Abstract
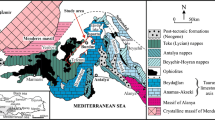
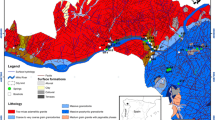
The study area is located at Eastern Anatolian Fault Zone and at the western shore of Lake Hazar (Elazig, Turkey). This study aims to identify the hydrochemical features of groundwaters from fractured igneous aquifers and to correlate them with the alluvial aquifer’s groundwaters. The water samples were collected in April and September during the rainy and dry periods, respectively. As a result of active tectonism in this region, hard rocks have gained secondary porosity and permeability. According to major ion composition, the fractured igneous and alluvial aquifer groundwaters can be grouped into the Ca-Mg-HCO3 type, whereas the groundwaters emerging very close to the thrust fault locations can be classified as the Mg-Ca-HCO3 type. The water-rock interaction process represents the primary factor controlling the hydrochemistry of the investigated groundwaters. Generally, the alluvial aquifer’s groundwaters are characterized by low pH values. Clay minerals in the alluvial material may act as H+ buffers and cause decreased pH values. According to the isotopic tracers of 18O, 2H, and 3H, the spring water discharging at higher altitudes from the fractured igneous aquifer reflects rapid circulation and recharging from recent precipitation compared to alluvial aquifer groundwater. The groundwaters’ major ions fall well within the permissible limits for drinking water in Turkey. In contrast, the NO3− and NH4+ concentrations from groundwaters, especially those recharging from fractured igneous aquifers, are very close to or in excess of the limit values. The high concentrations of NO3− and NH4+ in groundwaters presumably result from landfills and the use of agricultural fertilizers in the study area. The surface waters (Lake Hazar and man-made wetland (MMW)) also are investigated within the scope of the hydrochemistry studies. Higher TDS, Cl−, and Na+ concentrations in the MMW reflect salinity that could result from lake water intrusion and evaporation processes.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla F, Khalil R (2018) Potential effects of groundwater and surface water contamination in an urban area, Qus City, Upper Egypt. J Afr Earth Sci 141:164–178
Acero P, Gutiérrez F, Galve JP, Auqué LF, Carbonel D, Gimeno MJ, Gómez JB, Asta MP, Yechieli Y (2013) Hydrogeochemical characterization of an evaporite karst area affected by sinkholes (Ebro Valley, NE Spain). Geol Acta 11(4):389–407
Acreman MC, Harding RJ, Lloyd CR, Mcneil DD (2003) Evaporation characteristics of wetlands: experience from a wetgrassland and a reedbed using eddy correlation measurements. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 7(1):11–21
Aggarwal PK, Froehlich K, Kulkarni KM (2007) Environmental isotopes in groundwater studies. In: Silveira L, Usunoff EJ (eds) Groundwater—encyclopedia of live support systems. EOLSS Publishers/UNESCO, Paris, pp 69–92
Ako AA, Shimada J, Hosono T, Ichiyanga K, Nkeng GE, Fantong WY, Eyong GET, Roger NN (2011) Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking, domestic, and agricultural uses in the Banana Plain (Mbanga, Njombe, Penja) of the Cameroon volcanic line. Environ Geochem Health 33(6):559–575
Aksoy E (1993) General geological characteristics of western and southern Elazığ region. Turk J Earth Sci 2:113–123
Aksoy E, İnceöz M, Koçyiğit A (2007) Lake Hazar Basin: a negative flower structure on the East Anatolian Fault System (EAFS), SE Turkey. Turkish J Earth Sci 16:319–338
Al-Ahmadi ME, El-Fiky AA (2009) Hydrogeochemical evaluation of shallow alluvial aquifer of Wadi Marwani, western Saudi Arabia. J King Saud Univ Sci 21:179–190
