Abstract
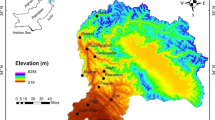
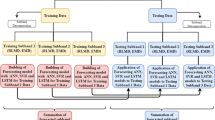
Reliable prediction of the water flow entering a reservoir is a crucial concern for agricultural-based countries like Pakistan. This study applies a hybrid method to model the daily river inflow of different tributaries of the Indus river basin (IRB), Pakistan. The hybrid method is composed of hybrid decomposition and three data-driven models. The hybrid decomposition (HD) is based on local mean decomposition and ensemble empirical mode decomposition that decompose river inflow series into different components. Next, the HD components are used as inputs to support vector regression (SVR), K-nearest neighbor (KNN), and autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models. The predictions of the HD-SVR, HD-KNN, and HD-ARIMA models are aggregated. The final prediction is the mean of the predictions of the HD-SVR, HD-KNN, and HD-ARIMA models (combined as HD-SKA). The potential of the HD-SKA model is explored on the Jhelum, Indus, Kabul, and Chenab rivers in the IRB system in Pakistan. The performance of the HD-SKA model is compared to twelve models using different performance measures. For the Chenab river, the root mean squared error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and root-relative squared error (RRSE) of the HD-SKA model on test data are 7.9314, 3.5315, and 0.2676, respectively, which are smaller than all competing models in the study. Similar findings are achieved for Kabul, Indus, and Jhelum rivers where the HD-SKA model outperformed all other considered models. The results show that the HD-SKA model has a superior capability of capturing the randomness of river inflow.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
These will be provided on request.
Code availability
Will be provided on request.
References
Adamowski J, Chan HF (2011) A wavelet neural network conjunction model for groundwater level forecasting. J Hydrol 407:28–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.06.013
Aghelpour P, Varshavian V (2020) Evaluation of stochastic and artificial intelligence models in modeling and predicting of river daily flow time series. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 34:33–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-019-01761-4
Aghelpour P, Bahrami-Pichaghchi H, Varshavian V (2021a) Hydrological drought forecasting using multi-scalar streamflow drought index, stochastic models and machine learning approaches, in northern Iran. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 35:1615–1635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01949-z
Aghelpour P, Mohammadi B, Mehdizadeh S, Bahrami-Pichaghchi H, Duan Z (2021b) A novel hybrid dragonfly optimization algorithm for agricultural drought prediction. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 35:2459–2477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-021-02011-2
Aghelpour P, Singh VP, Varshavian V (2021c) Time series prediction of seasonal precipitation in Iran, using data-driven models: a comparison under different climatic conditions. Arab J of Geosci 14:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06910-0
Akhbari M, Overloop PJ, Afshar A (2011) Clustered K nearest neighbor algorithm for daily inflow forecasting. W Resour Manag 25:1341–1357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9748-z
Al-Juboor AM (2021) A hybrid model to predict monthly streamflow using neighboring rivers annual flows. W Resour Manag 35:729–743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02757-4
Araghinejad S (2013) Data-driven modeling: using MATLAB in water resources and environmental, 67th edn. Springer Science & Business Media, New York
Araghinejad S, Fayyaz N, Hosseini-Moghari SM (2018) Development of a hybrid data driven model for hydrological estimation. W Resour Manag 32:3737–3750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2016-3
Bashir A, Shehzad MA, Hussain I, Ishaq M, Rehmani A, Bhatti SH (2019) Reservoir inflow prediction by ensembling wavelet and bootstrap techniques to multiple linear regression model. W Resour Manag 33:5121–5136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02418-1
Baydaroğlu Ö, Koçak K, Duran K (2018) River flow prediction using hybrid models of support vector regression with the wavelet transform, singular spectrum analysis and chaotic approach. Meteorol Atmos Phys 130:349–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-017-0518-9
Boulariah O, Meddi M, Longobardi A (2019) Assessment of prediction performances of stochastic and conceptual hydrological models: monthly stream flow prediction in northwestern Algeria. Arab J of Geosci 12:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4847-5
Box GE, Jenkins GM (1976) Time series analysis: forecasting and control. Hold Day 3226:10
Box GE, Jenkins GM, Reinsel GC (2008) Forecasting. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York
Chen L, Guo S (2019) Copulas and its application in hydrology and water resources, 1st edn. Springer, Singapore
Cover T, Hart P (1967) Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 13:21–27
