Abstract
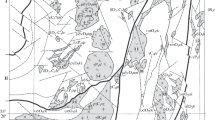
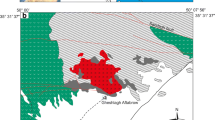
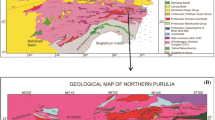
The Haji Abad intrusion is a well-exposed Middle Eocene I-type granodioritc pluton in the Urumieh–Dokhtar magmatic assemblage (UDMA). The major constituents of the investigated rocks are K-feldspar, quartz, plagioclase, pyroxene, and minor Fe–Ti oxide and hornblende. The plagioclase compositions fall in the labradorite, andesine, and oligoclase fields. The amphiboles range in composition from magnesio-hornblende to tremolite–hornblende of the calcic-amphibole group. Most pyroxenes principally plot in the field of diopside. The calculated average pressure of emplacement is 1.9 kbar for the granodioritic rocks, crystallizing at depths of about 6.7 km. The highest pressure estimated from clinopyroxene geobarometry (5 kbar) reflects initial pyroxene crystallization pressure, indicating initial crystallization depth (17.5 km) in the Haji Abad granodiorite. The estimated temperatures using two-feldspar thermometry give an average 724 °C. The calculated average temperature for clinopyroxene crystallization is 1090 °C. The pyroxene temperatures are higher than the estimated temperature by feldspar thermometry, indicating that the pyroxene and feldspar temperatures represent the first and late stages of magmatic crystallization of Haji Abad granodiorite, respectively. Most pyroxenes plot above the line of Fe3+ = 0, indicating they crystallized under relatively high oxygen fugacity or oxidized conditions. Furthermore, the results show that the Middle Eocene granitoids crystallized from magmas with H2O content about 3.2 wt%. The relatively high water content is consistent with the generation environment of HAG rocks in an active continental margin and has allowed the magma to reach shallower crustal levels. The MMEs with ellipsoidal and spherical shapes show igneous microgranular textures and chilled margins, probably indicating the presence of magma mixing. Besides, core to rim compositional oscillations (An and FeO) for the plagioclase crystals serve as robust evidence to support magma mixing. The studied amphiboles and pyroxenes are grouped in the subalkaline fields that are consistent with crystallization from I-type calc-alkaine magma in the subduction environment related to active continental margin. Mineral chemistry data indicate that Haji Abad granodiorites were generated in an orogenic belt related to the volcanic arc setting consistent with the subduction of Neo-Tethyan oceanic crust beneath the central Iranian microcontinent.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi S, Tabatabaei Manesha SM, Karimia S, Parfenova OV (2014) Relative contributions of crust and mantle to generation of Oligo–Miocene medium-K calc-alkaline I-type granitoids in a subduction setting—a case study from the Nabar pluton, central Iran. Petrology 22:310–328
Abbott RN Jr (1985) Muscovite-bearing granites in the AFM liquidus projection. Can Mineral 23:553–561
Aghanabati A (1998) Major sedimentary and structural units of Iran (map). Geosciences 7, Geological Survey of Iran
Alavi M (2004) Regional stratigraphy of the Zagros Fold-Thrust Belt of Iran and its proforeland evolution. Am J Sci 304:1–20
Allen MB (2009) Discussion on the Eocene bimodal Piranshahr massif of the Sanandaj–Sirjan zone, west Iran: a marker of the end of collision in the Zagros orogen. J Geol Soc London 166:981–982
Anderson AT Jr (1980) Significance of hornblende in calc-alkaline andesites and basalts. Am Mineral 65:837–851
Anderson JL (1996) Status of thermo-barometry in granitic batholiths. Earth Sci Rev 87:125–138
