Abstract
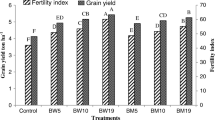
He Kang (HK) is a widely used organic amendment for saline-alkali land improvement because of its effectiveness. This research evaluated HK’s effects on secondary saline soil amelioration in gully land consolidation area in the north part of Shaanxi, China. Experiments were conducted in field plots (4 m × 5 m) to test the effects of different HK contents (2.99 g/m2 (HK1), 3.74 g/m2 (HK2), 4.49 g/m2 (HK3), and 5.24 g/m2 (HK4)) on soil moisture water and salt content, nitrate nitrogen, available phosphorus, available potassium, and maize growth. The results showed that the salt contents in experimental plots with HK were lower compared with CK (no amendments), and soil water movement to deep soil was inhibited, and evapotranspiration was also decreased. HK improved the soil nutrient content and delayed the transport and leaching process of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in the soil, which kept the nutrients in the root layer of spring maize plants in a higher concentration range. The uptake and utilization of soil nutrients by maize was promoted. Maize yields in plots with HK1, HK2, HK3, and HK4 were significantly increased by 21.51%, 34.34%, 22.10%, and 27.31%, respectively, compared with CK. The results indicated that HK is an effective method with 3.74 g/m2 (HK2) application rate of secondary saline soil amelioration in gully land treatment, which is beneficial to local crop growth.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar K, Wang WY (2019) Wheat straw mulching offset soil moisture deficient for improving physiological and growth performance of summer sown soybean. Agric Water Manag 211:16–25
Bai J, Gao H, Xiao R, Wang J, Huang C (2012) A review of soil nitrogen mineralization as affected by water and salt in coastal wetlands: issues and methods. Clean–Soil Air Water 40(10):1099–1105
Chen FJ (2010) Water erosion response to rainfall and land use in different drought-level years in a loess hilly area of China. Catena 81(1):24–31
Ershaidat NM, Abu-Jaber NS, Al-Bataina BA, Shobaki JM, Jaradat AS (2009) Relationship between the effective diffusion coefficient of soil radon and groundwater recharge in semi-arid areas. Environmental Earth Ences 59(2):261–268
Fu B, Chen L, Ma K, Zhou H, Wang J (2000) The relationships between land use and soil conditions in the hilly area of the loess plateau in northern Shaanxi, China. Catena 39(1):69–78
Gong XP, Liang X, Guo Y, Wu CH, Zhao Y, Li XH (2015) Quantitative trait locus mapping for potassium use efficiency traits at the seedling stage in wheat under different nitrogen and phosphorus treatments. Crop Ence 55(6):2690
Guo YD, Cheng M, Zhao XF, Hao BP, Zhang YF, Cao WD, Zheng PS (2018) Effects of green manure rotation on soil properties and yield and quality of silage maize in saline-alkali soils. Chin J Eco-Agric 26(6):856–864
Hou E, Tan X, Heenan M, Wen DA (2018) Global dataset of plant available and unavailable phosphorus in natural soils derived by Hedley method. Entific Data 5:180166
Hou WF, Zhang YZ, Chen XY, Sun JY, Gao P (2019) Effects of different subsoiling treatments on soil physical properties and maize yield. Journal of Northern Agriculture 047(003):70–73.
Hu C, Song JY, Li J, Liu CQ, Tao XE, Chen YF (2012) Profile distribution of soil available phosphorus and available potassium concentrations and crop grain yields in long-term fertilization experiment. Ecology & Environmental Ences 21(04):673–676.