Almadani S, Alfaifi H, Al-Amri A, Fnais M, Ibrahim E, Abdelrahman K, Shehata M, Zaidi F (2017) Hydrochemical characteristics and evaluation of the granite aquifer in the Alwadeen area, southwest Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 10:139
Al-Shaibani AM (2008) Hydrogeology and hydrochemistry of a shallow alluvial aquifer, western Saudi Arabia. Hydrogeol J 16:155–165
Anku YS, Banoeng-Yakubo B, Asiedu DK, Yidana SM (2009) Water quality analysis of groundwater in crystalline basement rocks, Northern Ghana. Environ Geol 58:989–997
Boughton CJ, Mccoy KJ (2006) Hydrogeology, aquifer chemistry and groundwater quality in Morgan county, West Virginia. Scientific investigations report 2006–5198, U.S. Geological survey, Reston, Virginia
Bouwer H (1978) Groundwater hydrology. Mc Graw Hill Book Company, New York
Burnik Sturm M, Ganbaatar O, Voigt CC, Kaczensky P (2017) First field-based observations of δ2H and δ18O values of event-based precipitation, rivers and other water bodies in the Dzungarian Gobi, SW Mongolia. Isotopes Environ Health Stud 53(2):157–171
Calmbach L (1999) Aquachem computer code-version 3.7: aqueous geochemical analyses, plotting and modelling. Waterloo Hydrogeologic, Waterloo, p 184
Cartwright I, Morgenstern U (2016) Using tritium to document the mean transit time and sources of water contributing to a chain-of-ponds river system: implications for resource protection. Appl Geochem 75:9–19
Çelik H (2003) Stratigraphical and tectonic characteristics of master mountain and adjacent area (SE of Elazığ). PhD Thesis, Fırat University (in Turkish with English abstract, unpublished)
Çeliker M (2008) Hydrogeological assessment of Uluova (Elazığ) by geographical information systems. Master’s thesis, Çukurova University (in Turkish with English abstract)
Çetin H, Güneyli H, Mayer L (2003) Palaeoseismology of the Palu-Lake Hazar segment of the East Anatolian fault zone, Turkey. Tectonophysics 374:163–197
Chidambaram S, Prasanna MV, Karmegam U, Singaraja C, Pethaperumal S, Manivannan R, Anandhan P, Tirumalesh K (2011) Significance of pCO2 values in determining carbonate chemistry in groundwater of Pondicherry region, India. Front Earth Sci 5(2):197–206
Clark I, Frıtz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton
Cooper HH, Jacob CE (1946) A generalized graphical method for evaluating formation constants and summarizing well-field history. Eos Trans AGU 27(4):526–534
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16:436–438
Dassi L (2010) Use of chloride mass balance and tritium data for estimation of groundwater recharge and renewal rate in an unconfined aquifer from North Africa: a case study from Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 60:861–871
El-Sayed SA, Morsy SM, Zakaria KM (2018) Recharge sources and geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Quaternary aquifer at Atfih area, the northeastern Nile Valley, Egypt. J Afr Earth Sci 142:82–92
Emiroğlu ME, Baylar A, Balı S (1998) Features of Lake Hazar and its water budget for the future. İstanbul Technical University IIth National Hydrology Congress (in Turkish with English abstract)
Eriş K (2013) Late Pleistocene-Holocene sedimentary records of climate and lake-level changes in Lake Hazar, eastern Anatolia, Turkey. Quat Int 302:123–134
Fetter CW (1994) Applied hydrogeology, 3rd edn. Macmillan College Publication, New York
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Sci J 170:795–840
Guideal R, Bala AE, Ikpokonte AE (2011) Estimates of the hydraulic properties of the quaternary aquifer in N’Djamena area, Chad Republic. J Appl Sci 11(3):542–548
Guiheneuf N, Boisson A, Bour O, Dewandel B, Perrin J, Dausse A, Viossanges M, Chandra S, Ahmed S, Marechal JC (2014) J Hydrol 511:320–334