Andrews BJ, Gardner JE, Housh TB (2008) Repeated recharge, assimilation, and hybridization in magmas erupted from El Chichón as recorded by plagioclase and amphibole phenocrysts. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 175:415–426
Arvin M, Pan Y, Dargahi S, Malekizadeh A, Babaei A (2007) Petrochemistry of the Siah Kuh granitoid stock southwest of Kerman, Iran: implications for initiation of Neotethys subduction. J Asian Earth Sci 30:474–489
Ayati F, Yavuz F, Asadi HH, Richards JP, Jourdan F (2013) Petrology and geochemistry of calc-alkaline volcanic and subvolcanic rocks, Dalli porphyry copper-gold deposit, Markazi Province, Iran. Int Geol Rev 55:158–184
Barbarin B (2005) Mafic magmatic enclaves and mafic rocks associated with some granitoids of the Central Sierra Nevada batholiths, California: nature, origin, and relations with the hosts. Lithos 80:155–177
Baxter S, Feely M (2002) Magma mixing and mingling textures in granitoids: examples from the Galway granite, Connemara, Ireland. Mineralogy and Petrology 76:63–74
Beccaluva L, Macciotta G, Piccardo GB, Zeda O (1989) Clinopyroxene composition of ophiolite basalts as petrogenetic indicator. Chem Geol 77:165–182
Berberian F, Berberian M (1981) Tectono-plutonic episodes in Iran. In: Gupta HK, Delany FM (eds) Zagroz Hindu Kush Himalaya geodynamic evolution. American Geophysical Union & Geological Society of America, Washington, pp 5–32
Berberian M, King GCP (1981) Towards a paleogeography and tectonic evolution of Iran. Can J Earth Sci 18:210–265
Bonin B (2004) Do coeval mafic and felsic magmas in post-collisional to within-plate regimes necessarily imply two constrasting, mantle and crust, sources? A review. Lithos 78:1–24
Botcharnikov R, Koepke J, Holtz F, McCammon C, Wilke M (2005) The effect of water activity on the oxidation and structural state of Fe in a ferro-basaltic melt. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:5071–5085
Bottinga Y, Weill DF (1970) Densities of liquid silicate systems calculated from partial molar volumes of oxide components. Am J Sci 269:169–182
Caillat C, Dehlavi P, Martel-Jantin B (1978) Géologie de la région de Saveh (Iran); contribution à l'étude du volcanisme et du plutonisme tertiaires de la zone de l’Iran Central. Thèse de Doctorat de Specialities, Grenoble University, France 325 pp.
Cao M, Qin K, Li J, Yang Y, Evans NJ, Zhang R, Jin L (2014) Magmatic process recorded in plagioclase at the Baogutu reduced porphyry Cu deposit, western Junggar, NW-China. J Asian Earth Sci 82:136–150
Chappel BW, White AJR (1974) Two contrasting granite types. Pacific Geology 8:173–174
Chappell BW, White AJR, Williams IS, Wyborn D, Wyborn LAI (2000) Lachlan Fold Belt granites revisited: high- and low-temperature granites and their implications. Aust J Earth Sci 47:123–138
Chappell BW, White AJR, Wyborn D (1987) The importance of residual source material (restite) in granite petrogenesis. J Petrol 28:1111–1138
Chen B, Chen ZC, Jahn BM (2009) Origin of the mafic enclaves from the Taihang Mesozoic orogen, North China craton. Lithos 110:343–358
Chen CJ, Chen B, Li Z, Wang ZQ (2016) Important role of magma mixing in generating the Mesozoic monzodioritic–granodioritic intrusions related to Cu mineralization, Tongling, East China: evidence from petrological and in situ Sr-Hf isotopic data. Lithos 248–251:80–93
Chen WT, Zhou MF, Gao JF, Zhao TP (2015) Oscillatory Sr isotopic signature in plagioclase megacrysts from the Damiao anorthosite complex, North China: implication for petrogenesis of massif-type anorthosite. Chem Geol 393–394:1–15
Claeson DT, Meurer WP (2004) Fractional crystallization of hydrous basaltic “arctype” magmas and the formation of amphibole-bearing gabbroic cumulates. Contrib Mineral Petrol 147:288–304
