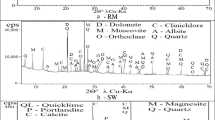
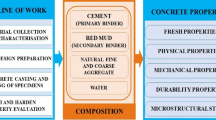
Abstract
Engineering mud treatment has always been a difficult problem in engineering construction. Disposing the engineering construction waste mud efficiently and economically is of great significance to engineering construction. In order to achieve better treatment, this paper introduces a new research method, which is to treat engineering mud through a new composite material made of slag, quicklime, and sodium silicate. The effect of different curing material ratios, water glass dosing, and age on the unconfined compressive strength of the solidified on the treated mud was carried out in the study. The curing effect of the mud was the best when the mass ratio of slag and quicklime was 17:3 and the content of water glass was 5%, and the 28-day unconfined compressive strength could reach 2.752 MPa. The strength of curing mud increased with the curing age, and the growth rate would be slowed down with age. The cementitious substances such as calcium silicate hydrate, calcium aluminate hydrate, and calcium hydroxide produced by the slag mixed with quicklime and water glass are the main factors affecting the strength. The prediction equation of unconfined compressive strength at different ages is obtained for the actual reference.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao YP, Bian X, Deng YF (2011) Experimental study on new composite curing materials for dredged silts with high water content. Geotechnics 32:321–326
Cong AS, Yang XD, Tian B (2012) Design, construction and application of impervious core for deep foundation pit. Intellectual Property Press, Beijing
Deepak R, Narayanan N (2012) Effects of activator characteristics on the reaction product formation in slag binders activated using alkali silicate powder and NaOH. Cem Concr Compos 34:809–818
Dong YW (2009) Research on the treatment technology of waste drilling mud curing. Master's thesis, Chang'an University, Shanxi, China
Lei MZ (2018) Research on strength characteristics of engineering mud cured soil. Master’s thesis, Anhui University of Science and Technology, Anhui, China
Li XG, Yang HT, Jian SW, Tian Z, Li ML (2012) Research on the performance of drilling waste curing road base materials. J Wuhan Univ Technol 34:61–65
Lian HQ, Yang JW, Lei YJ (2018) Experimental study on Influencing Factors of strength of cement fly ash water glass grouting material. Coal Eng 50:107–112
Ou MX, Zheng WW, Wang MS, Chen YH (2016) Experimental study on preparation of engineering mud with expansive soil. J Northwest Univ Agri Forestry Sci Technol (Natural Science Edition) 44:230–234
Peng YZ, Zou SY, Chen XB, Liu BK (2017) Construction technology of roadbed filled with industrial waste combined with solidified dredged sludg. Cons Technol 48:332–335
Sun XL, Tong Q, Liu WH, Yao J, Li ZQ (2017) Study on mechanical properties and microstructure of dredged sludge modified by alkali activated fly ash and mineral powder. J Dalian Univ Technol 57:622–628
Wang DX, Xiao J, Gao XY (2019) Strength gain and microstructure of carbonated reactive MgO-fly ash solidified sludge from East Lake, China. Eng Geol 251:37–47
Xie GH, Du HQ, Zhu SJ (2011) Experimental study on solidification of dredged sludge with new ash adhesive material. Fly Ash 23:26–28
Yi YL, Qing XW, Zhuang Y, Liu SY, Du GY (2013) Application of granulated blast furnace slag powder in soft soil solidification and its reinforcement mechanism. J Geotech Eng 35:829–833
Zhang XL, Yao AL (2007) Effect of lime on strength of slag cementitious material. Silicate Bull 01:87–91
Zhou WJ, Wang Q, Yang JD, Li M, Yin YT, Guo XL (2021) Study on strength characteristics of CFG solidified expansive soil under dry wet cycle. J Henan Inst Urban Cons 30:51–59
Funding
The authors received financial support from the Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Building Structure and Underground Engineering, Anhui Jianzhu University, Hefei (Grant Number KLBSUE2021-01), and the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Anhui (Grant Number 2016B116)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zeynal Abiddin Erguler
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, JS., Wang, YX., Pang, JY. et al. Experimental study on the characteristics of slag-lime-water glass composite cured mud. Arab J Geosci 15, 1489 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10772-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10772-5