Abstract
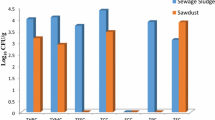
The aim of study was to evaluate physicochemical properties of sewage sludge degradation under aerobic and anaerobic conditions in municipal wastewater treatment plant in Serkan, Hamedan province, west of Iran. The evaluated parameters included temperature, carbon to nitrogen ratio (C:N), total C, total N, moisture content, volatile solids, ash, electrical conductivity (EC), pH, and fecal and total coliforms. Experiments were conducted over a period of 100 days during which the sampling from the mixtures was performed every 5 days. Properties of the waste sludge and both treatments including windrow composting and anaerobic digestion were assessed at the initial stage, and during and end of the degradation period. The pH of the compost piles was found to be 6.28 at the beginning of the process and about 7–7.5 after 100 days in both treatments. Based on field observations, it could be concluded that after 14 weeks of degradation, compared with the aerobic degradation, the anaerobic digestion would yield a digestate of a higher quality with the final total nitrogen of 2.8%, final total carbon (TOC) of 44%, and C:N of 15.7. This higher rate of final total nitrogen and the lower amount of total coliform could indicate the suitability of degradation quality through anaerobic digestion. Based on the results, a substantial reduction was observed in C:N ratio, total carbon content, and the moisture content in waste sludge following degradation, while an increase in nitrogen content as well as pH was observed in digestate.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Also, my submission does not include data in brief and I do not need research data support.
References
Abdullah N, Chin NL, Mokhtar MN, Saleena FT (2013) Effects of bulking agents, load size or starter cultures in kitchen waste composting. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agric 3:1–10
Adams JDW, Frostick LE (2009) Analysis of bacterial activity, biomass and diversity during windrow composting. Waste Manage 29:598–605
Atchley SH, Clark JB (1979) Variability of temperature, pH, and moisture in an aerobic composting process. Appl Environ Microbiol 38(6):1040–1044
Awasthi MK, Pandey AK, Bundela PS, Wong JWC, Li R, Zhang Z (2016) Co-composting of gelatin industry sludge combined with organic fraction of municipal solid waste and poultry waste employing zeolite mixed with enriched nitrifying bacterial consortium. Bioresour Technol 213:181–189
Awasthi MK, Li J, Kumar S, Awasthi SK, Wang Q, Chen H, Wang M, Ren X, Zhang Z (2017) Effects of biochar amendment on bacterial and fungal diversity for co-composting of gelatin industry sludge mixed with organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Bioresour Technol 246:214–223
Batham M, Gupta R, Tiwari A (2013) Implementation of bulking agents in composting: a review. J Bioremediat Biodegrad 4(7):1–3
Bazrafshan E, Zarei A, KordMostafapour F, Poormollae N, Mahmoodi S, Zazouli MA (2016) Maturity and stability evaluation of composted municipal solid wastes. Health Scope 5(1):33202
Bertoncini EI, D’Orazio V, Senesi N, Mattiazzo ME (2008) Effects of sewage sludge amendment on the properties of two Brazilians oxisols and their humic acids. Bioresour Technol 99:4972–4979
Bernal MP, Alburquerque JA, Moral R (2009) Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment. A review. Bioresour Technol 100:5444–5453
Brito LM, Coutinho J, Smith SR (2008) Methods to improve the composting process of the solid fraction of dairy cattle slurry. Bioresour Technol 99:8955–8960
Brown D, Li Y (2013) Solid state anaerobic co-digestion of yard waste and food waste for biogas production. Bioresour Technol 127:275–280
Bustamante MA, Paredes C, Marhuenda-Egea FC, Perez-Espinosa A, Bernal MP, Moral R (2008) Co-composting of distillery wastes with animal manures: carbon and nitrogen transformations in the evaluation of compost stability. Chemosphere 72:551–557
Cayuela ML, Sánchez-Monedero MA, Roig A, Sinicco T, Mondini C (2012) Biochemical changes and GHG emissions during composting of lignocellulosic residues with different N-rich by-products. Chemosphere 88(2):196–203
Chang JI, Chen YJ (2010) Effects of bulking agents on food waste composting. Bioresour Technol 101:5917–5924
Chan M, Selvam A, Wong JWC (2016) Reducing nitrogen loss and salinity during ‘struvite’ food waste composting by zeolite amendment. Bioresour Technol 200:838–844
Civeira G (2010) Influence of municipal solid waste compost on soil properties and plant reestablishment in peri-urban environments. Chil J Agric Res 70:446–453
Correa RS, White RE, Weatherley AJ (2006) Effect of compost treatment of sewage sludge on nitrogen behavior in two soils. Waste Manage 26:614–619
