Abstract
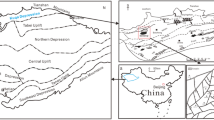
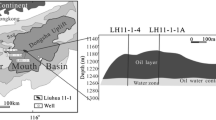
A suite of crude oils from the Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs in the eastern Chepaizi Uplift, Junggar Basin, was analyzed to study the alteration of molecular compositions by severe biodegradation and the accumulation mechanisms of the crude oils. The investigation indicates that most of the crude oils of the Carboniferous reservoirs in the eastern Chepaizi Uplift are typical heavy oil with low wax and sulfur contents. The density of crude oils in the study area increases gradually from east to west, and as the burial depth increases, the density of crude oil decreases. All selected oil samples were severely degraded, with a degree of biodegradation (DOB) ranging from PM 7 to PM 9. The C21–22 steranes and diasteranes remain stable when the level of biodegradation is lower than PM 8, and they can be used as conserved “internal standards” to evaluate the biodegradation of hopanes, regular steranes, and tricyclic terpanes. However, the C21–22 steranes and diasteranes are degraded when the DOB is over PM 9. The biodegradation of tricyclic terpanes begins when the level of biodegradation reaches PM 8. Among the tricyclic terpane family, the C21 and C23 tricyclic terpanes are the most readily degraded members, while the C24-26 tricyclic terpanes seem more resistant to biodegradation. Most of the heavy oil accumulations are formed by the adjustment and remigration of paleoaccumulations due to the activity of the Hongche Fault and tectonic movement. During the remigration of hydrocarbons, biodegradation and water washing occurred in the pathways, controlling the formation of heavy oil.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberdi M, Moldowan JM, Peters KE, Dahl JE (2001) Stereoselective biodegradation of tricyclic terpanes in heavy oils from the Bolivar Coastal Fields, Venezuela. Org Geochem 32:181–191
Alexander R, Kagi RI, Woodhouse GW, Volkman JK (1983) The geochemistry of some biodegraded Australian oils. The APPEA Journal 23:53–63
Cao J, Zhang YJ, Hu WX, Yao SP, Wang XL, Zhang YQ, Tang Y (2005) The Permian hybrid petroleum system in the northwest margin of the Junggar Basin, northwest China. Mar Pet Geol 22(3):331–349
Cao J, Yao SP, Jin ZJ, Hu WX, Zhang YJ, Wang XL, Zhang YQ, Tang Y (2006) Petroleum migration and mixing in the northwestern Junggar Basin (NW China): constraints from oil-bearing fluid inclusion analyses. Org Geochem 37(7):827–846
Cao J, Jin ZJ, Hu WX, Zhang YJ, Yao SP, Wang XL, Zhang YQ, Tang Y (2010) Improved understanding of petroleum migration history in the Hongche fault zone, northwestern Junggar Basin (northwest China): Constrained by vein–calcite fluid inclusions and trace elements. Mar Pet Geol 27:61–68
Chang XC, Wang TG, Li QM, Cheng B, Zhang LP (2012) Maturity assessment of severely biodegraded marine oils from the Halahatang Depression in Tarim Basin. Energy Explor Exploit 30:331–350
Chang XC, Wang TG, Li QM, Cheng B, Tao XW (2013a) Geochemistry and possible origin of petroleum in Palaeozoic reservoirs from Halahatang Depression. J Asian Earth Sci 74:129–141
Chang XC, Wang TG, Li QM, Ou GX (2013b) Charging of Ordovician reservoirs in the Halahatang Depression (Tarim Basin, NW China) determined by oil geochemistry. J Pet Geol 36:383–398
Chang XC, Li Y, Xu YD, Guo HH (2016a) The effect of waterflooding on the occurrence of alkyl naphthalenes and phenanthrenes in crude oil. Pet Sci Technol 34:1503–1511
Chang XC, Wang GL, Guo HH, Cui J, Wang T (2016b) A case study of crude oil alternation in a clastic reservoir by waterflooding. J Pet Sci Eng 146:380–391
Chang XC, Zhao HG, He WX, Xu YH, Xu YD, Wang Y (2018a) Improved Understanding of the Alteration of Molecular Compositions by Severe to Extreme Biodegradation: A Case Study from the Carboniferous Oils in the Eastern Chepaizi Uplift, Junggar Basin, Northwest China. Energy Fuel 32:7557–7568
Chang XC, Wang Y, Xu YH, Cui J, Wang T (2018b) On the changes of polycyclic aromatic compounds in waterflooded oil and their implications for geochemical interpretation. Org Geochem 120:56–74
Chang XC, Wang Y, Shi BB, Xu YD (2019) Charging of Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs in the eastern Chepaizi Uplift, Junggar Basin (NW China) constrained by oil geochemistry and fluid inclusion. AAPG Bulletin 103: 1625–1652
