Abstract
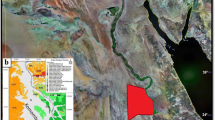
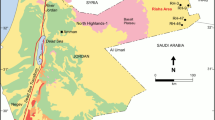
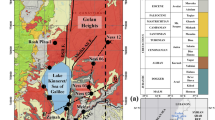
The most accumulated oil in the main reservoir intervals in the Abu Rudeis-Sidri area is generated from the Duwi and Thebes source rocks. Therefore, the present study focuses on modeling their maturity and hydrocarbon potential using the available data of five wells by the BasinMod program for petroleum system and basin analysis. The input data include formation ages, erosions and hiatuses, lithologies, formation thicknesses and eroded thicknesses, hydrogen index, oxygen index, production index, total organic carbon, and vitrinite reflectance. These data are modeled, and the results are presented in the form of a variety of models, including burial and thermal maturity, generation, and expulsion models. Duwi and Thebes source rocks began the maturation and generation at different times in different wells. The Duwi source rock started the maturation at 20.1 Ma and the generation at 15.6 Ma, while the Thebes source rock started the maturation at 15.72 Ma and the generation at 15.2 Ma. Moreover, the Duwi reached the top of the peak-late generation oil phase at 13.3 Ma, while the Thebes reached this stage at 1.95 Ma. The high potential for Duwi and Thebes source rocks is promoted by many factors, including high overburden thicknesses, high tectonic subsidence and sedimentation rates, high burial temperatures, shallow depths to maturity, and reaching late mature stage with long mid mature duration. These factors increase the transformation ratio and consequently the expelled oil. The generated and expelled hydrocarbons are mainly oil with small amounts of gas.