Diacono M, Montemurro F (2015) Effectiveness of organic wastes as fertilizers and amendments in salt-affected soils. Agriculture 5:221–230
Doublet J, Francou B, Poitrenaud M, Houot S (2010) Sewage sludge composting: Influence of initial mixtures on organic matter evolution and N availability in the final composts. Waste Manage 30(10):1922–1930
Doublet J, Francou C, Poitrenaud M, Houot S (2011) Influence of bulking agents on organic matter evolution during sewage sludge composting; consequences on compost organic matter stability and N availability. Bioresour Technol 102:1298–1307
Du J, Zhang Y, Hu B, Qv M, Ma C, Wei M, Zhang H (2019) Insight into the potentiality of big biochar particle as an amendment in aerobic composting of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 288:121469
Eftoda G, Mc Cartney D (2004) Determining the critical bulking agent requirement for municipal biosolids composting. Compost Sci Util 12:208–218
El Fels L, Zamama M, El Asli A, Hafidi M (2014) Assessment of biotransformation of organic matter during co-composting of sewage sludge-lignocelullosic waste by chemical, FTIR analyses, and phytotoxicity tests. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 87:128–137
Feng Y, Zhang Y, Quan X, Chen S (2014) Enhanced anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge digestion by the addition of zero valent iron. Water Res 52:242–250
García C, Hernández T, Costa F (1990) The influence of composting and maturation processes on the heavy-metal extractability from some organic wastes. Biol Waste 31:291–301
GolbabaeiKootenaei F, Aminirad H, Ramezani M (2014) Composting of sewage sludge and municipal solid waste. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 13(3):553–558
Hassen A, Belguith K, Jedidi N, Cherif A, Cherif M, Boudabous A (2001) Microbial characterization during composting of municipal solid waste. Bioresour Technol 80(3):217–225
Heerden IV, Cronjé C, Swart SH, Kotzé JM (2002) Microbial, chemical and physical aspects of citrus waste composting. Bioresour Technol 81(1):71–76
Himanen M, Hänninen K (2011) Composting of bio-waste, aerobic and anaerobic sludges–effect of feedstock on the process and quality of compost. Bioresour Technol 102(3):2842–2852
Hock LS, Baharuddin AS, Ahmad MN, Shah UK (2009) Physicochemical changes in windrow co-composting process of oil palm mesocrap fiber and palm oil mill effluent anaerobic sludge. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 3(3):2809–2816
Hua L, Wu W, Liu Y, McBride MB, Chen Y (2009) Reduction of nitrogen loss and Cu and Zn mobility during sludge composting with bamboo charcoal amendment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16:1–9
Hwang HY, Kim SH, Kim MS, Park SJ, Lee CH (2020) Co-composting of chicken manure with organic wastes: characterization of gases emissions and compost quality. Appl Biol Chem 63:3
Iglesias-Jimenez E, Perez-Garcia V (1991) Composting of domestic refuse and sewage sludge. Part. 1. Evaluation of temperature, pH, C: N ratio and cation exchange capacity. Res Conserv Recycl 6:45–60
Jakubus MB, Czekała J (2010) Chromium and nickel speciation during composting process of different biosolids. Fresen Environ Bull 19(2):289–299
Jouraiphy A, Amir S, Gharous M, Revel JC, Hafidi M (2005) Chemical and spectroscopic analysis of organic matter transformation during composting of sewage sludge and green plant waste. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 56:101–108
Jurado M, Suárez-Estrella F, López M, Vargas-García M, López-González J, Moreno J (2015) Enhanced turnover of organic matter fractions by microbial stimulation during lignocellulosic waste composting. Bioresour Technol 186:15–24
Karanja AW, Njeru EM, Maingi JM (2019) Assessment of physicochemical changes during composting rice straw with chicken and donkey manure. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agric 8(1):65–72
Khalil AI, Hassouna MS, El-Ashqar HMA, Fawzi M (2011) Changes in physical, chemical, and microbial parameters during the composting of municipal sewage sludge. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27(10):2359–2369
Kosobucki P, Chmarzyński A, Buszewski B (2000) Sewage sludge composting. Pol J Environ Stud 9(4):243–248
Kong Z, Wang X, Liu Q, Li T, Chen X, Chai L, Liu D, Shen Q (2018) Evolution of various fractions during the windrow composting of chicken manure with rice chaff. J Environ Manag 207:366–377
Kulikowska D, Klimiuk E (2010) Co-composting of sewage sludge with lignocellulosic amendments assessment of compost quality. J Biotechnol 150:282–283
Kulikowska D, Klimiuk E (2011) Organic matter transformations and kinetics during sewage sludge composting in a two-stage system. Bioresour Technol 102:10951–10958
Lin L, Yang L, Xu F, Michel FC, Li Y (2014) Comparison of solid-state anaerobic digestion and composting of yard trimmings with effluent from liquid anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 169:439–446