Güler C, Thyne GD, Tağa H, Yıldırım Ü (2017) Processes governing alkaline groundwater chemistry within a fractured rock (ophiolitic melange) aquifer underlying a seasonally inhabited headwater area in the Aladağlar range (Adana, Turkey). Geofluids 2:1–21
Gupta SK, Deshpande RD (2005) Groundwater isotopic investigations in India: what has been learned? Curr Sci 89:5
Gürocak Z (1993) The geology of Sivrice (Elazığ) region. Master’s Thesis, Fırat University, p 65 (in Turkish with English abstract)
Gurunadha Rao VVS, Tamma Rao G, Surinaidu L, Mahesh J, Mallikharjuna Rao ST, Mangaraja Rao B (2013) Assessment of geochemical processes occurring in groundwaters in the coastal alluvial aquifer. Environ Monit Assess 185:8259–8272
Güven A (2013) The hydrogeological investigation of the alluvium aquifers surrounding the Lake Hazar (Elazığ). Master’s thesis Fırat University, p 76 (in Turkish with English abstract)
Han D, Lıang X, Jin M, Currell MJ, Han Y, Song X (2009) Hydrogeochemical indicators of groundwater flow systems in the Yangwu river alluvial fan, Xinzhou Basin, Shanxi, China. Environ Manag 44:243–255
Helmut K (2000) Soil and groundwater contamination remediation technology in Europe. In: Sato K (ed) Groundwater updates. Springer, Best-set Typesetter Ltd., Hong Kong, pp 3–8
Hempton MR (1985) Structure and deformation history of the Bitlis suture near Lake Hazar, southeastern Turkey. Geol Soc Am Bull 96:233–243
Herece E and Akay E (1992) East Anatolian Fault between Karlıova and Çelikhan. Abstracts, 9th Petroleum Congress of Turkey, 361–372
Janardhana Raju N, Reddy TVK, Kotaiah BPT (1992) A study on seasonal variations of ground water quality in Upper Gunjanaeru River basin, Cuddapah District, Andhra Pradesh. Fresenius Environ Bull 1:98–103
Jeyavel Raja Kumar T, Dushiyanthan C, Thiruneelakandan B, Suresh R, Senthilkumar M, Karthikeyan K, Davidraju D (2013) Quality and suitability assessment of Khan Sahib canal and groundwater in part of Annamalainagar, Chidambaram taluk of Cuddalore district, Tamilnadu. Int J Environ Sci 3(4):1290–1299
Jin L, Whitehead PG, Rodda H, Macadam I, Sarkar S (2018) Simulating climate change and socio-economic change impacts on flows and water quality in the Mahanadi River system, India. Sci Total Environ 637–638:907–917
Kaya A (1992) Geological investigations around Gezin-Maden (Elazığ). Master’s Thesis, Fırat University, p 72 (in Turkish with English abstract)
Kaya A (2004) Geology of Gezin region (Maden-Elazığ). Pamukkale University Journal of Engineering Sciences 10:41–50
Kazakis N, Voudouris KS (2015) Groundwater vulnerability and pollution risk assessment of porous aquifers to nitrate: modifying the DRASTIC method using quantitative parameters. J Hydrol 525:13–25
Kim JJ, Comstock J, Ryan P, Heindel C, Koenigsberger S (2016) Denitrification and dilution along fracture flowpaths influence the recovery of a bedrock aquifer from nitrate contamination. Sci Total Environ 569–570:450–468
Koçer N (1995) Hazar Gölü ve çevresindeki tuğla ve kiremit fabrikalarının çevresel etkileri. I. Hazar Gölü ve Çevresi Sempozyumu Bildiriler, 20 Mayıs 1995, Sivrice Kaymakamlığı Yayınları 2: 273–277 (in Turkish with English abstract)
Koh D-C, Ko K-S, Kim Y, Lee S-G, Chang H-W (2007) Effect of agricultural land use on the chemistry of groundwater from basaltic aquifers, Jeju Island, South Korea. Hydrogeol J 15:727–743
Koh D-C, Ha K, Lee K-S, Yoon Y-Y, Ko K-S (2012) Flow paths and mixing properties of groundwater using hydrogeochemistry and environmental tracers in the southwestern area of Jeju volcanic island. J Hydrol 432–433:61–74
Kolbe T, Marçais J, Thomas Z, Abbott BW, De Dreuzy J-R, Rousseau-Gueutin P, Aquilina L, Labasque T, Pinay G (2016) Coupling 3D groundwater modeling with CFC-based age dating to classify local groundwater circulation in an unconfined crystalline aquifer. J Hydrol 543:31–46
