Abstract
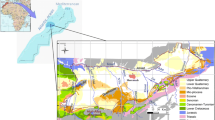
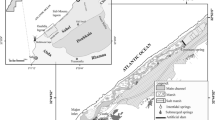
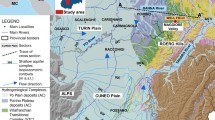
In El Haouaria region located in the Cap Bon peninsula (N.E. Tunisia), the hydrodynamic survey revealed a decrease in unconfined groundwater reserves of approximately 11% over the last 30 years due to the abstraction of water. Over that same time period, the groundwater table displayed a natural decrease of about 10 m in depth over an area of 230 km2. Hydrogeological investigations have shown that two aquifers which vertically integrate all of the permeable zones in the region can be distinguished: a shallow aquifer formed by filling the Quaternary and another deeper one in the Pliocene. These two aquifers are separated by a semi-permeable layer through which vertical exchange by seepage is possible. Different methods using geochemistry (Na+, Cl−, Br−) and stable isotopes (18O, 2H) are compared with the hydrodynamic information for identifying the main processes involved in the salinization and recharge. Forty groundwater wells were sampled to obtain additional information on the hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of the groundwater defined in previous studies. Estimation of groundwater recharge in this semi-arid area is difficult due to the low amount and variability of recharge. Two analytical models, taking into account the long term decrease of the water table, were used to interpret 3H and 14C content in groundwater. The median annual renewal rate (recharge as a fraction of saturated aquifer volume) varies between 0.2 and 0.3%. For representative characteristics of the aquifer (30 m of saturated thickness, porosity 14%) this implies a recharge of 10 to 12 mm/yr.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal P, Froehlich K, Gonfiantini R, Gat JR (2005) Isotope hydrology: a historical perspective from the IAEA. In: Aggarwal PK, Gat JR, Froehlich KF (eds) Isotopes in the water cycle. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3023-1_1
Ben Hamouda MF (2008) Hydrogeological, Geochimical and Isotopic Approach of the Coastal Aquifers systems Of Cap Bon: Case of the Eastern coastal and El Haouaria aquifer, Tunisia, 2008. PhD in Agronomic Sciences of the National Agronomic Institute of Tunisia [in french].
Ben Hamouda MF, Tarhouni J, Leduc C et al (2011) Understanding the origin of salinization of the Plio-quaternary eastern coastal aquifer of cap bon (Tunisia) using geochemical and isotope investigations. Environ Earth Sci 63:889–901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0758-1
Ben Hamouda MF, Carreira P, Marques JM, Egenkamp H (2013) Geochemical and isotopic investigations to study the origin of mineralization of the coastal aquifer of Sousse, Tunisia. Procedia Earth Planet Sci 7:61–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2013.03.106
Ben Hamouda MF, Kondash AJ, Lauer N, Mejri L, Tarhouni J, Vengosh A (2015) Assessment of groundwater salinity mechanisms in the coastal aquifer of El Haouaria, northern Tunisia. Procedia Earth Planet Sci 13:194–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2015.07.046
Bouchaou L, Michelot JL, Vengosh A, Hsissou Y, Qurtobi M, Gaye CB, Bullen TD, Zuppi GM (2008) Application of multiple isotopic and geochemical tracers for investigation of recharge, salinization, and residence time of water in the Souss–Massa aquifer, southwest of Morocco. J Hydrol 352:267–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.01.022
Cartwright I, Weaver TR, Stone D, Reid M (2007) Constraining modern and historical recharge from bore hydrographs, 3H, 14C, and chloride concentrations: applications to dual-porosity aquifers in dryland salinity areas, Murray Basin, Australia. J Hydrol 332:69–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.06.034
Celle-Jeanton H, Zouari K, Travi Y, Daoud A (2001) Isotopic characterisation of the precipitation in Tunisia. Variations of the stable isotope compositions of rainfall events related to the origin of air masses. CR Acad Sc Series IIA - Earth Planet Sci 333:625–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1251-8050(01)01671-8
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. CRC Lewis Publishers, New York 328 p
Coleman ML, Shepherd TJ, Durham JJ, Rouse JE, Moore GR (1982) Reduction of water with zinc for hydrogen isotope analysis. Anal Chem 54:993–995. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00243a035
Coplen TB (1988) Normalization of oxygen and hydrogen isotope data. Chem Geol 72:293–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-9622(88)90042-5
De Montety V, Radakovitch O, Vallet-Coulomb C, Blavoux B, Hermitte D, Valles V (2008) Origin of groundwater salinity and hydrogeochemical processes in a confined coastal aquifer: case of the Rhône delta (southern France). Appl Geochem 23:2337–2349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.03.011
Ennabli M (1980) Hydrogeologic study of the aquifers of the North-East of Tunisia for an integrated management of the water resources. PhD, University of Nice, France [in French].