Liu Y, Ding L, Wang B, He Q, Wan D (2020) Using the modified pine wood as a novel recyclable bulking agent for sewage sludge composting: Effect on nitrogen conversion and microbial community structures. Bioresour Technol 309:123357
Liu Y, Ma L, Li Y, Zheng L (2007) Evolution of heavy metal speciation during the aerobic composting process of sewage sludge. Chemosphere 67:1025–1032
Liu L, Ye Q, Wu Q, Liu T, Peng S (2021) Effect of biochar addition on sludge aerobic composting and greenbelt utilization. Environ Technol Innov 21:101279
Liu N, Zhou J, Han L, Ma S, Sun X, Huang G (2017) Role and multi-scale characterization of bamboo biochar during poultry manure aerobic composting. Bioresour Technol 241:190–199
Liu DY, Zhang RF, Wu HS, Xu DB, Tang Z, Yu GH, Xu ZH, Shen QR (2011) Changes in biochemical and microbiological parameters during the period of rapid composting of dairy manure with rice chaff. Bioresour Technol 102:9040–9049
Martínez-Blanco J, Lazcano C, Christensen TH (2013) Compost benefits for agriculture evaluated by life cycle assessment-a review. Agron Sustain Dev 33:721–732
Mehta CM, Sirari K (2018) Comparative study of aerobic and anaerobic composting for better understanding of organic waste management: a mini review. Plant Arch 18(1):44–48
Mello Leite Moretti S, IvaniBertoncini E, Hamilton Abreu-Junior C (2015) Composting sewage sludge with green waste from tree pruning. Scientia Agricola 72(5):432–439
Mokhtari M, SalehiVaziri A, Zareei T, Jalili M (2016) Investigating the possibility of producing compost from the dewatered sludge of Yazd wastewater treatment plant by Windows method with different treatments. Iran J Health Environ 9(4):493–502 ((In Persian))
Moldes A, Cendón Y, Barral MT (2007) Evaluation of municipal solid waste compost as a plant growing media component, by applying mixture design. Bioresour Technol 98:3069–3075
Moretti SML, Bertoncini EI, Hamilton Abreu-Junior C (2015) Composting sewage sludge with green waste from tree pruning. Scientia Agricola 72(5):432–439
Naserian ES, Cheraghi M, Lorestani B, Sobhanardakani S, Kaini Sadr M (2021) Qualitative investigation of sewage sludge composting: effect of aerobic/anaerobic pretreatments. Arab J Geosci 14:836
Nikaeen M, Nafez AH, Bina B, Nabavi BF, Hassanzadeh A (2015) Respiration and enzymatic activities as indicators of stabilization of sewage sludge composting. Waste Manage 39:104–110
Noguera P, Abad M, Puchades R, Maquieira A, Noguera V (2003) Influence of particle size on physical and chemical properties of coconut coir dust as container medium. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 34:593–605
Papadimitriou EK, Balis C (1996) Comparative study of parameters to evaluate and monitor the rate of a composting process. Compost Sci Util 4(4):52–61
Rashad FM, Saleh WD, Moselhy MA (2010) Bioconversion of rice straw and certain agro-industrial wastes to amendments for organic farming systems: 1. Composting, quality, stability and maturity indices. Bioresour Technol 101:5952–5960
Roca-Pérez L, Martínez C, Marcilla P, Boluda R (2009) Composting rice straw with sewage sludge and compost effects on the soil–plant system. Chemosphere 75:781–787
Rodríguez-Rodríguez CE, Jelić A, Llorca M, Farré M, Caminal G, Petrović M, Vicent T (2011) Solid-phase treatment with the fungus Trametes versicolor substantially reduces pharmaceutical concentrations and toxicity from sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 102(10):5602–5608
Rydine E, Otabborg E (1997) Potential release of phosphorus from soil mixed with sewage sludge. J Environ Qual 26:529
Sadaka S, El–Taweel A, (2003) Effects of aeration and C: N ratio on household waste composting in Egypt. Compost Sci Util 11(1):36–40
Sagoo E, Williams JR, Chambers BJ, Boyles LO, Matthews R, Chadwick DR (2007) Integrated management practices to minimise losses and maximise the crop nitrogen value of broiler litter. Biosys Eng 97:512–519
Sangodoyin A, Amori A (2013) Aerobic composting of cassava peels using cow dung, sewage sludge and poultry manure as supplements. Eur Int J Sci Technol 2:22–34
Satisha G, Devarajan L (2007) Effect of amendments on windrow composting of sugar industry pressmud. Waste Manage 27(9):1083–1091
Shah GM, Shah GA, Groot JCJ, Oenema O, Raza AS, Lantinga EA (2016a) Effect of storage conditions on losses and crop utilization of nitrogen from solid cattle manure. J Agric Sci 154(1):1–14
Shah GM, Shah GA, Groot JCJ, Raza MAS, Shahid N, Lantinga EA (2016b) Maize nitrogen recovery and dry matter production as affected by application of solid cattle manure subjected to various storage conditions. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 16(3):591–603