Liu A, Qu Z, Nachshon U (2020) On the potential impact of root system size and density on salt distribution in the root zone. Agric Water Manag 234:106118
Lü Y, Fu B, Feng X, Zeng Y, Liu Y, Chang R, Sun G, Wu BA (2012) Policy-driven large scale ecological restoration: quantifying ecosystem services changes in the loess plateau of China. PLoS One 7(2):e31782
Mandal UK, Bhardwaj AK, Warrington DN, Goldstein D, Tal AB, Levy GJ (2008) Changes in soil hydraulic conductivity, runoff, and soil loss due to irrigation with different types of saline–sodic water. Geoderma 144(3–4):509–516
Noyce GL, Jones T, Fulthorpe R, Basiliko N (2017) Phosphorus uptake and availability and short-term seedling growth in three Ontario soils amended with ash and biochar. Canadian Journal of Soil Ence 97(4)
Rens H, Bera T, Alva AK (2018) Effects of biochar and biosolid on adsorption of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in two soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 229(8):281
Ru G (2013) Application effect test of Hekang saline-alkali soil improver in cotton field. Rural Science and Technology 05:26–27
Shuai XF, Ma LW, Wendroth O (2018) Unified weak and strong soil tests to estimate intrinsic plant available phosphorus pools. Agron J 110(3):859
Shukla J, Maldar NN, Sharon M, Tripathi S, Sharon M (2012) Synthesis of carbon nano material from different parts of maize using transition metal catalysts. Der Chemica Sinica, 1058–1070
Verstraeten WW, Veroustraete F, Feyen J (2008) Assessment of evapotranspiration and soil moisture content across different scales of observation. Sensors 8:70–117
Wei W, Chen L, Fu B, Huang Z, Wu D, Gui L (2007) The effect of land uses and rainfall regimes on runoff and soil erosion in the semi-arid loess hilly area. China Journal of Hydrology 335(3–4):247–258
Yu JH (2014) Preliminary report on the application of Hekang saline-alkali soil improver in rice. North Rice 000(003):66–67
Yu YL, Henry L, Jin Z, Zhang J (2015) Ammonia dynamics in reservoirs in response to rainfall events in a gully-filled loess catchment in yan’ an city, Shaanxi province. Quaternary Sciences 37(6):1204–1121
Zhan GJ, Xu JS, Li CK, Yu YQ, Huang H (2012) Experiment on the application of He Kang soil conditioner in rice. North Rice 42(01):10–12.
Zhang L, Sun X, Zhang L (2007) Effect of Hekang soil improver on cotton field secondary salinization. Xinjiang Agricultural Science and Technology 000(005):13
Zhang H, Wang JA, Lei YD, Gilkes RJ, Prakongkep N (2010) Research on soil desalinization through platform fields and by irrigation using sea-ice water. World Congress of Soil Science: Soil Solutions for A Changing World 06:65–68.
Zhang Y, Wang H, Liu S, Lei Q, Liu J, He J (2015) Identifying critical nitrogen application rate for maize yield and nitrate leaching in a haplic luvisol soil using the dndc model. Ence of the Total Environment 514:388–398
Zhang GC, Dai LX, Ding H, Ci DW, Ning TY, Yang JS, Zhao XH, Yu HQ, Zhang ZM (2020) Response and adaptation to the accumulation and distribution of photosynthetic product in peanut under salt stress. J Integr Agric 19(3):690–699
Zhao X, Yang J, Yao R (2010) Relationship between soil salt dynamics and factors of water balance in the typical coastal area of northern Jiangsu province. Journal of Agricultural Engineering 026(003):52–57
Zhao X, Peng P, Xu W (2013) Experimental study on soil amelioration of saline-alkali land A case study of saline-alkali soil ameliorated by coal ash and coal gangue. International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering (RSETE 2013).
Zou XX, Wang WH, Wang JL, Jiang DF (2017) Time-spatial revolution characteristics of soil salinity in the yellow river delta under different land cultivation and natural conditions. Journal of Soil Water Conservation 31(02):309–316.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41807131 and 41977007), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019 M653707), and Research project of State Key Laboratory of Eco-hydraulics in Northwest Arid Region of China (2019KJCXTD-4 and QJNY-2019-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Y.: conceptualization, writing, review and editing. B.Z.: supervision, project administration and funding acquisition. All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Geological Modeling and Geospatial Data Analysis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Duan, M., Zhou, B. et al. Effect of organic acid amendment on secondary saline soil amelioration in gully land consolidation area in northern Shaanxi, China. Arab J Geosci 13, 1273 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06277-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06277-8