Epstein S, Mayeda TK (1953) Variations of 18O content of waters from natural sources. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 4:213–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(53)90051-9
Favreau G (2000) Caractérisation et modélisation d'une nappe phréatique en hausse au Sahel: Dynamique et géochimie de la depression piézomktrique naturelle du kori de Dantiandou (sud-ouest du Niger). Ph.D, thesis, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Paris-Sud, Orsay, France.
Favreau G, Leduc C, Marlin C, Dray M, Taupin JD, Massault M, Le Gal La Salle C, Babic M (2002a) Estimate of recharge of a rising water table in semiarid Niger from 3H and 14C modeling. Groundwater. 40:144–151
Favreau G, Leduc C, Marlin C, Guéro A (2002b) Une dépression piézométrique naturelle en hausse au Sahel (Sud-Ouest du Niger). CR Geoscience 334:395–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1631-0713(02)01763-7
Ferchichi H, Farhat B, Ben Hamouda MF, Ben Mammou A (2017) Understanding groundwater chemistry in Mediterranean semi-arid system using multivariate statistics techniques and GIS methods: case of Manouba aquifer (northeastern Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 10:530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3314-4
Fontes JC (1971) Un ensemble destiné à la mesure de l’activité du radiocarbone naturel par scintillation liquide [a unit intended for the measurement of the activity of natural radiocarbon by liquid scintillation]. Rev Geogr Phys Géol Dyn 13(1):67–86
Fontes JC (1976) Isotopes du milieu et cycle des eaux naturelles. La Houille Blanche 3:4:205–221. https://doi.org/10.1051/lhb/1976010
Fontes JC, Garnier JM (1979) Determination of the initial 14C activity of the total dissolved carbon; a review of the existing models and a new approach. Water Resour Res 15:399–413. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR015i002p00399
Geyh MA (2000) An overview of 14C analysis in the study of groundwater. Radiocarbon. 42:99–114. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033822200053078
Guo C, Shi J, Zhang Z et al (2019) Using tritium and radiocarbon to determine groundwater age and delineate the flow regime in the Taiyuan Basin, China. Arab J Geosci 12:185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4371-7
IAEA, WMO, (2015) Global Network for Isotopes in Precipitation. URL: https://www.iaea.org/services/networks/gnip Global Network of Isotopes in Precipitation (GNIP) | IAEA
Jemai S (1998) State evolution of the Korba aquifer: Hydrogeochemical study and numerical modelling, Master of Science, National Agronomic Institute of Tunisia. [in French]
Jones BF, Vengosh A, Rosenthal E, Yechieli Y (1999) Geochemical investigations. In: Bear J et al (eds) Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht, pp 51–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-2969-7_3
Kamel S (2013) Salinisation origin and hydrogeochemical behaviour of the Djerid oasis water table aquifer (southern Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 6:2103–2117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0502-5
Kaufman S, Libby WF (1954) The natural distribution of tritium. Phys Rev 93:1337–1344. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.93.1337
Khomsi S, Ben Jemia MG, Frizon de Lamotte D, Maherssi C, Echihi O, Mezni R (2009) An overview of the late cretaceous–Eocene positive inversions and oligo-Miocene subsidence events in the foreland of the Tunisian atlas: structural style and implications for the tectonic agenda of the Maghrebian atlas system. Tectonophysics 475:38–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2009.02.027
Khomsi S, Echihi O, Slimani N (2012) Structural control on the deep hydrogeological and geothermal aquifers related to the fractured Campanian-Miocene reservoirs of North-Eastern Tunisia for eland constrained by subsurface data. C R Géoscience 344:247–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crte.2012.02.002
Khomsi S, Frizon de Lamotte D, Bédir M, Echihi O (2016) The late Eocene and Late Miocene fronts of the Atlas Belt in eastern Maghreb: integration in the geodynamic evolution of the Mediterranean domain. Arab J Geosci 9:650–670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2609-1
