Abstract
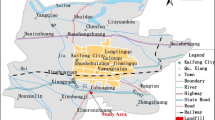
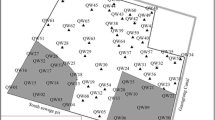
To study the organic pollution situation in groundwater in plain areas in Xinjiang, Shihezi region (SHZ), plain area of Yanqi Basin (YQ) and Ruoqiang-Qiemo area (RQ) were selected as the typical areas. 83 groundwater samples were collected, tested, and analyzed for 39 organic indexes for the first time. Results showed that the local groundwater in SHZ, YQ, and RQ had been slightly affected by organic pollution with the detection rates of 8.7, 33.3, and 33.3 %, respectively. Seven organic pollutants were detected, including chloroform (with the highest detection rate of 21.7 %), 1,2-dichloroethane, 1,2-dichlorobenzene, toluene, benzo(a)pyrene, α-BHC, and γ-BHC. The contents of all the detected organic pollutants were low, which were under the limits of the “Standards for Drinking Water Quality (GB5749-2006)”. Vertical distribution of detection rates was that in SHZ, shallow confined groundwater (12.5 %) > deep confined groundwater (10.0 %) > unconfined groundwater (0.0 %); in YQ, unconfined groundwater (66.7 %) > deep confined groundwater (29.2 %) > shallow confined groundwater (25.0 %); in RQ, shallow confined groundwater (66.7 %) > unconfined groundwater (33.3 %) > deep confined groundwater (16.7 %). The sources and properties of organic pollutants were the main factors that affected groundwater organic pollution in the study areas. The infiltration recharge of surface water mainly affected groundwater organic pollution in SHZ and YQ. Besides, the vadose zone had a certain restriction on the occurrence and migration of groundwater organic pollution components in RQ. Direct discharge of sewage came from human life and production without treatment, and leakage due to crude anti-seepage facilities had led to groundwater organic pollution. The organic wastewater produced in livestock and poultry breeding, chemical fertilizers, and insecticides in agricultural activities were also the main sources of groundwater organic pollution.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abudureyimu A, Han Q (2014) Clean energy development of silk road economic belt in Xinjiang. Appl Mech Mater 521:846–849
Avtar R, Kumar P, Singh CK, Sahu N, Verma RL, Thakur JK, Mukherjee S (2013) Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater quality of Bundelkhand, India using statistical approach. Expos Health 5(3):105–115
Borden RC, Carlos AG, Mark TB (1995) Geochemical indicators of intrinsic bioremediation. Groundwater 33(2):180–189
Concha-Grana E, Turnes-Carou MI, Muniategui-Lorenzo S, López-Mahía P, Prada-Rodríguez D, Fernández-Fernández E (2006) Evaluation of HCH isomers and metabolites in soils, leachates, river water and sediments of a highly contaminated area. Chemosphere 64(4):588–595
Cui XH, Li BH, Chen HH (2008) Contamination characteristics and pollutant sources analysis on PAHs in shallow groundwater in suburb of Taihu Plain. Environ Sci (Chin) 29(7):1806–1810
Dong HG, Wang D, Wang YT, Tong J, Liu T (2013) Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of mulch residues in cotton field in Shihezi, Xinjiang. J Arid Land Resour Environ (Chin) 27(9):182–186
Duan L, Wang WK, Cao YQ, Wang LJ, Liu B (2007) Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanics of groundwater in the middle of Northern Slope of Tianshan Mountains. J Arid Land Resour Environ (Chin) 21(9):29–34
Elfvendahl S, Mihale M, Kishimba MA, Kylin H (2004) Pesticide pollution remains severe after cleanup of a stockpile of obsolete pesticides at Vikuge, Tanzania. Ambio 33(8):503–508
Golfinopoulos SK (2000) The occurrence of trihalomethanes in the drinking water in Greece. Chemosphere 41(11):1761–1767