source rocks

source rocks




source rocks

source rocks

source rocks for the Duwi and Thebes formations
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MA, Hegab OA, Awadalla AS et al (2019) Hydrocarbon generation, in-source conversion of oil to gas and expulsion: petroleum system modeling of the Duwi Formation, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Nat Resour Res 28:1547–1573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09458-9
Allen G, Ayyad A, Desforges G, Haddadi M, Pizon J (1984) Subsurface sedimentological study of the Rudeis Formation in Kareem, Ayun, Yusr and Shukheir fields, in Proceedings of the 6th Exploration Conference: Cairo, Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation. Pp164–176
Alsharhan A (2003) Petroleum geology and potential hydrocarbon plays in the Gulf of Suez rift basin. Egypt AAPG Bulletin 87(1):143–180
Alsharhan AS, Salah MG (1997) Lithostratigraphy, sedimentology and hydrocarbon habitat of the pre-Cenomanian Nubian sandstone in the Gulf of Suez oil province. Egypt Geo Arabia 2(4):385–400
Awadalla A, Hegab AO, Ahmed AM, Hassan S (2017) Burial and thermal history simulation of the Abu Rudeis-Sidri oil field, Gulf of Suez-Egypt: A 1D basin modelingstudy. J Afr Earth Sc 138:86–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.10.009
Barakat H (1982) Geochemistry criteria for source rock, Gulf of Suez. 6 th Petroleum Exploration and Production Conference, Cairo. 224–252
Bartov Y, Steinitz G, Ayal M, Ayal Y (1980) Sinistral movement along the Gulf of Aqaba—its age and relation to the opening of the Red Sea. Nature 285:220–222
Beleity A (1982) The composite standard and definition of paleo events in the Gulf of Suez: 6th Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation. Petr Explor Prod Conf 1:181–199
Colletta B, LeQuellec P, Letouzey J, Moretti I (1988) Longitudinal evolution of the Suez rift structure. Egypt Tectonophys 153:221–233
El Nady MM, Mohamed NS (2016) Source rock evaluation for hydrocarbon generation in Halal oilfield, southern Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Egypt J Petrol 25(3):383–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2015.09.003
El Nady MM, Mohamed NS, Shahin AN (2016) Source-Rock Potential of Miocene-Paleozeoic Sediments in GH-376 Oilfield, South Gulf of Suez, Egypt. J Energy Sour A: Recover Util Environ Eff 38(1):100–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2012.754518
Elmaadawy KG (2021) Oil Characteristics and Source Rock Potential of Abu Rudeis-Abu Zenima Area, Central Province, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. https://doi.org/10.21608/jpme.2021.76044.1082
Evans AL (1988) Neogene tectonic and stratigraphic events in the Gulf of Suez rift area, Egypt. Tectonophysics 153:235–247
Fawzy H, Abdel Aal A (1984) Regional study of Miocene evaporites and Pliocene—recent sediments in the Gulf of Suez. In Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation (EGPC). 7th Exploration Seminar, Cairo 49–74
Gandino A, Giori L, Milad G (1990) Magnetic interpretation controlled by interactive 3D modelling in the southern Gulf of Suez: 10th Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation, Petroleum Exploration and Production Conference 1, 740–786
Hughes GW, Abdine S, Girgis MH (1992) Miocene biofacies development and geological history of the Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Mar Pet Geol 9:2–28
Issawi B (1973) Nubia Sandstone: Type Section: Geological Notes. AAPG Bull 57. https://doi.org/10.1306/819a431c-16c5-11d7-8645000102c1865d
Metwalli F, Pigott J (2005) Analysis of petroleum system criticals of the Matruh-Shushan Basin, Western Desert, Egypt. Pet Geosci 11(2):157–178
Mohamed NS, El Nady MM (2019) Potentiality and timing of generation of Kareem and Rudeis formations, Central Gulf of Suez. Pet Sci Technol 37(8):925–933. https://doi.org/10.1080/10916466.2018.1558245
Moustafa AR (1996) Internal structure and deformation of an accommodation zone in the northern part of the Suez rift. J Struct Geol 18:93–107
Patton TL, Moustafa AR, Nelson RA, Abdine SA (1994) Tectonic evolution and structural setting of the Suez rift. In: London SM (ed.) Interior rift basins. AAPG Memoir 59:7–55
Peijs JAMM, Bevan TG, Piombino JT (2012) The Gulf of Suez rift basin”, Regional Geology and Tectonics: Phanerozoic Rift Systems and Sedimentary Basins. Elsevier 164–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-56356-9.00007-9
Pepper AS, Corvi PJ (1995) Simple kinetic models of petroleum formation. Part i: Oil and Gas Generation from Kerogen. Mar Pet Geol 12(3):291–319
Salah MG (1992) Geochemical evaluation of the southern Gulf of Suez, Egypt, 11th Petroleum Exploration and Production Conference, Cairo. 383–395
Scott RW, Govean FM (1985) Early depositional history of a rift basin: Miocene in western Sinai. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 62:143–158
Sellwood BW, Netherwood RE (1984) Facies evolution in the Gulf of Suez area: sedimentation history as an indicator of rift initiation and development. Modern Geol 9:43–69
Shahin AN, Shehab M (1984) Petroleum Generation, Migration and Occurrence in the Gulf of Suez offshore, South Sinai. 7th Petroleum Exploration and Production Conference, Cairo. 126–152
Soliman AC, Oric S, Head MJ, Piller WE, El Beialy YS (2012) Lower and Middle Miocene biostratigraphy, Gulfof Suez, Egypt based on dinoflagellate cysts and calcareousnannofossils. Palynology 36(1):38–79
Steckler MS, Berthelot F, Lyberis N, Le Pichon X (1988) Subsidence in the Gulf of Suez: implications for rifting and plate kinematics. Tectonophysics 153:249–270
Wever HE (1999) A common source rock for Egyptian and Saudi hydrocarbons in the Red Sea: Discussion. Am\Assoc Pet Geol Bull 83(5), 802–804
Wever HE (2000) Petroleum and source rock characterization based on C7 plot results: Examples from Egypt. Am Asso Petrol Geol Bull 84(7):1041–1054
Younes MA, Afife MM, El Nady MM (2017) Geochemical characteristics of crude oils dependent specific and biomarker distributions in the central-southern Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Energy Sour A: Recover Util Environ Eff 39(2):191–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2016.1208306
Younes MA, Philp RP (2005) Source rock characterization based on biological marker distributions of crude oils in the southern Gulf of Suez. Egypt. J Pet Geol 28(3):301–317
Zahra HS, Nakhla AM (2016) Structural interpretation of seismic data of Abu Rudeis-Sidri area, northern Central Gulf of Suez, Egypt. ’Rev NRIAG J Astron Geophys 5(2):435–450
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on New Advances and Research Results on the Geology of Africa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elmaadawy, K.G., Bayan, M.F. & El-Shayeb, H.M. Source rock maturity and hydrocarbon potential of Abu Rudeis-Sidri area, central province, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 14, 2813 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09140-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09140-6