Khomsi S, Roure F, Khelil M, Mezni R, Echihi O (2019a) A review of the crustal architecture and related pre-saltoil/gas objectives of the eastern Maghreb atlas and tell: need for deep seismic reflection profiling. Tectonophysics 766:232–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2019.06.009
Khomsi S., Roure F., Brahim N.B., Maherssi C., Arab M., Khelil M. (2019b) Structural Styles, Petroleum Habitat and Traps in the Pelagian-Sirt Basins, Northern Africa: An Overview and Future Exploration Developments. In: Rossetti F. et al. (eds) The Structural Geology Contribution to the Africa-Eurasia Geology: Basement and Reservoir Structure, Ore Mineralization and Tectonic Modelling. CAJG 2018. Advances in Science, Technology& Innovation (IEREK Interdisciplinary Series for Sustainable Development). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01455-1_33
Lassoued S (1982) Hydrogéologie et géochimie isotopique de la plaine d’El Haouaria (Tunisie septentrionale). Thèse de doctorat de 3ème cycle. Université de Paris-Sud, France. 193p
Mook WG (2001) Environmental isotopes in the hydrological cycle, Principles and applications, 5 volumes, Unesco, IHP, Technical documents in hydrology, N° 39
Moussa AB, Salem SBH, Zouari K et al. (2017) Hydrochemical and stable isotopic investigation of groundwater quality and its sustainability for irrigation in the Hammamet-Nabeul basin, northeastern Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 10, 446 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3233-4
Negrel P, Petelet-Giraud E (2011) Isotopes in groundwater as indicators of climate changes. Trends Anal Chem 30:1279–1290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2011.06.001
Nydal R, Lovseth, K (1996)Carbon- measurements in atmospheric CO, from northern and southern hemisphere sites, 1962–1993. Oak Ridge National Laboratory NDP-057. https://doi.org/10.2172/461185
Paniconi C, Khlaifi I, Lecca G, Giacomelli A, Tarhouni J (2001) Modeling and analysis of seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifer of eastern cap-bon, Tunisia. Transp Porous Media 43(1):3–28. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010600921912
Riou C (1980) A simple empiric formula for estimating potential evapotranspiration in Tunisia. Cah. O.R.S.T.O.M., sér. Hydrol., vol. XVII, 2:129–137 [in french]
Tamers MA (1975) Validity of radiocarbon dates on groundwater. Geophys Surv 2:217–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01447909
Tarhouni J, Ben Hamouda MF, Kondash AJ, Mejri L, Vengosh A (2015) Modeling the recharge and the renewal rate based on 3H and 14C isotopes in the coastal aquifer of El Haouaria, northern Tunisia. Procedia Earth Planet Sci 13:199–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2015.07.047
Taylor CB (1977) Tritium enrichment of environmental waters by electrolysis: Development of cathodes exhibiting high isotopic separation and precise measurement of tritium enrichment factors. In: Proc. of the Int. Conf. of Low-Radioactivity Measurements and Applications. Slovenski Pedagogicke Nakladatelstvo, Bratislava, Slovakia, p. 131–140
Vengosh A (2014) Salinization and saline environments, reference module in earth systems and environmental sciences. In: Treatise on geochemistry, vol 11, 2nd edn, pp 325–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-095975-7.00909-8
Zuber A, Weise SM, Osenbruck K, Pajnowska H, Grabczak J (2000) Age and recharge pattern of water in the Oligocene of the Mazovian basin (Poland) as indicated by environmental tracers. J Hydrol 233:174–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(00)00224-9
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the IAEA Technical Cooperation Project TUN/8/015 and TUN/8/017 “Assessment of Marine Intrusion in Cap Bon’s Coastal Aquifer Systems.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Geology of North Africa and Mediterranean regions
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Hamouda, M.F. Study of the groundwater salinity and modeling the recharge and the renewal rate based on stable and radioactive isotopes in El Haouaria aquifer, Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 14, 2246 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08465-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08465-6