Kutschker AM, Epele LB, Miserendino ML (2014) Aquatic plant composition and environmental relationships in grazed Northwest Patagonian wetlands, Argentina. Ecol Eng 64:37–48
Macpherson GL, Roberts JA, Blair JM, Townsend MA, Fowle DA, Beisner KR (2008) Increasing shallow groundwater CO2 and limestone weathering, Konza Prairie, USA. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:5581–5599
MHTR (2004) Ministry of Health of the Turkish Republic drinking water regulations. Official Gazette No. 25730 and 17 February 2005 dated
Mora G, Zanazzi A (2017) Hydrogen isotope ratios of moss cellulose and source water in wetlands of Lake Superior, United States reveal their potential for quantitative paleoclimatic reconstructions. Chem Geol 468:75–83
Mortimer L, Aydin A, Simmons CT, Love AJ (2011) Is in situ stress important to groundwater flow in shallow fractured rock aquifers? J Hydrol 399:185–200
MTA (2008) General Directorate of mineral research and exploration, Atlas of East Anatolian fault, Palu and Şiro segments. Turkey
Nyende J, Tonder VG, Vermeulen D (2013) Application of isotopes and recharge analysis in investigating surface water and groundwater in fractured aquifer under influence of climate variability. J Earth Sci Clim Change 4:4
Onwuka OS, Omonona OV, Anika OC (2013) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of regolith aquifers in Enugu metropolis, southeastern Nigeria. Environ Earth Sci 70:1135–1141
Özler HM (2003) Hydrochemistry and salt-water intrusion in the Van aquifer, east Turkey. Environ Geol 43:759–775
Öztekin Ö (1998) The physico-chemical properties of drinking and using waters of Elazığ, Turkey. Master’s thesis, Fırat University, 124 p (in Turkish with English abstract)
Öztekin Okan Ö, Çetindağ B, Uçar S (2013) Hydrogeochemical investigation of the mineral waters located at Palu-Tohumlu segment of Eastern Anatolian Fault zone and their economical value. Final report of the Project numbered FÜBAP 1778, Fırat University
Öztekin Okan Ö, Güven A, Çetindağ B (2018) The hydrogeological investigation of Plajköy spring (Elazığ). Bulletin of The Mineral Research and Exploration 157: DOI: https://doi.org/10.19111/bulletinofmre.376767 (in press)
Parkhurst DL and Appelo CAJ (1999) Phreeqc (version 2), a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. U.S. Geological Survey Water Resources Investigation
Petalas C, Lambrakis N, Zaggana E (2006) Hydrochemistry of waters of Volcanıc rocks: the case of the volcanosedimentary rocks of Thrace, Greece. Water Air Soil Pollut 169:375–394
Raju NJ (2011) Evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes in the Pleistacene aquifers of Middle Ganga Plain, Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ Earth Sci 65:1291–1308
Ravikumar P, Somashekar RK, Angami M (2011) Hydrochemistry and evaluation of groundwater suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in the Markandeya River basin, Belgaum District, Karnataka State, India. Environ Monit Assess 173:459–487
Reddy AGS (2013) Evaluation of hydrogeochemical characteristics of phreatic alluvial aquifers in southeastern coastal belt of Prakasam district, South India. Environ Earth Sci 68:471–485
Salifu M, Aidoo F, Hayford MS, Adomako D, Asare E (2017) Evaluating the suitability of groundwater for irrigational purposes in some selected districts of the Upper West region of Ghana. Appl Water Sci 7:653–662
Sayın M, Eyüpoğlu SO (2005) Determination of local meteoric water lines using stable isotope contents of precipitation in Turkey. II. Use of Isotope Techniques in Hydrology Symposium, Ankara, pp. 323–344
