Abstract
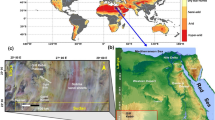
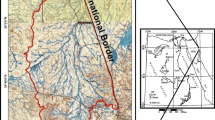
Geological evaluation and groundwater assessment, especially in arid areas, are considerable targets for constructing recent and sustainable development communities. The current work aims to apply an integrated approach to acquire geologic structures and groundwater potentiality at highly deformed area. As a case study, remote sensing (RS), aeromagnetic, and geoelectrical data are conducted to delineate the subsurface structures and hydrogeological regime at Aswan City. Initially, remote sensing data with GIS software are utilized to delineate the surface structures and watershed configuration. Moreover, the reduced to magnetic pole (RTP) aeromagnetic data is processed and interpreted using appropriate filters. In an attempt to demonstrate the subsurface structures and basement relief maps, the RTP map was analyzed considering the RS data which was stated in previous stage. In the light of RTP aeromagnetic results and well logging data, the direct current resistivity (DCR) sounding is executed particularly along paleochannel and flood plain portion. Due to the inversion process problem of DCR field data, advanced solutions and algorithms are applied to improve the property of the results. Based upon overall results mentioned above, the correlation between subsurface structures and aquifer formation can be monitored. The present approach can be applied for groundwater exploration in this and other similar geological and hydrogeological environments around the world.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Gawad AMS, Kotb ADM, Hussien GHG (2017) Geoelectrical contribution for delineation the groundwater potential and subsurface structures on Tushka Area, Egypt. NRIAG J Astronomy Geophys 6(2017):379–394
Abdalla F (2012) Mapping of groundwater prospective zones using remote sensing and GIS techniques: a case study from the Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. J Afr Earth Sci 70:8–17
Abdel-Shafy HI, Kamel AH (2016) Groundwater in Egypt issue: resources, location, amount, contamination, protection, renewal, future overview. Egypt J Chem 59(3):321–362
Aero-Service (1984) Final operational report of airborne magnetic/ radiation survey in the Eastern Desert, Egypt. For the Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation (EGPC) and the Egyptian Geological Survey and Mining Authority (EGSMA), Aero-Service Division, Houston, Texas, USA, Six Volumes
Ammar AI, Kamal KA (2019) Effect of structure and lithological heterogeneity on the correlation coefficient between the electric–hydraulic parameters of the aquifer, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Appl Water Sci 9(4):83
Ammar AA, Fouad KM, Meleik ML (1988) In evaluation of the efficiency of shortend low-pass filters computed by inverse Fourier transform for potential fields of spherical bodies and planar regionals, vol 1. Faculty of Earth Sciences, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, pp 133–148
Anomohanran O, Orhiunu ME (2018) Assessment of groundwater occurrence in Olomoro, Nigeria using borehole logging and electrical resistivity methods. Arab J Geosci 11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3582-7
Attia MI (1955) Topography, Geology and Iron Ore Deposits of East Aswan: Geol. Survey, Egypt, Cairo, Internal Report
Attwa M, Henaish A, Zamzam S (2020) Detection and prediction of geo-environmental hazards in urban areas and desert lands using an integrated structural and geophysical approach: cases from Egypt. In: Waste Management in MENA Regions. Springer, Cham, pp 71–92
Basokur AT (1999) Automated 1D interpretation of resistivity soundings by simultaneous use of the direct and iterative methods. Geophys Prospect 47:149e177
Butzer KW, Hansen CL (1968) Desert and river in Nubia; geomorphology and prehistoric environments at the Aswan reservoir. University of Wisconsin Press, Madison, p 562
EGSMA, NARSS, UNDP, UNESCO (2005) Geomorphologic map of Aswan Quadrangle, Egypt. Executed by UNESCO Cairo Office, EGY/97/011, scale 1:250.000
Egyptian Geological Survey and Mining Authority (2002) A geological map of Assiut Area, scale 1:100,000
El Bastawesy M, Faid A, El Gammal S (2010) The quaternary development of tributary channels to the Nile River at Kom Ombo area, Eastern Desert of Egypt, and their implication for groundwater resources. Hydrol Process 24:1856–1865
El Bastawesy M, Attwa M, Hafeez THA, Gad A (2019) Flash floods and groundwater evaluation for the non-gauged dryland catchment using remote sensing, GIS and DC resistivity data: a case study from the Eastern Desert of Egypt. J Afr Earth Sci 152:245–255
Earth Remote Sensing Data Analysis Center (ERSDAC) (2006) PALSAR user’s guide, 1st ed. (March)
ESRI (2013) Arc hydro: GIS for water resources. ESRI, Redlands
Gaber A, Soliman F, Koch M, El-Baz F (2015) Using fullpolarimetric SAR data to characterize the surface sediments in desert areas: a case study in El-Gallaba Plain, Egypt. Remote Sens Environ 162:11–28
Geosoft Program (Oasis Montaj) (2007) Geosoft mapping and application system Inc, Suit 500, Richmond St. West Toronto, ON Canada N5SIV6