Ghorbani MA, Zadeh HA, Isazadeh M, Terzi O (2016) A comparative study of artificial neural network (MLP, RBF) and support vector machine models for river flow prediction. Environ Earth Sci 75:476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5096-x
Golian S, Murphy C, Meresa H (2021) Regionalization of hydrological models for flow estimation in ungauged catchments in Ireland. J Hydrol Reg Stud 36:100859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2021.100859
Hu J, Liu J, Liu Y, Gao C (2013) EMD-KNN model for annual average rainfall forecasting. J Hydrol Eng 18:1450–1457. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000481
Huang NE, Shen Z, Long SR, Wu MC, Shih HH, Zheng Q, Yen NC, Tung CC, Liu HH (1998) The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc R Soc Lond Ser a: Math Phys Eng Sci 454:903–995. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1998.0193
Jain A, Kumar AM (2007) Hybrid neural network models for hydrologic time series forecasting. Appl Soft Comput 7:585–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2006.03.002
Khodakhah H, Aghelpour P, Hamedi Z (2022) Comparing linear and non-linear data-driven approaches in monthly river flow prediction, based on the models SARIMA, LSSVM, ANFIS, and GMDH. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:21935–21954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17443-0
Martinez F, Frias MP, Perez-Godoy MD, Rivera AJ (2018) Dealing with seasonality by narrowing the training set in time series forecasting with kNN. Expert Syst Appl 103:38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.03.005
Mishra A, Desai V (2005) Drought forecasting using stochastic models. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 19:326–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-005-0238-4
Nazir HM, Hussain I, Faisal M, Elashkar EE, Shoukry AM (2019a) Improving the prediction accuracy of river inflow using two data pre-processing techniques coupled with data-driven model. PeerJ e8043. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.8043
Nazir HM, Hussain I, Faisal M, Shoukry M, Gani S, Ahmad I (2019b) Development of multidecomposition hybrid model for hydrological time series analysis. CompLex 2019:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2782715
Nui WJ, Feng ZK, Yang WF, Zhang J (2020) Short-term streamflow time series prediction model by machine learning tool based on data preprocessing technique and swarm intelligence algorithm. Hydrol Sci J 65:2509–2603. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2020.1828889
Shabbir M, Chand S, Iqbal F (2022) A novel hybrid method for river discharge prediction. W Resour Manag 36:253–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-03026-8
Smith JS (2005) The local mean decomposition and its application to EEG perception data. J R Soc Interface 2:443–454. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2005.0058
Tahir AA, Chevalier P, Arnaud Y, Neppel L, Ahmad B (2011) Modeling snowmelt-runoff under climate scenarios in the Hunza River basin, Karakoram Range, Northern Pakistan. J Hydrol 409:104–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.08.035
Talaee PH (2014) Multilayer perceptron with different training algorithms for streamflow forecasting. Neural Comput Appl 24:695–703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-1287-5
Vapnik V (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Wang W, Chau K, Xu D, Chen X (2015) Improving forecasting accuracy of annual runoff time series using ARIMA based on EEMD decomposition. W Resour Manag 29:2655–2675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-0962-6
Wang ZY, Qiu J, Li FF (2018) Hybrid models combining EMD/EEMD and ARIMA for Long-term streamflow forecasting. W 10:853–866. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070853
WAPDA (2021) River inflow in Pakistan. http://www.wapda.gov.pk/index.php/river-flow-in-pakistan. Accessed 25 Nov 2021
Wu C, Chau K, Fan C (2010) Prediction of rainfall time series using modular artificial neural networks coupled with data-preprocessing techniques. J Hydrol 389:146–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.05.040
Wu Z, Huang NE (2009) Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv Adap Data Anal 1:1–41. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793536909000047
Zhang Z, Zhang Q, Singh VP, Shi P (2018) River flow modelling: comparison of performance and evaluation of uncertainty using data-driven models and conceptual hydrological model. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 32:2667–2682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-018-1536-y
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions, which certainly improved the presentation and quality of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
All authors give consent to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Broder J. Merkel
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shabbir, M., Chand, S. & Iqbal, F. Prediction of river inflow of the major tributaries of Indus river basin using hybrids of EEMD and LMD methods. Arab J Geosci 16, 257 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11351-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11351-y