Abstract
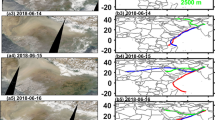
The Middle East is one of the most vulnerable regions to climate change and severe droughts. Climate change is associated with an increase of extreme weather frequency events across the globe. Climate change and droughts cause both severity and persistence dust storms in this area. In this study, the spatial and temporal variability of dust storms were characterized in the Middle East using satellite data (NDVI, TRMM, and AOD Aqua MODIS), synoptic station observation in Iran, and a numerical Weather Prediction for one dust event. The investigations of NDVI, precipitation rate, surface temperature, and AOD time series have shown that a significant increase in both surface temperature and AOD characterize this area from 2002 until 2018. While the rate of precipitation significantly declined, NDVI does not show specific trends because of its large variability and human influences. However, the study also showed a sharp decline in precipitation and consequently in vegetation cover in 2008, which caused a significant increase in both AOD and frequency of dust days in 2009. More than 100 dust days in five synoptic weather stations in the study area were observed in 2009. Also, this study shows that the number of dust storms has increased due to changes in governing atmospheric patterns over the area. The results (more than 100 dust days in five synoptic weather stations in the study area were observed for 1 year) showed both the effects of the earth surface respectively vegetation pattern changes (based on NDVI) and the atmospheric reasons (decline in precipitation) are the first time investigated in the study area. A numerical model simulation of three severe dust storms in July 2009 shows that dust emissions cover vast parts of the study area including east parts of Syria, Central Iraq, and northern and southern coasts of the Persian Gulf.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Dousari AM, Al-Enezi AK, Al-Awadhi J (2008) Textural variations within different representative types of dune sediments in Kuwait. Arab J Geosci 1(1):17–31
Al-Dousari AM, Al-Hazza A (2013) Physical properties of aeolian sediments within major dune corridor in Kuwait. Arab J Geosci 6(2):519–527
Al-Dousari AM, Ahmed M, Al-Dousari N, Al-Awadhi S (2019) Environmental and economic importance of native plants and green belts in controlling mobile sand and dust hazards. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:2415–2426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1879-4
Al-Dousari A, Ramadan A, Al-Qattan A, Al-Ateeqi S, Dashti H, Ahmed M, Al-Dousari N, Al-Hashash N, Othman A (2020) Cost and effect of native vegetation change on aeolian sand, dust, microclimate and sustainable energy in Kuwait. J Taibah Univ Sci 14(1):628–639
Al-Hemoud A, Al-Sudairawi M, Neelamanai S, Naseeb A, Behbehani W (2017) Socioeconomic effect of dust storms in Kuwait. Arab J Geosci 10(1):18
Al-Hemoud A, Al-Dousari A, Misak R, Al-Sudairawi M, Naseeb A, Al-Dashti H, Al-Dousari N (2019) Economic impact and risk assessment of sand and dust storms (SDS) on the oil and gas industry in Kuwait. Sustainability 11(1):200
Al-Jumaily KJ, Ibrahim MK (2013) Analysis of synoptic situation for dust storms in Iraq. Int J Energ Environ 4(5):851–858
Aba A, Al-Dousari AM, Ismaeel A (2018) Atmospheric deposition fluxes of 137Cs associated with dust fallout in the northeastern Arabian Gulf. J Environ Radioact 192:565–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2018.05.010
Abbasi HR, Opp C, Groll M, Rohipour H, Khosroshahi M, Khaksarian F, Gohardoust A (2018a) Spatial and temporal variation of the aeolian sediment transport in the ephemeral Baringak Lake (Sistan Plain, Iran) using field measurements and geostatistical analyses. Zeitschrift Geomorphol 61(4):315–326
Abbasi H, Opp R, Ch Groll M, Gohardoust A (2018b) Wind regime and sand transport in the Sistan and Registan regions (Iran/Afghanistan). Zeitschrift Geomorphol 62(Suppl. 1):41–57
Abbasi HR, Opp C, Groll M, Rohipur H, Gohardoust A (2019) Sand dunes systems in Iran; distribution and activity. Aeolian Res 41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeolia.2019.07.005
Al Enezi E, Al-Dousari A, Al-Shammeri F (2014) Modeling adsorption of inorganic phosphorous on dust fallout in Kuwait. J Eng Res 2(2):1–14
Alam K, Trautmann T, Blaschke T, Subhan F (2014) Changes in aerosol optical properties due to dust storms in the Middle East and Southwest Asia. Remote Sens Environ 143:216–227
Azizi G, Shamsipour AA, Miri M, Safarrad T (2012) Statistic and synoptic analysis of dust phenomena in west of Iran.