Clarke DB (1992) Granitoid rocks. Chapman and Hall, London
Clemens JD, Wall VJ (1984) Origin and evolution of a peraluminous silicic ignimbrite suite: the Violet Town Volcanics. Contrib Mineral Petrol 88:354–371
Coltorti M, Bondaiman C, Faccini B, Gregoire M, OReilly SY, Powell W (2007) Amphiboles from suprasubduction and intraplate lithospheric mantle. Lithos 99:68–84
Davidson J, Turner S, Handley H, Macpherson C, Dosseto A (2007) Amphibole “sponge” in arc crust. Geology 35:787–790
Davidson JP, Tepley F III, Palacz Z, Meffan-Main S (2001) Magma recharge, contamination and residence times revealed by in situ laser ablation isotopic analysis of feldspar in volcanic rocks. Earth Planet Sci Lett 184:427–442
Davidson JP, Tepley FJ (1997) Recharge in volcanic systems: evidence from isotope profiles of phenocrysts. Science 275:826–829
Deer WA, Howie RA, Zussman J (1992) An introduction to the rock-forming minerals. Longman, Essex
Dessimoz M, Müntener O, Ulmer P (2012) A case for hornblende dominated fractionation of arc magmas: the Chelan complex (Washington cascades). Contrib Mineral Petrol 163:567–589
Didier J, Barbarin B (1991) Enclaves and granite petrology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–626
Dorouzi T, Vosoughi Abedini M (2009) The role of magmatic fractionation and crustal contamination in the genesis of south and south eastern Buin-Zahra Eocene volcanic rocks. Iran J Geol 3:15–23 (In Persian with English abstract)
Eghlimi B (2000) Geological map of Danesphahan 1:100000 survey sheet. Geological Survey of Iran
Elkins LT, Grove TL (1990) Ternary feldspar experiments and thermodynamic models. Am Mineral 75:544–559
Ernst WG (1999) Hornblende, the continental maker—evolution of H2O during circumPacific subduction versus continental collision. Geology 27:675–678
Faak K, Chakraborty S, Coogan LA (2013) Mg in plagioclase: experimental calibration of a new geothermometer and diffusion coefficients. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 123:195–217
Förster H, Fesefeldt K, Kürsten M (1972) Magmatic and orogenic evolution of the central Iranian volcanic belt. In: Armstrong JE, Hedberg HD (eds.) 24th international geologic congress, Montreal, QC, Canada 198–210
France L, Koepke J, Ildefonse B, Cichy SB, Deschamps F (2010) Hydrous partial melting in the sheeted dike complex at fast spreading ridges: experimental and natural observations. Contrib Mineral Petrol 160:683–704
Fuhrman ML, Lindsley DH (1988) Ternary-feldspar modeling and thermometry. Am Mineral 73:201–215
Grogan SE, Reavy RJ (2002) Disequilibrium textures in the Leinster granite complex, SE Ireland: evidence for acid-acid magma mixing. Mineral Mag 66:929–939
Halama R, Waight T, Markl G (2002) Geochemical and isotopic zoning patterns of plagioclase megacrysts in gabbroic dykes from the Gardar Province, South Greenland: implications for crystallization processes in anorthositic magmas. Contrib Mineral Petrol 144:109–127
Hammarstrom JM, Zen E (1986) Aluminum in hornblende: an empirical igneous geobarometer. Am Mineral 71:1297–1313
Hattori K, Sato H (1996) Magma evolution recorded in plagioclase zoning in 1991 Pinatubo eruption products. Am Mineral 81:982–994
Helz RT (1973) Phase relations of basalts in their melting range at PH2O=5 kb as a function of oxygen fugacity, part I: mafic phases. J Petrol 14:249–302
Honarmand M, Ahmadian J, Nabatian G, Murata M (2012) Reconstructing physicochemical conditions by application of mineral chemistry: a case study from the Natanz pluton, Central Iran. Neues Jahrbuch fur Mineralogie, Abhandlungen 189:138–153
