Abstract
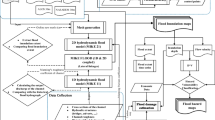
Human‐induced land use/land cover (LULC) changes are among the most important processes that shape the dynamics of the earth’s surface. This phenomenon, which is occurring at an astonishing rate, and its consequential environmental impacts have become an important area of research for scientists.Therefore, a wide range of methods and models have been developed to detect and predict these alterations, among which cellular automata (CA) models such as the CA‐Markov model, due to their affinity to geographic information system (GIS) and remote sensing (RS), are appropriate for detailed resolution modelling and simulating dynamic spatial processes. In Iran, the district of Ravansar has undergone severe LULC changes recently, thus to take the necessary precautions, decision‐makers need to predict and determine the extent of these changes. In this study, using spatial analysis methods the LULC changes in Ravansar were investigated from 1992 to 2015. Subsequently, the CA‐Markov model was applied to simulate the spatial pattern changes of LULC until 2030. Our results indicated that from 1992 to 2015, this region has witnessed a noticeable increase in the areas of the built‐up and agricultural lands (both aquatic and non‐aquatic), resulting in the decrease of the gardens, range, and bare lands. The simulated LULC map showed that this trend will continue due to more urbanization and development of agricultural areas.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bozkaya AG, Balcik FB, Goksel C, Esbah H (2015) Forecasting land-cover growth using remotely sensed data: a case study of the Igneada protection area in Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 187:59
Clarke KC, Hoppen S, Gaydos L (1997) A self-modifying cellular automaton model of historical urbanization in the San Francisco Bay Area. Environ Plan B: Plan Design 24:247–261
Chen X, Yu SX, Zhang YP (2013) Evaluation of spatiotemporal dynamics of simulated land use/cover in China using a probabilistic cellular automata-Markov model. Pedosphere 23(2):243–255
Dadhich PN, Hanaoka S (2010) Remote sensing, GIS and Markov’s method for land use change detection and prediction of Jaipur district. J Geom 4:9–15
Deep S, Saklani A (2014) Urban sprawl modeling using cellular automata. Egypt J Remote Sensing Space Sci 17:179–187
Dewan AM, Yamaguchi Y (2009) Land use and land cover change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: using remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization. Appl Geogr 29:390–401
Du Y-K, Yan Q, Luo C-F (2016) Monitoring and predicting the changes of vegetation coverage in Shijiazhuang from 1995 to 2015. In: Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), 2016 IEEE International. IEEE, pp 2324–2327
Gajbhiye S, Sharma S (2012) Land use and land cover change detection of Indra river watershed through remote sensing using multi-temporal satellite data. Int J Geomatics Geosci 3:89
Gao J, Liu Y (2010) Determination of land degradation causes in Tongyu County, Northeast China via land cover change detection. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 12:9–16
Ghosh P et al (2017) Application of cellular automata and Markov-chain model in geospatial environmental modeling—a review. Remote Sensing Appl: Soc Environ 5:64–77
Gong W, Yuan L, Fan W, Stott P (2015) Analysis and simulation of land use spatial pattern in Harbin prefecture based on trajectories and cellular automata—Markov modelling. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 34:207–216
Guan D, Li H, Inohae T, Su W, Nagaie T, Hokao K (2011) Modeling urban land use change by the integration of cellular automaton and Markov model. Ecol Model 222:3761–3772
Halmy MWA, Gessler PE, Hicke JA, Salem BB (2015) Land use/land cover change detection and prediction in the north-western coastal desert of Egypt using Markov-CA. Appl Geogr 63:101–112
Haque MI, Basak R (2017) Land cover change detection using GIS and remote sensing techniques: a spatio-temporal study on Tanguar Haor, Sunamganj, Bangladesh. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 20:251–263
Hu H-B, Liu H-Y, Hao J-F, An J (2012) Analysis of land use change characteristics based on remote sensing and gis in the Jiuxiang River watershed. Int J Smart Sens Intelligent Systems 5
Hyandye C, Martz LW (2017) A Markovian and cellular automata land-use change predictive model of the Usangu Catchment. Int J Remote Sens 38:64–81