Grøndahl-Rosado RC, Tryland I, Myrmel M, Aanes KJ, Robertson LJ (2014) Detection of microbial pathogens and indicators in sewage effluent and river water during the temporary interruption of a wastewater treatment plant. Expo Health 6(3):155–159
Guo GX (2012) Comprehensive assessment of groundwater quality of different aquifers in Beijing Plain. Geol China (Chin) 39(2):518–523
Huang DY, Zhou SG, Hong W, Feng WF, Tao L (2013) Pollution characteristics of volatile organic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalate esters emitted from plastic wastes recycling granulation plants in Xingtan Town, South China. Atmos Environ 71(3):327–334
Kazumi J, Caldwell ME, Suflita JM, Lovley DR, Young LY (1997) Anaerobic degradation of Benzene in diverse anoxic environments. Environ Sci Technol 31(3):813–818
Lee SA, Dai Q, Zheng W, Gao YT, Blair A, Tessari JD, Ji BT, Shu XO (2007) Association of serum concentration of organochlorine pesticides with dietary intake and other life style factors among urban Chinese women. Environ Int 33(2):157–163
Li HM, Chen HH, Zheng XL, Zhang DZ (2006) A discussion of the source of B[a]p in groundwater. Hydrogeol Eng Geol (Chin) 33(6):21–24
Li YS, Fei YH, Wang Z (2011) Occurrence features and leaching of chloroform in shallow groundwater. Environl Pollut Control (Chin) 33(7):36–42
Li PY, Wu JH, Qian H (2012) Groundwater quality assessment based on rough sets attribute reduction and TOPSIS method in a semi-arid area, China. Environ Monit Assess 184(8):4841–4854
Li PY, Wu JH, Qian H (2013) Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical evolution mechanisms in Pengyang County, China. Environ Earth Sci 69(7):2211–2225
Li PY, Wu JH, Qian H, Lyu XS, Liu HW (2014a) Origin and assessment of groundwater pollution and associated health risk: a case study in an industrial park, northwest China. Environ Geochem Health 36(4):1–20
Li Q, Zhou JL, Zhou YZ, Bai CY, Tao HF, Jia RL, Ji YY, Yang GY (2014b) Variation of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics in the plain area of the Tarim Basin, Xinjiang Region, China. Environ Earth Sci 72(11):4249–4263
Li PY, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu JH (2015a) Building a new and sustainable “Silk Road economic belt”. Environ Earth Sci 74(10):7267–7270
Li Q, Zhou JL, Gao YX, Cheng F, Li FX, Meng Q (2015b) Groundwater hydro-geochemistry in plain of Manasi River Basin, Xinjiang. Geoscience (Chinese) 29(2):238–244
Libert B, Orolbaev E, Steklov Y (2008) Water and energy crisis in Central Asia. China Eurasia Forum Q 6(3):9–20
Liu YL, Miao DR, Liu F, Chen HH (2008) Adsorption and desorption of 1,2-dichloroethane and 1,2-dichloropropane by soils in an unsaturated zone. Earth Sci Front (Chin) 15(6):185–191
Lu YJ (2007) Assessment of Groundwater Resources in the Ruoqiang County. Master dissertation, Xinjiang University (Chinese)
Lu XC, Jiang JC (2009) Research progress in treatment of VOCs and application of activated Carbon. Biomass Chem Eng (Chin) 43(1):45–51
Luo L (2008) Research on groundwater pollution and its prevention-control policy in China. J China Uni Geosci (Soc Sci Edi) 8(2):72–75
Seth R, Mohan M, Dobhal R, Gupta VK, Singh P, Singh R, Gupta S (2014) Application of chemometric techniques in the assessment of groundwater quality of Udham Singh Nagar, Uttarakhand, India. Expo Health 6(4):199–216
Squillace PJ, Moran MJ, Lapham WW, Clawges RM, Zogorski JS (1999) Volatile organic compounds in untreated ambient groundwater of the United States, 1985–1995. Environ Sci Technol 33(23):4176–4187
Wang SX (2013) Groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in the Yanqi Basin of Xinjiang Province, Northwest China. Environ Monit Assess 185(9):7469–7484
