Abstract
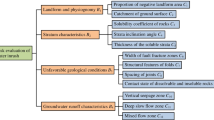
A feasible and accurate method named two-class fuzzy comprehensive evaluation is put forward to assess the risk of water inrush in karst tunnels. In view of regarding tunnel face as the evaluation object, 12 influencing factors of water inrush are selected as the evaluation index system consisting of 4 first-class and 12 second-class indices. Based on fuzzy mathematics theory and expert evaluation method, all the indices are quantitatively graded according to five risk grades. The weights of indices affecting water inrush are rationally distributed by using analytic hierarchy process. Membership functions and weights of indices are utilized to stepwise compute the membership degree of indices corresponding to risk grade, and the principle of maximum membership degree is carried out to discern the risk grade of water inrush. The tunnel faces in seven segments of Qiyueshan tunnel are chosen as the case studies. Evaluation results are derived from the proposed method, and they are generally consistent with the actual results through comparisons. This method provides a cogent way for evaluating the risk of water inrush in karst tunnels.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bukowski P (2011) Water hazard assessment in active shafts in Upper Silesian Coal Basin mines. Mine Water Environment 30(4):302–311
Dumpleton S, Robins NS, Walker JA, Merrin PD (2001) Mine water rebound in south Nottinghamshire: risk evaluation using 3-D visualization and predictive modeling. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 34(3):307–319
Ge YH (2010) Study on water inrush risk and early warning mechanism of karst tunnel. Phd thesis. Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong
Han XR (2004) Karst water bursting in tunnel and expert judging system. Carsologica Sinica 23(3):213–218
Hodlur GK, Prakash MR, Deshmukh SD, Singh VS (2002) Role of some salient geophysical, geochemical, and hydrogeological parameters in the exploration of fresh groundwater in a brackish terrain. Environ Geol 41(7):861–866
Jiang GY (2012) Study on the security risk assessment model of karst water burst in deep buried tunnel. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering 8(2):274–279
Li BN (2007) Fuzzy mathematics and its application. Hefei University of Technology Publishing House, Hefei
Li LP, Li SC, Chen J, Li JL, Xu ZH, Shi SS (2011) Construction license mechanism and its application based on karst water inrush risk evaluation. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 30(7):1345–1355
Li B, Guo J, Li HK, Ding JP, Qiu HT, Wang XQ (2012a) Comprehensive assessment on coal roof water bursting risk in karst area based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. China Coal 38(8):51–55
Li XP, Li YA, Zhou SP (2012b) Study and application of forecasting system for water inrush under high pressure in Xiamen submarine tunnel construction based on GIS. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering 10(1):999–1005
Li SC, Zhou ZQ, Li LP, Xu ZH, Zhang QQ, Shi SS (2013) Risk assessment of water inrush in karst tunnels based on attribute synthetic evaluation system. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 38:50–58
Mao BY, Xu M, Jiang LW (2010) Preliminary study on risk assessment of water and mud inrush in karst tunnel. Carsologica Sinica 29(2):183–189
McFeat-Smith I, Harman KW (2004) IMS risk evaluation system for financing and insuring tunnel projects. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 19(4–5):334
Meng ZP, Li GQ, Xie XT (2012) A geological assessment method of floor water inrush risk and its application. Eng Geol 143-144(4):51–60
Saaty TL (1994) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48(1):9–26
Shang YH (2010) The fuzzy synthesis evaluation of the water-inrush risk of Baixiangshan Iron Mine and the establishment of its spatial database system. Master’s Thesis. Qingdao University of Technology, Qingdao, Shandong
Shen XM, Liu PL, Wang JF (2010) Evaluation of water-inrush risks of karst tunnel with analytic hierarchy process. Journal of Railway Engineering Society 12:56–63
Sturk R, Olsson L, Johansson J (1996) Risk and decision analysis for large underground projects, as applied to the Stockholm Ring Road tunnels. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 11(2):157–164
Wang Y, Yang WF, Li M, Liu X (2012) Risk assessment of floor water inrush in coal mines based on secondary fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 52(6):50–55
Wei JC, Li ZJ, Shi LQ, Guan YZ, Yin HY (2010) Comprehensive evaluation of water-inrush risk from coal floors. Min Sci Technol 20(1):121–125
Wu Q, Xu H, Pang W (2008) GIS and ANN coupling model: an innovative approach to evaluate vulnerability of karst water inrush in coalmines of north China. Environ Geol 54(5):937–943
Wu QH, Peng ZB, Chen KP, Peng WX, Chen LQ (2010) Synthetic judgment on two-stage fuzzy of stability of mine gob area. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology) 41(2):661–667
Xu ZH, Li SC, Li LP, Chen J, Shi SS (2011a) Construction permit mechanism of karst tunnels based on dynamic assessment and management of risk. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 33(11):1714–1725
Xu ZH, Li SC, Li LP, Hou JG, Sui B, Shi SS (2011b) Risk assessment of water or mud inrush of karst tunnels based on analytic hierarchy process. Rock Soil Mech 32(6):1757–1766
Yang YN (2009) Research of karst tunnel water bursting hazard risk assessment system in the southwest mountains area. Phd thesis. Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, Sichuan
Yang LB, Gao YY (2006) The principle and application of fuzzy mathematics. South China University of Technology Press, Guangzhou
Yuan DX (1994) China karst study. Geology Publishing House, Beijing
Zhou ZQ, Li SC, Li LP, Shi SS, Song S, Wang K (2013) Attribute recognition model of fatalness assessment of water inrush in karst tunnels and its application. Rock Soil Mech 34(3):818–826
Zou CJ, Zhang RQ, Guang YH, Xu FX, Lin RH, Wang JJ (1994) Karst engineering geology of water conservancy and hydropower. China Water & Power Press, Beijing
Acknowledgments
The support from National Construction of High-quality University Project of Graduates provided by China Scholarship Council is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, H., Xu, G., Yasufuku, N. et al. Risk assessment of water inrush in karst tunnels based on two-class fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method. Arab J Geosci 10, 179 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2957-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2957-5