Honarmand M, Rashidnejad Omran N, Neubauer F, Nabatian G, Emami MH, Bernroider M, Ahmadian J, Ebrahimi M, Liu X (2016) Mineral chemistry of a Cenozoic igneous complex, the Urumieh–Dokhtar magmatic belt, Iran: petrological implications for the plutonic rocks. Island Arc 25:137–153
Housh TB, Luhr JF (1991) Plagioclase-melt equilibria in hydrous systems. Am Mineral 76:477–492
Huang H, Niu YL, Nowell G, Zhao ZD, Yu XH, Zhu DC, Mo XX, Ding S (2014) Geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of granitoids in the east Kunlun orogenic belt, northern Tibetan plateau: implications for continental crust growth through syn-collisional felsic magmatism. Chem Geol 370:1–18
Kananian A, Sarjoughian F, Nadimi A, Ahmadian J, Ling W (2014) Geochemical characteristics of the Kuh-e Dom intrusion, Urumieh Dokhtar Magmatic Arc (Iran): implications for source regions and magmatic evolution. J Asian Earth Sci 90:137–148
Kazemi K, Kananian A, Xiao Y, Sarjoughian F (2018) Petrogenesis of Middle-Eocene granitoids and their mafic microgranular enclaves in central Urmia-Dokhtar Magmatic Arc (Iran): evidence for interaction between felsic and mafic magmas. Geosci Front. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2018.04.006
Krawczynski MJ, Grove TL, Behren H (2012) Amphibole stability in primitive arc magmas: effects of temperature, H2O content, and oxygen fugacity. Contrib Mineral Petrol 164:317–339
Kretz R (1983) Symbols for rock-forming minerals. Am Mineral 68:277–279
Kudo AM, Weill DF (1970) An igneous plagioclase thermometer. Contrib Mineral Petrol 25:52–65
Lange RA, Frey HM, Hector J (2009) A thermodynamic model for the plagioclase liquid hygrometer/thermometer. Am Mineral 94:494–506
Larocque J, Canil D (2010) The role of amphibole in the evolution of arc magmas and crust: the case from the Jurassic Bonanza arc section, Vancouver Island, Canada. Contrib Mineral Petrol 159:475–492
Le Base MJ (1962) The role of aluminum in igneous clinopyroxenes with relation to their parentage. Am J Sci 260:267–288
Leake BE, Woolly AR, Arps CES, Birch WD, Gilbert MC, Grice JD, Hawthorne FC, Kato A, Kisch HJ, Krivovichev VG et al (1997) Nomenclature of amphiboles. Report of the Subcommittee on Amphiboles of the International Mineralogical Association Commission on New Minerals Names. Eur J Mineral 9:623–651
Leterrier J, Maury RC, Thonon P, Girard D, Marchal M (1982) Clinopyroxene composition as a method of identification of the magmatic affinities of paleo-volcanic series. Earth Planet Sci Lett 59:139–154
Martin RF (2007) Amphiboles in the igneous environment, in: Hawthorne FC, Oberti R (Eds.), Amphiboles: crystal chemistry, occurrence and human health. Reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry 67:323–358
Maulana A, Watanabe K, Imai A, Yonezu K (2012) Geochemical signature of granitic rocks from Sulawesi, Indonesia: evidence of Gondwana involvement. Mineralogical Magazine 76:2081pp
Mcbirny AR (2007) Igneous petrology, third edn. Jones and Bartlett, Boston
Moine-Vaziri H (1985) Volcanisme tertiarie et quaternaire en Iran: These d Etat. Univers. Paris-Sud, Orsay
Molina J, Scarrow J, Montero PG, Bea F (2009) High-Ti amphibole as a petrogenetic indicator of magma chemistry: evidence for mildly alkalic-hybrid melts during evolution of Variscan basic–ultrabasic magmatism of Central Iberia. Contrib Mineral Petrol 158:69–98
Morimoto N, Fabries J, Ferguson AK, Ginzburg IV, Ross M, Seifert FA, Zussman J, Aoki K, Gottardi D (1988) Nomenclature of pyroxenes. Am Mineral 62:53–62
Morimoto N, Fabries J, Ferguson AK, Ginzburg IV, Ross M, Seifert FA, Zussman J, Aoki K, Gottardi G (1989) Nomenclature of pyroxenes. Subcommittee on pyroxenes. Am Mineral 73:1123–1133