Şen B, Koçer MAT, Alp MT (2002) Physical and chemical properties of rivers drained into Lake Hazar. Fırat University Journal of Engineering Science 14(1):241–248 (in Turkish with English abstract)
Shedlock RJ, Wilcox DA, Thompson TA, Cohen DA (1993) Interactions between ground water and wetlands, southern shore of Lake Michigan, USA. J Hydrol 141(1–4):127–155
Shin W-J, Park Y, Koh D-C, Lee K-S, Kim Y, Kim Y (2017) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic features of the groundwater flow systems in the central-northern part of Jeju Island (Republic of Korea). J Geochem Explor 175:99–109
Sjöström J (1993) Ionic composition and mineral equilibria of acidic groundwater on the west coast of Sweden. Environ Geol 21:219–226
Smith I, Schallenberg M (2013) Occurrence of the agricultural nitrification inhibitor, dicyandiamide, in surface waters and its effects on nitrogen dynamics in an experimental aquatic system. Agric Ecosyst Environ 164:23–31
Smith RL, Baumgartner LK, Miller DN, Repert DA, Böhlke JK (2006) Assessment of nitrification potential in groundwater using short term, single-well injection experiments. Microb Ecol 51:22–35
Soldatova E, Guseva N, Sun Z, Bychinsky V, Boeckx P, Gao B (2017) Sources and behaviour of nitrogen compounds in the shallow groundwater of agricultural areas (Poyang Lake basin, China). J Contam Hydrol 202:59–69
Solomon DK (2000) 3H and 3He. Chapter 13, pp 397–424. In: Cook PG, Herczeg AL (eds) Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology. Kluwer, Boston, p 529
Sungurlu O, Perinçek D, Kurt G, Tuna E, Dülger S, Çelikdemir E, Naz H (1985) Geology of Elazığ-Hazar-Palu area. Journal of General Directorate of Turkish Petroleum Affairs 29:83–191 (in Turkish with English abstract)
SWQMR (2015) Surface Water Quality Management Regulation. Official Gazette No. 29327 and 15 April 2015 dated
Turan M and Gürocak Z (1997) Tectonic characteristics of East Anatolian Fault Zone around Sivrice (Elazığ). Proceedings, 20th Geology Symposium, Selçuk University, Faculty of Engineering, Department of Geological Engineering, 465-477, 1997 (in Turkish with English abstract)
USSL (1954) U.S. Salinity Laboratory. Diagenesis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. U.S. Dept. Agriculture Handbook-60, Washington DC
Venterea RT, Rolston DE (2000) Nitric and nitrous oxide emissions following fertilizer application to agricultural soil: biotic and abiotic mechanisms and kinetics. J Geophys Res Atmos 105:15117–15129
West AG, February EC, Bowen GJ (2014) Spatial analysis of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes (“isoscapes”) in ground water and tap water across South Africa. J Geochem Explor 145:213–222
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation water. U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, vol 969, Washington
Williams AJ, Crossey LJ, Karlstrom KE, Newell D, Person M, Woolsey E (2013) Hydrogeochemistry of the middle Rio Grande aquifer system—fluid mixing and salinization of the Rio Grande due to fault inputs. Chem Geol 351:281–298
Zhou X, Shen Y, Zhang H, Song C, Li J, Liu Y (2015) Hydrochemistry of the natural low pH groundwater in the coastal aquifers near Beihai, China. J Ocean Univ China 14(3):475–483
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Fırat University for its financial support for the project numbered MF. 12. 28. The authors also would like to thank the anonymous reviewers and editor for their critical input in the production of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okan, Ö.Ö., Güven, A. Hydrochemistry of groundwaters from alluvial and fractured igneous aquifers at the western region of Lake Hazar (Elazığ, Turkey). Arab J Geosci 12, 52 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4209-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4209-8