Chen ZH, Cao YC, Wang XL, Qiu LW, Tang Y, Yuan GH (2016) Oil origin and accumulation in the Paleozoic Chepaizi–Xinguang field, Junggar Basin, China. J Asian Earth Sci 115:1–15
Chen ZH, Wang TG, Li MJ, Yang FL, Cheng B (2018) Biomarker geochemistry of crude oils and Lower Paleozoic source rocks in the Tarim Basin, western China: An oil-source rock correlation study. Mar Pet Geol 96:94–112
Cheng X, Hou DJ, Xu CG, Wang FL (2016) Biodegradation of tricyclic terpanes in crude oils from the Bohai Bay Basin. Org Geochem 101:11–21
Connan J (1984) Biodegradation of crude oils in reservoirs. Advances in petroleum geochemistry. Academic Press, London, pp 299–335
Elias R, Vieth A, Riva A, Horsfield B, Wilkes H (2007) Improved assessment of biodegradation extent and prediction of petroleum quality. Org Geochem 38:2111–2130
Garcia DFB, Santos Neto EV, Penteado HLB (2015) Controls on petroleum composition in the Llanos Basin, Colombia: implications for exploration. AAPG Bulletin 99:1503–1535
He DF, Chen XF, Kuang J, Zhou L, Tang Y, Liu DG (2008). Development and genetic mechanism of Chepaizi-Mosuowan Uplift in Junggar Basin. Earth Science Frontiers 15(In Chinese, with English Abstract):42–55
He DF, Chen XF, Kuang J, Yuan H, Fan C, Tang Y, Wu XZ (2010) Distribution of Carboniferous source rocks and petroleum systems in the Junggar Basin. Pet Explor Dev 37:397–408
Hosseiny E, Rabbani AR, Moallemi SA (2016) Source rock characterization of the Cretaceous Sarvak Formations in the eastern part of the Iranian sector of Persian Gulf. Org Geochem 99:53–66
Hu ZQ (2004) Hydrocarbon reservoir formation model of Chepaizi area in northwest edge of Junggar basin. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field 11:12–15
Kuo L (1994) An experimental study of crude oil alteration in reservoir rocks by water washing. Org Geochem 21:465–479
Lafargue E, Barker C (1988) Effect of water washing on crude oil compositions. Am Assoc Pet Geol Bull 72:263–276
Larter SR, Huang H, Adams J, Bennett B, Snowdon LR (2012) A practical biodegradation scale for use in reservoir geochemical studies of biodegraded oils. Org Geochem 45:66–76
Liu LF, Meng JH, Wang WB, Jin J, Wu L, Zhao YD, Wang P, Zhi DM (2011) Differences in geochemical characteristics of oils trapped in the upper and the lower series of strata of Chepaizi Swell along northwest margin of Junggar Basin and their significances. J Jilin Univ (Earth Sci Ed) 41(in Chinese, with English Abstract):377–390
Liu Y, Wu K, Wang X, Pei Y, Liu B, Guo J (2017) Geochemical characteristics of fault core and damage zones of the Hong-Che Fault Zone of the Junggar Basin (NW China) with implications for the fault sealing process. J Asian Earth Sci 143:141–155
Meng F, Cao YC, Cui Y, Xu T, Liu ZC, Wang YZ (2016) Genesis of Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs in Chepaizi salient in western margin of Junggar Basin. Journal of China University of Petroleum 40(In Chinese, with English Abstract):22–31
Palacas JG, Monopolis D, Nicolaou CA, Anders DE (1986) Geochemical correlation of surface and subsurface oils, western Greece. Org Geochem 10:417–423
Palmer SE (1993) Effect of biodegradation and water washing on crude oil composition. In: Engel MH, Macko SA (eds) Organic Geochemistry. Plenum Press, New York, pp 511–533
Peters KE, Moldowan JM (1993) The Biomarker Guide: Interpreting Molecular Fossils in Petroleum and Ancient Sediments. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Peters KE, Walters CC, Moldowan JM (2005) The Biomarker Guide: Biomarkers and Isotopes in Petroleum Exploration and Earth History, 2nd ed. 2. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. pp 499, 566–589, 685–686
Price LC (1976) Aqueous solubility of petroleum as applied to its origin and primary migration. AAPG Bulletin 60:213–244
Seifert WK, Moldowan JM (1978) Applications of steranes, terpanes and monoaromatics to the maturation, migration and source of crude oils. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 42:77–95
Seifert WK, Moldowan JM (1979) The effect of biodegradation on steranes and terpanes in crude oils. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 43:111–126
Seifert WK, Moldowan JM, Demaison GJ (1984) Source correlation of biodegraded oils. Org Geochem 6:633–643