Jafarnezhad J, Salmanmahiny A, Sakieh Y (2015) Subjectivity versus objectivity: comparative study between brute force method and genetic algorithm for calibrating the SLEUTH urban growth model. J Urban Plan Dev 142:05015015
Kabba VTS, Li J (2011) Analysis of land use and land cover changes, and their ecological implications in Wuhan, China. J Geogr Geol 3:104
Keken Z, Panagiotidis D, Skaloš J (2015) The influence of damming on landscape structure change in the vicinity of flooded areas: case studies in Greece and the Czech Republic. Ecol Eng 74:448–457
Kennedy RE, Townsend PA, Gross JE, Cohen WB, Bolstad P, Wang Y, Adams P (2009) Remote sensing change detection tools for natural resource managers: Understanding concepts and tradeoffs in the design of landscape monitoring projects. Remote Sens Environ 113:1382–1396
Kumar S, Radhakrishnan N, Mathew S (2014) Land use change modelling using a Markov model and remote sensing. Geomatics Nat Hazards and Risk 5:145–156
Lambin EF et al (2001) The causes of land-use and land-cover change: moving beyond the myths. Glob Environ Chang 11:261–269
Luo G, Amuti T, Zhu L, Mambetov BT, Maisupova B, Zhang C (2015) Dynamics of landscape patterns in an inland river delta of Central Asia based on a cellular automata-Markov model. Reg Environ Chang 15:277–289
Maddah S, Karimi S, Rezai H, Khaledi J (2015) Detecting land use changes affected by human activities using remote sensing (case study: Karkheh River Basin). Curr World Environ 10:473–481
Mehta A, Sinha VK, Ayachit G (2012) Land-use/land-cover study using remote sensing and GIS in an arid environment. Bull Environ Sci Res 1:4–8
Misra A, Vethamony P (2015) Assessment of the land use/land cover (LU/LC) and mangrove changes along the Mandovi–Zuari estuarine complex of Goa, India. Arab J Geosci 8:267–279
Mubea K, Ngigi T, Mundia C (2011) Assessing application of Markov chain analysis in predicting land cover change: a case study of Nakuru municipality. J Agric Sci Technol 12
O’sullivan D, Torrens PM (2001) Cellular models of urban systems. In: Theory and practical issues on cellular automata. Springer, pp 108–116
Rahman MTU et al (2017) Temporal dynamics of land use/land cover change and its prediction using CA-ANN model for southwestern coastal Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 189:565
Rawat J, Kumar M (2015) Monitoring land use/cover change using remote sensing and GIS techniques: a case study of Hawalbagh block, district Almora, Uttarakhand, India. Egypt J Remote Sens Space Sci 18:77–84
Seif A, Mokarram M (2012) Change detection of Gil Playa in the northeast of Fars Province Iran. Am J Sci Res 86:122–130
Soares-Filho BS, Cerqueira GC, Pennachin CL (2002) DINAMICA—a stochastic cellular automata model designed to simulate the landscape dynamics in an Amazonian colonization frontier. Ecol Model 154:217–235
Sohl TL, Sohl LB (2012) Land-use change in the atlantic coastal pine barrens ecoregion. Geogr Rev 102:180–201
Stevens D, Dragićević S (2007) A GIS-based irregular cellular automata model of land-use change. Environ Plan B: Plan Design 34:708–724
Vázquez-Quintero G, Solís-Moreno R, Pompa-García M, Villarreal-Guerrero F, Pinedo-Alvarez C, Pinedo-Alvarez A (2016) Detection and projection of forest changes by using the Markov Chain Model and cellular automata. Sustainability 8:236
Verburg PH, Soepboer W, Veldkamp A, Limpiada R, Espaldon V, Mastura SS (2002) Modeling the spatial dynamics of regional land use: the CLUE-S model. Environ Manag 30:391–405
Vilà-Cabrera A, Martínez-Vilalta J, Galiano L, Retana J (2013) Patterns of forest decline and regeneration across Scots pine populations. Ecosystems 16:323–335
Wang Y, Zhang X (2001) A dynamic modeling approach to simulating socioeconomic effects on landscape changes. Ecol Model 140:141–162
Ye B, Bai Z (2007) Simulating land use/cover changes of Nenjiang County based on CA-Markov model. In: International Conference on Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture. Springer, pp 321–329
Zhang R, Tang C, Ma S, Yuan H, Gao L, Fan W (2011) Using Markov chains to analyze changes in wetland trends in arid Yinchuan Plain, China. Math Comput Model 54:924–930
Zheng HW, Shen GQ, Wang H, Hong J (2015) Simulating land use change in urban renewal areas: A case study in Hong Kong. Habitat Int 46:23–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karimi, H., Jafarnezhad, J., Khaledi, J. et al. Monitoring and prediction of land use/land cover changes using CA-Markov model: a case study of Ravansar County in Iran. Arab J Geosci 11, 592 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3940-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3940-5