Morley CK, Kongwung B, Julapour AA, Abdolghafourian M, Hajian M, Waples D, Warren J, Otterdoom H, Srisuriyon K, Kazemi H (2009) Structural development of a major late Cenozoic basin and transpressional belt in central Iran: the Central Basin in the Qom-Saveh area. Geosphere 5:325–362
Murphy JB, Blais SA, Tubrett M, McNeil D, Middleton M (2012) Microchemistry of amphiboles near the roof of a mafic magma chamber: insights into high level melt evolution. Lithos 148:162–175
Nekvasil H, Burnham CW (1987) The calculated individual effects of pressure and water content on phase equilibria in the granites system. In: Mysen BO (eds) Magmatic process: physicochemical principles. Geochemical Society, University Park, Pennsylvania. 500 p
Nogole-Sadat MAA, Hoshmandzadeh A (1984) Saveh geological map, scale 1:250000, Geological Survey of Iran
Noyes H, Frey FA, Wones DR (1983) A tale of two plutons: geochemical evidence bearing on the origin and differentiation of the Red Lake and Eagle Peak plutons, central Sierra Nevada, California. J Geol 91:487–509
Panjasawatwong Y, Danyushevsky LV, Crawford AJ, Harris KL (1995) An experimental study of the effects of melt composition on plagioclase-melt equilibria at 5 and 10 kbar: implications for the origin of magmatic high-An plagioclase. Contrib Mineral Petrol 118:420–432
Papike JJ, Cameron M (1976) Crystal chemistry of silicate minerals of geophysical interest. Rev Geophys 14:37–80
Perugini D, Poli G, Christofides G, Eleftheriadis G (2003) Magma mixing in the Sithonia Plutonic Complex, Greece: evidence from mafic microgranular enclaves. Mineral Petrol 78:173–200
Phinney WC (1992) Partition coefficients for iron between plagioclase and basalt as a function of oxygen fugacity: implications for Archean and lunar anorthosites. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:1885–1895
Putirka KD (2005) Igneous thermometers and barometers based on plagioclase + liquid equilibria: tests of some existing models and new calibrations. Am Mineral 90:336–346
Putirka KD (2008) Thermometers and barometers for volcanic systems. Rev Mineral Geochem 69:61–120
Putirka KD, Mikaelian H, Ryerson F, Shaw H (2003) New clinopyroxene-liquid thermobarometers for mafic, evolved, and volatile-bearing lava compositions, with applications to lavas from Tibet and the Snake River Plain, Idaho. Am Mineral 88:1542–1554
Rezaei-Kahkhaei M, Galindo G, Pankhurst RJ, Esmaeily D (2011) Magmatic differentiation in the calc-alkaline Khalkhab Neshveh pluton, Central Iran. J Asian Earth Sci 42:499–514
Ridolfi F, Renzulli A, Puerini M (2010) Stability and chemical equilibrium of amphibole in calc-alkaline magmas: an overview, new thermobarometric formulations and application to subduction-related volcanoes. Contrib Mineral Petrol 160:45–66
Ruprecht P, Wörner G (2007) Variable regimes in magma systems documented in plagioclase zoning patterns: El Misti stratovolcano and Andahua monogenetic cones. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 165:142–162
Rutter MJ, Van der laan SR, Wyllie PJ (1989) Experimental data for a proposed empirical igneous geobarometer: aluminium in hornblende at 10 kbar pressure. Geology 17:897–900
Safarzadeh E, Vosoughi Abedini M, Ghorbani M (2007) Nature and source of Haji Abad granitoidic pluton. 11th symposium of Geological Society of Iran, Ferdowsi University of Mashahd, Iran (In Persian with English abstract)
Sarjoughian F (2012) Nature of the Kuh-e Dom plutonism (NE Ardestan), geological events and its magmatic evolution. Ph.D thesis, University of Tehran, Tehran (In Persian with English abstract)
