosci 16, 320 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11412-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11412-2