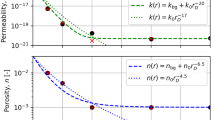
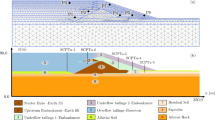
Abstract
The fracture characterization using a geostatistical tool with conditioning data is a computationally efficient tool for subsurface flow and transport applications. The main objective of the paper is to propose a framework of the geostatistical methods to model the fracture network. In the method, we have chosen a neighborhood area to apply the Gaussian Sequential Simulation in order to generate the fracture network in the unknown region. The angle was propagated from the seed where the neighborhood data guide direction. The Poisson procedure is used to distribute initial seeds. The method is applied for geological faults from Central Kazakhstan and for field data from Scotland, UK. The simulation results are compatible with the original fracture network in the flow and transport modeling setting. From the research that has been carried out, it is possible to conclude that the numerical simulation of fracture network is a valuable tool in subsurface flow and transport applications.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almani T, Lee S, Wheeler MF, Wick T et al (2017) Multirate coupling for flow and geomechanics applied to hydraulic fracturing using an adaptive phase-field technique
Amanbek Y, Singh G, Pencheva G, Wheeler MF (2020) Error indicators for incompressible darcy flow problems using enhanced velocity mixed finite element method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 363:112884
Amanbek Y, Singh G, Wheeler MF (2019a) Recovery of the interface velocity for the incompressible flow in enhanced velocity mixed finite element method. In: International conference on computational science. Springer, pp 510–523
Amanbek Y, Singh G, Wheeler MF, van Duijn H (2019b) Adaptive numerical homogenization for upscaling single phase flow and transport. J Comput Phys 387:117–133
Amanbek Y, Wheeler MF (2019) A priori error analysis for transient problems using enhanced velocity approach in the discrete-time setting. J Comput Appl Math 361:459–471
Bishop CM (2006) Pattern recognition. Machine Learning, vol 128
Chandna A, Srinivasan S (2019) Modeling natural fracture networks using improved geostatistical inferences. Energy Procedia 158:6073–6078
Chugunova T, Corpel V, Gomez JP (2017) Explicit fracture network modelling: from multiple point statistics to dynamic simulation. Math Geosci 49:541–553
Doke J (2005) Grabit. MATLAB central file exchange
Goovaerts P et al (1997) Geostatistics for natural resources evaluation. Oxford University Press on demand
Gringarten EJ (1999) Geometric modeling of fracture networks
Healy D, Rizzo RE, Cornwell DG, Farrell NJ, Watkins H, Timms NE, Gomez-Rivas E, Smith M (2017) Fracpaq: a MATLAB toolbox for the quantification of fracture patterns. J Struct Geol 95:1–16
Hyman JD, Karra S, Makedonska N, Gable CW, Painter SL, Viswanathan HS (2015) dfnworks: a discrete fracture network framework for modeling subsurface flow and transport. Comput Geosci 84:10–19
Jung A, Fenwick DH, Caers J (2013) Training image-based scenario modeling of fractured reservoirs for flow uncertainty quantification. Comput Geosci 17:1015–1031
Junkin W, Fava L, Ben-Awuah E, Srivastava M et al (2018) Analysis of MoFrac-generated deterministic and stochastic discrete fracture network models. In: 2nd international discrete fracture network engineering conference,american rock mechanics association
Kullback S, Leibler RA (1951) On information and sufficiency. Annals Math Stat 22:79–86
Liu R, Li B, Jiang Y, Huang N (2016) Mathematical expressions for estimating equivalent permeability of rock fracture networks. Hydrogeol J 24:1623–1649
Liu X, Srinivasan S, Wong D et al (2002) Geological characterization of naturally fractured reservoirs using multiple point geostatistics. In: SPE/DOE improved oil recovery symposium,society of petroleum engineers
Mikelic A, Wheeler MF, Wick T (2015) A phase-field method for propagating fluid-filled fractures coupled to a surrounding porous medium. Multiscale Modeling Simulation 13:367–398
Remy N, Boucher A, Wu J (2009) Applied geostatistics with SGeMS: a user’s guide. Cambridge University Press
Shiozawa S, Lee S, Wheeler MF (2019) The effect of stress boundary conditions on fluid-driven fracture propagation in porous media using a phase-field modeling approach. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 43:1316–1340
Shovkun I, Espinoza DN (2019) Fracture propagation in heterogeneous porous media: pore-scale implications of mineral dissolution. Rock Mech Rock Eng, pp 1–15
Singh G, Amanbek Y, Wheeler MF (2017) Adaptive homogenization for upscaling heterogeneous porous medium. In: SPE annual technical conference and exhibition,society of petroleum engineers
Srivastava RM, Frykman P, Jensen M (2005) Geostatistical simulation of fracture networks. In: Geostatistics Banff 2004. Springer, pp 295–304
Steele JM (1987) Non-uniform random variate generation (luc devroye)
Syusyura B, Box SE, Wallis JC (2010) Spatial databases of geological, geophysical, and mineral resource data relevant to sandstone-hosted copper deposits in central Kazakhstan. Technical report. US geological survey
Thomas SG, Wheeler MF (2011) Enhanced velocity mixed finite element methods for modeling coupled flow and transport on non-matching multiblock grids. Comput Geosci 15:605–625
Wick T, Singh G, Wheeler MF et al (2014) Pressurized-fracture propagation using a phase-field approach coupled to a reservoir simulator. In: SPE hydraulic fracturing technology conference,society of petroleum engineers
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of the research grant, no. AP19575428, from the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan. TM wishes to acknowledge the Nazarbayev University Faculty Development Competitive Research Grant (NUFDCRG), Grant No. 0122022FD4141.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by: Murat Karakus
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Amanbek, Y., Merembayev, T. & Srinivasan, S. Framework of fracture network modeling using conditioned data with sequential Gaussian simulation. Arab J Geosci 16, 219 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-11073-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-11073-7