Sarjoughian F, Kananian A, Haschke M, Ahmadian J, Ling W (2012) Magma mingling and hybridization in the Kuh-e Dom pluton, Central Iran. J Asian Earth Sci 54-55:49–63
Sarjoughian F, Kananian A, Lentz DR, Ahmadian J (2015) Nature and physicochemical conditions of crystallization in the South Dehgolan intrusion, NW Iran: mineral-chemical evidence. Turk J Earth Sci 24:249–275
Sarjoughian F, Lentz D, Kananian A, Ao S, Xiao W (2018) Geochemical and isotopic constraints on the role of juvenile crust and magma mixing in the UDMA magmatism, Iran: evidence from mafic microgranular enclaves and cogenetic granitoids in the Zafarghand igneous complex. Int J Earth Sci 107(3):1127–1151
Schmidt MW (1992) Amphibole composition in tonalite as a function of pressure an experimental calibration of the Alhornblende barometer. Contrib Mineral Petr 110:304–310
Schweitzer EL, Papike JJ, bence AE (1979) Statitical analysis of clinopyroxenes from deep sea basalts. Am Mineral 64:501–513
Sepahi AA, Maanijou M, Salami S et al (2012) Mineral chemistry and geothermobarometry of Moshirabad pluton, Qorveh, Kurdistan, western Iran. Island Arc 21(3):170–187
Shcherbakov V, Plechov P, Izbekov P, Shipman J (2011) Plagioclase zoning as an indicator of magma processes at Bezymianny volcano, Kamchatka. Contrib Mineral Petrol 162:83–99
Shelley D (1993) Igneous and metamorphic rocks under the microscope. Chapman and Hall, London
Shellnutt JG, Jahn BM, Dostal J (2010) Elemental and Sr–Nd isotope geochemistry of microgranular enclaves from peralkaline A-type granitic plutons of the Emeishan large igneous province, SW China. Lithos 19:34–46
Sherafat S, Yavuz F, Noorbehesht I, Yıldırım DK (2012) Mineral chemistry of Plio-Quaternary subvolcanic rocks, Southwest Yazd Province, Iran. Int Geol Rev 54(13):1497–1531
Singer BS, Dungan M, Layne GD (1995) Textures and Sr, Ba, Mg, Fe, K, and Ti compositional profiles in volcanic plagioclase: clues to the dynamics of calcalkaline magma chambers. Am Mineral 80:776–798
Snelling AA, Woodmorappe J (1998) In: The cooling of thick igneous bodies on a young earth. Fourth international conference on creationism, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, August 527–545
Soesoo A (1997) A multivariate statistical analysis of clinopyroxene composition: empirical coordinates for the crystallisation PT-estimations. Geol Soc Sweden (Geologiska Föreningen) 119:55–60
Stamatelopoulou-Seymour K, Vlassopoulos D, Pearce TH, Rice C (1990) The record of magma chamber processes in plagioclase phenocrysts at Thera Volcano, Aegean Volcanic Arc, Greece. Contrib Mineral Petrol 104:73–84
Stein E, Dietl E (2001) Hornblende thermobarometry of granitoids from the central Odenwald (Germany) and their implication for the geotectonic development of the Odenwald. Mineral Petrol 72:185–207
Sun CM, Bertrand J (1991) Geochemistry of clinopyroxenes in plutonic and volcanic sequences from the Yanbian Proterozoic ophiolites (Sichuan Province, China): petrogenetic and geotectonic implications. Schweiz Mineralogische Petrologische Mitteilungen 71:243–259
Tabbakh Shabani A (1991) Petrogeraphy and petrology of Boin zahra igneouse intrusive bodies, M.S. thesis, Tarbiat Moalem University, Tehran (In Persian with English abstract)
Tepley FJ III, Davidson JP (2003) Mineral-scale Sr-isotope constraints on magma evolution and chamber dynamics in the rum layered intrusion, Scotland. Mineral Petrol 145:628–641
Tepley FJ III, Davidson JP, Tilling RI, Arth JG (2000) Magma mixing, recharge and eruption histories recorded in plagioclase phenocrysts from El Chichon volcano, Mexico. J Petrol 41:1397–1411