Barati GR, Lashkari H, Karami F (2011) The role of pressure systems convergence in occurrence of dust storms in Khuzestan province. J Geogr Devel 22:39–56
Barnum BH, Winstead NS, Wesely J, Hakola A, Colarco PR, Toon OB, Ginoux P, Brooks G, Hasselbarth L, Toth B (2004) Forecasting dust storms using the CARMA-dust model and MM5 weather data. Environ Model Softw 19(2):129–140
Behrooz RD, Kaskaoutis DG, Grivas G, Mihalopoulos N (2020) Human health risk assessment for toxic elements in the extreme ambient dust conditions observed in Sistan, Iran. Chemosphere 262:127835
Blott SJ, Al-Dousari AM, Pye K, Saye SE (2004) Three-dimensional characterization of sand grain shape and surface texture using a nitrogen gas adsorption technique. J Sed Res 74(1):156–159
Brooks N, Legrand M (2000) Dust variability over northern Africa and rainfall in the Sahel. In: Linking climate change to land surface change (pp. 1–25). Springer, Dordrecht
Chen YS, Sheen PC, Chen ER, Liu YK, Wu TN, Yang CY (2004) Effects of Asian dust storm events on daily mortality in Taipei, Taiwan. Environ Res 95(2):151–155
Chou MD, Suarez MJ (1994) An efficient thermal infrared radiation parameterization for use in general circulation models, NASA Tech. Memo., TM-104606, vol. 3, 84 pp.
Draxler RR, Gillette DA, Kirkpatrick JS, Heller J (2001) Estimating PM10 air concentrations from dust storms in Iraq, Kuwait and Saudi Arabia. Atmos Environ 35(25):4315–4330
Foroushani MA (2020) Aeolian dust deposition rates in sourthwest of Iran. Dissertation thesis. Philipps-Universität Marburg. Faculty of Geography.
Foroushani MA, Opp C, Groll M, Nikfal A (2020a) Evaluation of WRF-Chem predictions for dust deposition in Southwestern Iran. Atmosphere 11:757. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070757
Foroushani MA Opp C, Groll M (2019) Evaluation of the model performance for simulating the dust deposition and distribution forecast in Southwestern Iran. J Environ Monitor Assess. Submitted.
Foroushani MA, Opp C, Groll M (2020b) Investigation of dust deposition rates in different climatic zones. Aeolian Res (under-review)
Furman HKH (2003) Dust storms in the Middle East: sources of origin and their temporal characteristics. Indoor Built Environ 12(6):419–426
Gonzalez-Martin C, Teigell-Perez N, Valladares B, Griffin DW (2014) The global dispersion of pathogenic microorganisms by dust storms and its relevance to agriculture. In: Advances in agronomy (Vol. 127, pp. 1-41). Academic Press.
