Abstract
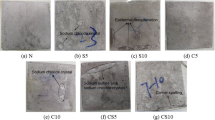
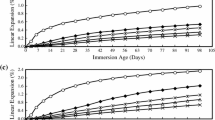
In order to study the strength and chloride, ion diffusion characteristics of fly ash fill material under the action of chloride salt erosion and dry–wet cycles were investigated. Using both X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy analyses, the microstructural changes of the material were analyzed. Subsequently, the material damage and deterioration mechanisms were verified. The results indicate that both the strength and elastic modulus of the material increase first and then rapidly decrease. The chloride ions diffuse rapidly in the initial stage and then diffuse gradually into the deep part of the material in the later stage. Under the action of dry–wet cycles, the chloride ions accelerate and accumulate inside. Based on the microstructural analysis, the fill material deterioration process can be roughly divided into three stages, namely erosion benefit, damage accumulation, and deterioration and instability stages. The material deterioration accelerates under the action of dry–wet cycles, leading to instability and destruction of the fill body.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang Q, Zhou H, Bai J, Duan C, Li Y (2011) Stability study and practice of overlying strata with paste backfilling. J Min Saf Eng 28:279–282
Cheng H, Wu A, Wang Y, Wang H, Wang S (2016) Fractal features and dynamical characters of the microstructure of paste backfill prepared from fly ash based binder. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 35:4241–4248
Fall M, Pokharel M (2010) Coupled effects of sulphate and temperature on the strength development of cemented tailings backfills: portland cement-paste backfill. Cem Concr Compos 32:819–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2010.08.002
Gao M, Liu J, Wu A, Zhao X (2016) Corrosion and deterioration mechanism of rich-water filling materials in typical chloride salt environment. J Cent South Univ (Science and Technology) 47:2776–2783
GB/T50082-2009 (2009) Standard for long-term performance and durability manuscript methods of ordinary concrete (China)
Geng O, Sun Q, Li DH (2020) Study on the inhibitory effect of chloride on sulfate erosion of recycled concrete. J Build Sci Eng 37(06):108–116
Ghirian A, Fall M (2014) Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical–chemical behavior of cemented paste backfill in column experiments: part II: mechanical, chemical and microstructural processes and characteristics. Eng Geol 170:11–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.12.004
Guo W (2013) Filling mining technology in coal mines. Coal Industry Press, China
He FQ, Shi CJ, An X (2010) Silver nitrate color method to measure the apparent diffusion coefficient of chloride ion in concrete. J Chin Ceram Soc 38(11):2178–2184
He FQ, Shi CJ, Yuan Q, An X, Tong B (2011) Calculation of chloride concentration at color change boundary of AgNO3 colorimetric measurement. Cem Concr Res 41:1095–1103
He FQ, Shi CJ, Yuan Q, Chen C, Zheng K (2012) AgNO3-based colorimetric methods for measurement of chloride penetration in concrete. Constr Build Mater 26:1–8
Houri AA, Habib A, Elzokra A, Habib M (2020) Tensile testing of soils: history, equipment and methodologies. Civ Eng J 6(3):591–601
Huang Y (2017) Study on mechanical properties of full tailings cemented backfills in acidic solution. Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Jiangxi, China
Li T (2014) Study on groundwater pollution risk assessment of abandoned coal mine. China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China
Li MH, Yang ZQ, Wang YT (2015) Study on the strength and hydration mechanism of fly ash composite cementitious material. J China Univ Min Technol 44(04):650–655 +695
Liu Q, Shen XD, Xue HJ, Wang RY, Liu Z (2018) Durability of pumice concrete under chloride salt erosion and dry-wet cycles. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 34(21):137–143
Liu ZQ, Song CY, Ji HG, Liu SJ, Tan J, Cheng SY, Ning FB (2021) The construction mode and key technology of mining wells for deep mineral resources. J China Coal Soc 46(03):826–845
Menéndez E, Argiz C, Sanjuán MN (2021) Coal ash portland cement mortars sulphate resistance. Civ Eng J 7(1):98–106
Miao XX, Qian MG (2009) Research on green mining of coal resources in China: current status and future prospects. J Min Saf Eng 26:1–14
Pokharel M, Fall M (2013) Combined influence of sulphate and temperature on the saturated hydraulic conductivity of hardened cemented paste backfill. Cem Concr Compos 38:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.03.015
Ren A, Feng G, Guo Y, Qi T, Guo J, Zhang M, Kang L, Han Y, Zhang P (2014) Influence on performance of coal mine filling paste with fly ash. J China Coal Soc 39:2374–2380
Sam J (2020) Compressive strength of concrete using fly ash and rice husk ash: a review. Civ Eng J 6(7):1400–1410
Sun Q, Li X, Wei X, Mu Q (2015a) Experimental study on the influence of mine water corrosion over filling paste strength. Bull Chin Ceram Soc 34:1246–1251
Sun Q, Li X, Wei X, Mu Q (2015b) Study on creep property of paste filling materials under sulfate corrosion. J Saf Sci Technol 11:12–18
Wang XG, Shi CJ, He FQ, Yuan Q, Wang DH, Huang Y, Li QL (2013) Combination of chloride ions and its effect on the microstructure of cement-based materials. J Chin Ceram Soc 41(02):187–198
Wang Q, Liu Y, Zhang H, Jiang N (2014) Durability test of gangue paste stowing material. Coal Min 19:3–6
Wu D, Deng T, Zhao R (2017) A coupled THMC modeling application of cemented coal gangue-fly ash backfill. Constr Build Mater 158:326–336
Yin B (2018) Research on fly ash paste filling material and its modification and application. Taiyuan University of Technology
Zhang ZH, Wang AH (2016) Research on the transmission mechanism of moisture and chloride ions in concrete under dry-wet cycles. Shandong Industrial Technology 270+299
Funding
This research was funded by the SDUST Research Fund (grant 2018TDJH102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Murat Karakus
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Liu, Y., Wu, H. et al. Deterioration mechanisms of fill material under the action of chlorine salt erosion and dry–wet cycles. Arab J Geosci 14, 1372 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07811-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07811-y