Shah GM, Tufail N, FaiqBakha H, Imran M, Murtaza B, Umer Farooq AB, Saeed F, Waqar A, Imtiaz Rashid M (2017) Anaerobic degradation of municipal organic waste among others composting techniques improves N cycling through waste-soil-plant continuum. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 17(2):529–542
Tang J, Katayama A (2005) Relating quinine profile to the aerobic biodegradation in thermophilic composting processes of cattle manure with various bulking agents. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:1249–1254
Tibu C, Annang TY, Solomon N, Tawiah DY (2019) Effect of the composting process on physicochemical properties and concentration of heavy metals in market waste with additive materials in the Ga West Municipality, Ghana. Int J Recycl Organ Waste Agric 8:393–403
Torres-Climent A, Martin-Mata J, Marhuenda-Egea F, Moral R, Barber X, Perez-Murcia MD, Paredes C (2015) Composting of the solid phase of digestate from biogas production: optimization of the moisture, C/N ratio and pH conditions. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 46(S1):197–207
Tchobanoglous G, Stensel H, Tsuchihashi R, Burton F (2013) Wastewater engineering: treatment and resource recovery, 5th edition. 2013: McGraw-Hill Education, p 2048
Tuomela M, Vikman M, Hatakka A, Itavaara M (2000) Biodegradation of lignin in a compost environment: a review. Bioresour Technol 72(2):169–183
USEPA (1983) Methods for chemical analysis of water and wastes. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Washington, DC, 20450
USEPA (1994) A plain english guide to the EPA Part 503 biosolids rule. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Wastewater Management, Washington, DC, EPA 832-R-93-003
Varma V, Ramu K, Kalamdhad A (2015) Carbon decomposition by inoculating Phanerochaete chrysosporium during drum composting of agricultural waste. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:7851–7858
Wang P, Yu Z, Zhao J, Zhang H (2017) Do microbial communities in an anaerobic bioreactor change with continuous feeding sludge into a full-scale anaerobic digestion system. Bioresour Technol 249:89–98
Wu C, Li W, Wang K, Li Y (2015) Usage of pumice as bulking agent in sewage sludge composting. Bioresour Technol 190:516–521
Yang Y, Awasthi MK, Ren X, Guo H, Lv J (2019) Effect of bean dregs on nitrogen transformation and bacterial dynamics during pig manure composting. Bioresour Technol 288:121430
Yang G, Fan M, Zhang G (2014) Emerging contaminants in surface waters in China-a short review. Environ Res Lett 9(7):1195–1206
Zhang H, Li G, Gu J, Wang G, Li Y, Zhang D (2016) Influence of aeration on volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) and NH3 emissions during aerobic composting of kitchen waste. Waste Manage 58:369–375
Zheng GD, Gao D, Chen TB, Luo W (2007) Stabilization of nickel and chromium in sewage sludge during aerobic composting. J Hazard Mater 142:216–221
Zhu N (2006) Composting of high moisture content swine manure with corncob in a pilot-scale aerated static bin system. Bioresour Technol 97:1870–1875
Zorpas AA, Arapoglou D, Karlis P (2003) Waste paper and clinoptilolite as a bulking material with dewatered anaerobically stabilized primary sewage sludge (DASPSS) for compost production. Waste Manage 23:27–35
Zuokaitė E, Zigmontienė A (2013) Application of a natural cover during sewage sludge composting to reduce gaseous emissions. Pol J Environ Stud 22(2):621–626
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Hamedan Branch, Islamic Azad University for providing facilities to conduct and complete this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Maryam Younesian, Mehrdad Cheraghi, Soheil Sobhan Ardakani, Bahareh Lorestani, and Hajar Merrikhpour. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Hajar Merrikhpour and Soheil Sobhan Ardakani, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. The corresponding author makes sure that all authors have approved the manuscript before submission, which includes the names and arrangement of authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with animals and human subjects. The authors confirm that all the research meets ethical guidelines and adheres to the legal requirements of the study country. Also, this manuscript has not been published previously in any form (partially or in full) or language and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that this manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data and material in any form.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Haroun Chenchouni
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Younesian, M., Cheraghi, M., Sobhanardakani, S. et al. Assessment of the differences between composting and anaerobic digestion of sludge. Arab J Geosci 14, 2500 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08891-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08891-6