Goudie AS (2009) Dust storms: recent developments. J Environ Manag 90(1):89–94
Goudie AS, Middleton NJ (2001) Saharan dust storms: nature and consequences. Earth Sci Rev 56(1-4):179–204
Goudie AS (2014) Desert dust and human health disorders. Environ Int 63:101–113
Grell GA (1993) Prognostic evaluation of assumptions used by cumulus parameterizations. Mon Weather Rev 121:764–787. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1993)121<0764:PEOAUB>2.0.CO;2
Grell GA, Devenyi D (2002) A generalized approach to parameterizing convection combining ensemble and data assimilation techniques. Geophys Res Lett 29(14):38–1
Grell GA, Peckham SE, Schmitz R, McKeen SA, Frost G, Skamarock WC, Eder B (2005) Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model. Atmos Environ 39(37):6957–6975
Grousset FE, Ginoux P, Bory A, Biscaye PE (2003) Case study of a Chinese dust plume reaching the French Alps. Geophys Res Lett 30(6)
Hamidi M, Kavianpour MR, Shao Y (2013) Synoptic analysis of dust storms in the Middle East. Asia-Pac J Atmos Sci 49(3):279–286
Hong S-Y, Dudhia J, Chen S-H (2004) A revised approach to ice microphysical processes for the bulk parameterization of clouds and precipitation. Mon Weather Rev 132:103–120
Hsu NC, Gautam R, Sayer AM, Bettenhausen C, Li C, Jeong MJ, Tsay SC, Holben BN (2012) Global and regional trends of aerosol optical depth over land and ocean using SeaWiFS measurements from 1997 to 2010. Atmos Chem Phys 12(17):8037–8053
Jalali N, Davoudi MH (2008). Inspecting the origins and causes of the dust storms in the Southwest and West parts of Iran and the regions affected. Internal reports of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management Research Institute (SCWMRI), Iran.
Levy RC, Mattoo S, Munchak LA, Remer LA, Sayer AM, Patadia F, Hsu NC (2013) The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmosph Measur Tech 6(11):2989–3034
Kaufman YJ, Wald AE, Remer LA, Gao BC, Li RR, Flynn L (1997) The MODIS 2.1-/spl mu/m channel-correlation with visible reflectance for use in remote sensing of aerosol. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 35(5):1286–1298
Keramat A, Marivani B, Samsami M (2011) Climatic change, drought and dust crisis in Iran. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 6:10–13
Klingmüller K, Pozzer A, Metzger S, Stenchikov GL, Lelieveld J (2016) Aerosol optical depth trend over the Middle East
Krasnov H, Katra I, Friger M (2016) Increase in dust storm related PM10 concentrations: a time series analysis of 2001–2015. Environ Pollut 213:36–42
Laity JJ (2009) Deserts and desert environments. Wiley
Langmann B (2000) Numerical modelling of regional scale transport and photochemistry directly together with meteorological processes. Atmos Environ 34(21):3585–3598
Ledari DG, Hamidi M, Shao Y (2020) Evaluation of the 13 April 2011 frontal dust storm in west Asia. Aeolian Res 44:100592 ISSN 1875-9637
Maleki H, Sorooshian A, Goudarzi G, Nikfal A, Baneshi MM (2016) Temporal profile of PM10 and associated health effects in one of the most polluted cities of the world (Ahvaz, Iran) between 2009 and 2014. Aeolian Res 22:135–140
Marticorena B, Bergametti G (1995) Modeling the atmospheric dust cycle: 1. Design of a soil-derived dust emission scheme. J Geophys Res Atmos 100.D8:16415–16430
Miller RL, Tegen I (1998) Climate response to soil dust aerosols. J Clim 11:3247–3267
Mlawer EJ, Taubman SJ, Brown PD, Iacono MJ, Clough SA (1997) Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J Geophys Res Atmos 102(D14):16663–16682
Modarres R (2020) Dust storm frequency change in relation to climate drivers. Int J Climatol 41:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6675
Najafi MS, Khoshakhllagh F, Zamanzadeh SM, Shirazi MH, Samadi M, Hajikhani S (2014) Characteristics of TSP loads during the Middle East springtime dust storm (MESDS) in Western Iran. Arab J Geosci 7(12):5367–5381
Namdari S, Valizade KK, Rasuly AA, Sarraf BS (2016) Spatio-temporal analysis of MODIS AOD over western part of Iran. Arab J Geosci 9(3):191