Spigolon ALD, Cerqueira JR, Binotto R, Fontes RA, Silva TF, Bautista DFG (2010) Source rock characteristics predicted based on MSSV pyrolysis of asphaltenes from a severely biodegraded oil. Revista Latino Americana de Geoquímica Orgânica 1:14–24
Taylor P, Bennett B, Jones M, Larter S (2001) The effect of biodegradation and water washing on the occurrence of alkylphenols in crude oils. Org Geochem 32(2):341–358
Tissot BP, Welte DH (1984) Petroleum Formations and Occurrence, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 416–420 470–480
Volkman JK, Alexander R, Kagi RI, Noble RA, Woodhouse GW (1983a) A geochemical reconstruction of oil generation in the Barrow Sub-basin of Western Australia. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 47:2091–2106
Volkman JK, Alexander R, Kagi RI, Woodhouse GW (1983b) Demethylated hopanes in crude oils and their application in petroleum geochemistry. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 47:785–794
Wang YT, Jiang SB (1998) An approach to the distribution and origin of heavy oil in the northwest margin of Junggar basin. Pet Explor Dev 25:18–20
Wang GL, Xue YC, Wang DW, Shi SB, Grice K, Greenwood PF (2016) Biodegradation and water washing within a series of petroleum reservoirs of the Panyu Oil Field. Org Geochem 96:65–76
Wenger LM, Davis CL, Isaksen GH (2002) Multiple controls on petroleum biodegradation and impact in oil quality. SPE Reserv Eval Eng 5:375–383
Williams JA, Bjorøy M, Dolcater DL, Winters JC (1986) Biodegradation in South Texas Eocene oils – effects on aromatics and biomarkers. Org Geochem 10:451–461
Xi WJ, Zhang ZH, Xu XY, Shi CE (2014) Application of fluid inclusion techniques to the study of super-heavy oil accumulation in Chunfeng oilfield, Junggar Basin. Oil Gas Geol 35(3)(in Chinese, with English Abstract):350–358
Xia XB, Jin J (2003) Characteristics of Jurassic structural geology and analysis of exploration potential in Che-Guai area of Junggar Basin. China Petroleum Exploration 8(In Chinese, with English Abstract):29–33
Xiao F, Liu LF, Zeng LY, Wu KJ, Xu ZJ, Zhou CX (2014) Geochemical characteristics and oil source of crude oils in the east edge of Chepaizi High, Junggar Basin. J China Univ Min Technol 43(in Chinese, with English Abstract):646–655
Xu YD, Chang XC, Shi BB, Wang Y, Li Y (2018) Geochemistry of severely biodegraded oils in the Carboniferous volcanic reservoir if the Chepaizi Uplift, Junggar Basin, NW China. Energy Explor Exploit 36:1461–1481
Yu Y, Wang X, Rao G, Wang R (2016) Mesozoic reactivated transpressional structures and multi-stage tectonic deformation along the Hong-che fault zone in the northwestern Junggar basin, nw China. Tectonophysics 679:156–168
Zhang M, Zhang J (2000) Effect of water washing on hydrocarbon compositions of petroleum sandstone reservoir rocks in Tarim Basin, NW China. Chin J Geochem 2:167–174
Zhang ZH, Li W, Meng XL, Qin LM, Zhang ZY, Yuan DS (2007) Petroleum geochemistry and oil-source analysis in the southwest of Chepaizi Uplift, Junggar Basin. Geoscience 21(in Chinese, with English Abstract):133–140
Zhang ZH, Xiang K, Qin LM, Zhuang WS, Xi WJ, Zhao SF (2012). Geochemical characteristics of source rocks and their contribution to petroleum accumulation of Chepaizi area in Sikeshu depression, Junggar Basin. Geol China 39(in Chinese, with English Abstract):326–337
Zhang ZH, Liu HJ, Li W, Fei JJ, Xiang K, Qin LM, Xi WJ, Zhu L (2014). Origin and Accumulation Process of Heavy Oil in Chepaizi Area of Junggar Basin. J Earth Sci Environ 36(2)(in Chinese, with English Abstract):18–32
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41772120), the Shandong Province Natural Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. JQ201311), the SDUST Research Fund (Grant No. 2015TDJH101) and the Open fund of Shandong Key Laboratory of Depositional Mineralization and Sedimentary Mineral (Grant No. DMSMX2019013) .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Domenico M. Doronzo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Chang, X., Zhang, J. et al. Genetic mechanism of heavy oil in the Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs of the eastern Chepaizi Uplift, Junggar Basin. Arab J Geosci 12, 648 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4849-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4849-3