Wang C, Feng YJ, Zhao SS, Li BL (2012) A dynamic contaminant fate model of organic compound: a case study of Nitrobenzene pollution in Songhua River, China. Chemosphere 88(1):69–76
Wei LF, Yang YY, Li QX, Wang J (2015) Composition, distribution, and risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in drinking water sources in South China. Expo Health 7(1):89–97
Wen DG, Lin LJ, Sun JC, Zhang ZJ, Jiang YH, Ye NJ, Fei YH, Qian Y, Gong JS, Zhou X, Zhang YX (2012) Groundwater quality and contamination assessment in the main plains of Eastern China. Earth Sci J China Univ Geosci (Chin) 37(2):220–228
Wu B (2007) Study on groundwater system evolvement law and water environment effect of Shihezi City. Doctoral dissertation, Xinjiang Agricultural University (Chinese)
Wu JH, Sun ZC (2015) Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, mid-west China. Expo Health 7:1–19
Wu JH, Li PY, Qian H (2015) Hydrochemical characterization of drinking groundwater with special reference to fluoride in an arid area of China and the control of aquifer leakage on its concentrations. Environ Earth Sci 73(12):8575–8588
Xu XQ, Yang HH, Li QL, Yang BJ, Wang XR, Lee FS (2007) Residues of organochlorine pesticides in near shore waters of LaiZhou Bay and JiaoZhou Bay, Shandong Peninsula, China. Chemosphere 68(1):126–139
Yao LQ, Huo ZL, Feng SY, Mao XM, Kang SZ, Chen J, Xu JJ, Steenhuis TS (2014) Evaluation of spatial interpolation methods for groundwater level in an arid inland oasis, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 71(4):1911–1924
Yu GM, Liu HY, Zhang TL, Su JW, Sheng MT, Li W (2007) Assessment of the organic pollution and its risk for the surficial groundwater in Hangzhou City. Resour Surv Environ (Chin) 28(3):198–204
Zeng YY, Zhou JL, Li Q, Zhao JT, Meng Q (2015) Assessment of groundwater quality and pollution in Ruoqiang and Qiemo Region of Xinjiang. J Xinjiang Agric Univ (Chin) 38(1):72–78
Zhang HG, Chen DY, Luo DG, Zhou SQ (2009) Research on character of organic matters and heavy metals in the Landfill Leachate. J Shaanxi Univ Sci Technol (Chin) 27(1):86–89
Zhao JT, Zhou JL, Li Q, Du ML, Gao YX, Cui HH, Feng X (2015) Preliminary analysis on the organic contamination of groundwater in the plain area of Yanqi Basin, Xinjiang. Environ Chem (Chin) 34(8):1507–1514
Zhou JL, Li GM, Liu F, Wang YP, Guo XJ (2010) DRAV model and its application in assessing groundwater vulnerability in the arid areas: a case study of pore phreatic water in Tarim Basin, Xinjiang, Northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 60(5):1055–1063
Zhou JL, Li Q, Guo YC, Guo XJ, Li XW, Zhao YJ, Jia RL (2012) VLDA model and its application in assessing phreatic groundwater vulnerability: a case study of phreatic groundwater in the plain area of Yanji County, Xinjiang, China. Environ Earth Sci 67(6):1789–1799
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the supports provided to this study under the following grants: NSFC-Xinjiang project “Transport of typical organic pollutants in the groundwater flow system of arid region and its risk assessment” (U1503282); NSFC-Xinjiang project “Study on groundwater flow system and groundwater recharge and discharge in arid inland basins” (U1403282); China Geological Survey Bureau project“ Groundwater pollution survey of main cities in northwest China” (1212011220982); and key discipline project of hydrology and water resources of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (xjswszyzdxk20101202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Y., Zhou, J., Zhou, Y. et al. Assessment and Causes of Groundwater Organic Pollution in Typical Plain Areas in Xinjiang, China. Expo Health 8, 401–417 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0211-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0211-0