Nickovic S, Kallos G, Papadopoulos A, Kakaliagou O (2001) A model for prediction of desert dust cycle in the atmosphere. J Geophys Res Atmos 106(D16):18113–18129
Noh Y et al (2002) Simulation of more realistic upper-ocean processes from an OGCM with a new ocean mixed layer model. J Phys Oceanogr 32(5):1284–1307
Niu G-Y, Yang Z-L, Mitchell KE, Chen F, Michael BEK, Barlage M, Kumar A, Manning K, Niyogi D, Rosero E, Tewari M, Xia Y (2011) The community Noah land surface model with multiparameterization options (Noah–MP): 1. Model description and evaluation with local-scale measurements. J Geophys Res 116:D12109
O’Loingsigh T, McTainsh GH, Tews EK, Strong CL, Leys JF, Shinkfield P, Tapper NJ (2014) The Dust Storm Index (DSI): a method for monitoring broadscale wind erosion using meteorological records. Aeolian Res 12:29–40
Papageorgiou L, Metaxas AC, Georghiou GE (2011) Three-dimensional numerical modelling of gas discharges at atmospheric pressure incorporating photoionization phenomena. J Phys D Appl Phys 44(4):045203
Parajuli SP, Yang ZL, Lawrence DM (2016) Diagnostic evaluation of the Community Earth System Model in simulating mineral dust emission with insight into large-scale dust storm mobilization in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA). Aeolian Res 21:21–35
Prospero JM, Ginoux P, Torres O, Nicholson SE, Gill TE (2002) Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the Nimbus 7 Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) absorbing aerosol product. Rev Geophys 40:2–31
Rashki A, Kaskaoutis DG, Rautenbach CJdW, Eriksson PG, Qiang M, Gupta P (2012) Dust storms and their horizontal dust loading in the Sistan region, Iran. Aeolian Res 5:51–62
Rezazadeh M, Irannejad P, Shao Y (2013) Climatology of the Middle East dust events. Aeolian Res 10:103–109
Sarraf BS, Rasouli AA, Mohammadi GH, Sadr AH (2016) Long-term trends of seasonal dusty day characteristics—West Iran. Arab J Geosci 9(10):563
Schütz L (1980) Long-range transport of desert dust with special emphasis on the Sahara. Ann N Y Acad Sci 338:515–532
Shahraiyni HT, Karimi K, Nokhandan MH, Moghadas NH (2015) Monitoring of dust storm and estimation of aerosol concentration in the Middle East using remotely sensed images. Arab J Geosci 8(4):2095–2110
Shao Y, Dong CH (2006) A review on East Asian dust storm climate, modelling and monitoring. Glob Planet Chang 52(1-4):1–22
Shao Y, Ishizuka M, Mikami M, Leys JF (2011) Parameterization of size-resolved dust emission and validation with measurements. J Geophys Res Atmos 116(D8)
Shao Y, Li A (1999) Numerical modelling of saltation in the atmospheric surface layer. Bound-Layer Meteorol 91(2):199–225
Subramaniam N, Al-Sudairawi M, Al-Dousari A, Al-Dousari N (2015) Probability distribution and extreme value analysis of total suspended particulate matter in Kuwait. Arab J Geosci 8(12):11329–11344
Stefanski, R. and Sivakumar, M.V.K., 2009. Impacts of sand and dust storms on agriculture and potential agricultural applications of a SDSWS. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Vol. 7, No. 1, p. 012016). Bristol, UK: IOP Publishing.
Yang Z-L, Niu G-Y, Mitchell KE, Chen F, Ek MB, Barlage M, Longuevergne L, Manning K, Niyogi D, Tewari M, Xia Y (2011) The community Noah land surface model with multiparameterization options (Noah-MP): 2. Evaluation over global river basins. J Geophys Res 116:D12110
Zhang XY, Gong SL, Zhao TL, Arimoto R, Wang YQ, Zhou ZJ (2003) Sources of Asian dust and role of climate change versus desertification in Asian dust emission. Geophys Res Lett 30(24)
Zoljoodi M, Didevarasl A, Saadatabadi AR (2013) Dust events in the western parts of Iran and the relationship with drought expansion over the dust-source areas in Iraq and Syria. Atmosph Clim Sci 3(03):321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zhihua Zhang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamzeh, N.H., Karami, S., Opp, C. et al. Spatial and temporal variability in dust storms in the Middle East, 2002–2018: three case studies in July 2009. Arab J Geosci 14, 538 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06859-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06859-0