Geriesh MH, Mansour BM, Gaber A, Mamoun K (2019) Exploring groundwater resources and recharge potentialities at El-Gallaba plain, Western Desert, Egypt. Groundwater
Ghoneim E, Robinson C, El-Baz F (2007) Radar topography data reveal drainage relics in the eastern Sahara. Int J Remote Sens 28:1759–1772
Griffin WR (1949) Residual gravity in theory and practice. Geophysics 14:39–56
Gupta M, Srivastava PK (2010) Integrating GIS and remote sensing for identification of groundwater potential zones in the hilly terrain of Pavagarh, Gujarat, India. Water Int 35(2):233–245
Hendriks F, Luger P, Bowitz J, Kallenbach H (1987) Evolution of the depositional environments of SE- Egypt during the Cretaceous and Lower Tertiary. Berliner geowiss Abh (A) 75(1):49–82
Hinz EA, Stern RJ, Thurmond AK, Abdelsalam MG, Abdeen MM (2003) When did the Nile begin?: remote sensing analysis of paleo-drainages near Kom Ombo, Upper Egypt: Eos transactions, fall meeting supplement, abstract, v. 84
Igarashi T (2001) ALOS Mission requirement and sensor specifications. Adv Space Res 28(1):127–131
IPI2win program (2003) Resistivity Sounding Interpretation program Version 3.0.1.a7.01.03 (1990–2003). Moscow State University, Moscow
Issawi B (1969) The geology of Kurkur-Dungle area: Cairo, General Egyptian organization for Geological Research and Mining, 102 p
Issawi B, McCauley JF (1992) The Cenozoic rivers of Egypt: the Nile problem. In: Freidman R, Adams B (eds) The followers of Horus. Oxford Press, Oxford, pp 121–138
Kearey L, Brooks M, Hill I (2002) An introduction to geophysical exploration, 3rd edn. Blackwell Science Ltd., Hoboken
Kowalik WS, Glen W (1987) Image processing of aeromagnetic data and integration with Landsat images for improved structural interpretation. Geophysics 52:875–884
Meneisy AM, Al Deep M (2020) Investigation of groundwater potential using magnetic and satellite image data at Wadi El Amal, Aswan, Egypt. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2020.06.006 In press
Meshref WM (1990) Tectonic framework. In the Geology of Egypt (Said, R.; ed.). A. A. Balkema, Rotterdam, Brookfield. Ch. 8:113–155
Moorkamp M (2017) Integrating electromagnetic data with other geophysical observations for enhanced imaging of the earth: a tutorial and review. Surv Geophys 38(5):35–962
NGA (2004) GM-SYS (Version 4.9): Gravity/Magnetic Modeling Software; Northwest Geophysical Associates Inc.:Corvallis, OR, USA. Available online: https://www.nga.com/ (accessed on 1 June 2019)
Rabeh T, Meneisy AM, Abd el Gaber A (2019) Identification of the dynamic subsurface structures and their seismic implications based on geophysical methods at the southern part of Cairo area, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4722-4
Raji WO, Ibrahim OK (2017) Geophysical investigation for basement rock structures around a proposed dam site. Adamawa State Univ. J Sci Res 5(2):38–49
Reid AB, Allsop JM, Granser H, Millet AJ, Somerton IW (1990) Magnetic interpretation in three dimensions using Euler deconvolution. Geophysics 55:80–91
Rizzo E, Capozzoli L (2019) Integrated geophysical techniques for archaeological remains: real cases and full scale laboratory example. In: Archaeogeophysics. Springer, Cham, pp 243–253
Roden J, Abdelsalam MG, Atekwana E, El-Qady G, Tarabees EA (2011) Structural influence on the evolution of the pre-Eonile drainage system of southern Egypt: insights from magnetotelluric and gravity data. J Afr Earth Sci 61:358–368
Saleh AM, Belal AB, Mohamed ES (2015) Land resources assessment of El-Galaba basin, south Egypt for the potentiality of agriculture expansion using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 18:S19–S30
Salem A, Williams S, Fairhead JD, Ravat D, Smith R (2007) Tilt-depth method: a simple depth estimation method using first-order magnetic derivatives. Lead Edge 26:1502–1505
Telford WM, Geldart LP, Sheriff RE (1990) Applied geophysics, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, New York
Thakur JK, Singh SK, & Ekanthalu VS (2017) Integrating remote sensing, geographic information systems and global positioning system techniques with hydrological modeling. Appl Water Sci 7(4):1595–1608
Thurston JB, Smith RS (1997) Automatic conversion of magnetic data to depth, dip, and susceptibility contrast using the SPITM method. Geophysics 62:807–813. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1444190
Youssef MM (2003) Structural setting of central and south Egypt: an overview. Micropaleontology 49:1–13
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Mr. Ahmed Abdel-Fattah and Mr. Ahmed Abd elgaber (Geology dept. Aswan Uni.) for helpful during the hard field survey in this work. The author thanks Associate Prof. Mohamed Attwa (Zagazig Uni, Egypt) for deep discussions and valuable comments during finishing this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Advances of Geophysical and Geological Prospection for Natural Resources in Egypt and the Middle East
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meneisy, A.M. Impact of subsurface structures on groundwater exploration using aeromagnetic and geoelectrical data: a case study at Aswan City, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 13, 1213 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06201-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06201-0