Tepley FJ, Davidson JP, Clynne MA (1999) Magmatic interactions as recorded in plagioclase phenocrysts of Chaos Crags, Lassen Volcanic Center, California. J Petrol 40:787–806
Tulloch AJ, Challis GA (2000) Emplacement depths of Paleozoic-Mesozoic plutons from western New Zealand estimated by hornblende-Al geobarometry. N Z J Geol Geophys 43:555–567
Ustunisik G, Kilinc A, Nielsen RL (2014) New insights into the processes controlling compositional zoning in plagioclase. Lithos 200/201:80–93
Vernon RH (1984) Microgranitoid enclaves in granites-globules of hybrid magma quenched in a plutonic environment. Nature 309:438–439
Vernon RH (1990) Crystallization and hybridism in microgranitoid enclave magmas: microstructural evidence. J Geophys Res 95:17849–17859
Vyhnal CR, McSween HY Jr, Speer JA (1991) Hornblende chemistry in southern Appalachian granitoids: implications for aluminum hornblende thermobarometry and magmatic epidote stability. Am Mineral 76:176–188
White AJR, Chappell BW (1983) Granitoid types and their distribution in the Lachlan Fold Belt, southeastern Australia. Geol Soc Am Memory 159:21–34
White AJR, Chappell BW, Wyborn D (1999) Application of the restite model to the Deddick granodiorite and its enclaves—a reinterpretation of the observations and data of Maas et al (1997). J Petrol 40:413–421
Wilke M, Behrens H (1999) The dependence of the partitioning of iron and europium between plagioclase and hydrous tonalitic melt on oxygen fugacity. Contrib Mineral Petrol 137:102–114
Wyborn D, Chappell BW, Johnston RM (1981) Three S type volcanic suites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, Southeast Australia. J Geophys Res 86:10335–10348
Yang H, Ge W, Zhao G, Dong Y, Xu WL, Ji Z, Yu J (2015) Late Triassic intrusive complex in the Jidong region, Jiamusi–Khanka block, NE China: geochemistry, zircon U–Pb ages, Lu–Hf isotopes, and implications for magma mingling and mixing. Lithos 224-225:143–159
Yang JH, Wu FY, Chung SL, Wilde SA, Chu MF (2004) Multiple sources for the origin of granites: geochemical and Nd/Sr isotopic evidence from the Gudaoling granite and its mafic enclaves, NE China. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:4469–4483
Yang JH, Wu FY, Chung SL, Wilde SA, Chu MF (2006) A hybrid origin for the Qianshan A-type granite, northeast China: geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic evidence. Lithos 89:89–106
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Song B (2006) Hornblende thermobarometry of the carboniferous granitoids from the Inner Mongolia paleo-uplift: implications for the tectonic evolution of the northern margin of North China block. Mineral Petrol 87:123–141
Zorpi MJ, Coulon C, Orisini JB, Concirta C (1989) Magma mingling, zoning and emplacement in calk-alkaline granitoid plutons. Tectonophysics 157:315–326
Acknowledgements
This study is a synthesis of the Ph.D. thesis by K. Kazemi. The authors acknowledge the support of this project by the University of Tehran. The electron probe microanalyses (EPMA) of mineral were carried out at the Hefei University, China. We would like to thank Dr. Hou Zhenhui, Mr. Yangyang Wang, and Mr. Fengtai Tong for their help during sabbatical at USTC and for their technical assistance. This work is partly supported by projects from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41473033, 41673031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazemi, K., Kananian, A., Xiao, Y. et al. Chemical composition of rock-forming minerals and crystallization physicochemical conditions of the Middle Eocene I-type Haji Abad pluton, SW Buin-Zahra, Iran. Arab J Geosci 11, 717 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4083-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4083-4