Abstract
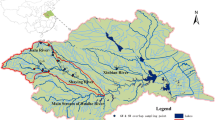
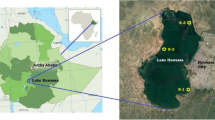
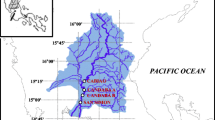
Samples were collected from nine drinking water sources in south China and were analyzed for concentrations of 15 organochlorine pesticides (OCPs). The average concentrations of total OCPs were in the range of 12.9–43.0 ng L\(^{-1}\) with an overall average of 25.7 ng L\(^{-1}\). The concentrations of HCHs (\(\upalpha \)-HCH, \(\upbeta \)-HCH, \(\upgamma \)-HCH, \(\updelta \)-HCH) and DDTs (p,\(p^\prime \)-DDD, p,\(p^\prime \)-DDT, p,\(p^\prime \)-DDE) were in the range of 5.54–13.08 and 0.17–4.47 ng L\(^{-1}\), respectively. HCHs, endrin-aldehyde, methoxychlor and endrin were the most dominant in all samples. The input of HCHs was a mixture of technical HCH and lindane, while the DDT may be mainly derived from DDT-treated aged and weathered agricultural soils. Health risk assessment of DDTs and HCHs suggested that water quality from nine drinking water sources in south China was safe for human drinking.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capriotti AL, Cavaliere C, Giansanti P, Gubbiotti R, Samperi R, Lagana A (2010) Recent developments in matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction. J Chromatogr A 1217:2521–2532
Chen JW, Liu C, Yang ZF, Wang JY (2008) Residues and characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in surface water in the suburb of Beijing. Front Earth Sci 15:242–247
Colborn T, Dumanoski D, Myers JP (1996) Our stolen future: are we threatening our fertility, intelligence, and survival? A scientific detective story. Dutton, New York
Hamidin N, Yu QJ, Connell DW (2008) Human health risk assessment of chlorinated disinfection by-products in drinking water using a probabilistic approach. Water Res 42:3263–3274
He W, Qin N, He QS, Wang Y, Kong XZ, Xu FL (2012) Characterization, ecological and health risks of DDTs and HCHs in water from a large shallow Chinese lake. Ecol Inform 12:77–84
Hites RK, Day HR (1992) Unusual persistence of DDT in some western USA soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 48:259–264
Hua XM, Shan ZJ (1996) The production and application of pesticides and factor analysis of their pollution in environment in China. Adv Environ Res 4:33–45
Lee SA et al (2007) Association of serum concentration of organochlorine pesticides with dietary intake and other lifestyle factors among urban Chinese women. Environ Int 33:157–163
Peček G, Pavlović DM (2012) Development and validation of a SPE-GC–MS method for the determination of pesticides in surface water. Int J Environ Anal Chem 93:1–18
Yang QS, Mai BX, Fu JM, Sheng GY, Wang JX (2004a) Spatial and temporal distribution of organochlorine pesticites (OCPs) in surface water from the Pearl River Artery Estuary. J Environ Sci (China) 25:150–156
Rissato SR, Galhiane MS, Ximenes VF et al (2006) Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in soil and water samples in the northeastern part of Sao Paulo state, Brazil. Chemosphere 65:1949–1958
Said TO, El Moselhy KM, Rashad AA, Shreadah MA (2008) Organochlorine contaminants in water, sediment and fish of Lake Burullus, Egyptian Mediterranean sea. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81:136–146
Schmitt CJ, Zajicek JL, Peterman PH (1990) National contaminant biomonitoring program: residues of organochlorine chemicals in U.S. freshwater fish, 1976–1984. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:748–781
Sheryl AL, Miriam LD, Paul AH et al (2001) Factors affecting the occurrence and enantiomeric degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers in northern and temperate aquatic systems. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2690–2698
Shinsuke T, Hisato I, Tatsukawa R (1994) Global contamination by persistent organochlorines and their ecotoxicological impact on marine mammals. Sci Total Environ 154:163–177
Singh KP, Malik A, Sinha S (2006) Persistent organochlorine pesticide residues in soil and surface water of northern Indo-Gangetic Alluvial Plains. Environ Monit Assess 125:147–155
Spyros KG, Anastasia DN, Maria NK et al (2003) Organochlorine pesticides in the surface waters of Northern Greece. Chemosphere 50:507–516
Strandberg B, Bavel B, Bergqvist PA et al (1998) Occurrence, sedimentation, and spatial variations of organochlorine contaminants in settling particulate matter and sediments in the northern part of the Baltic Sea. Environ Sci Technol 32:1754–1759
Sun JH, Chai Y, Zhang G, Li J, Wang GL (2009) Content and distribution of organic chlorine pesticide in the middle and lower yellow river. Yellow River (China) 31:43–45
Sun YZ, Wang XT, Li XH, Xu XB (2005) Distribution of persistent organochlorine pesticides in tissue/organ of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) from Guanting Reservoir, China. Environ Sci (China) 17:722–726
Tang Z, Yang Z, Shen Z, Niu J, Cai Y (2008) Residues of organochlorine pesticides in water and suspended particulate matter from the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. Environ Monit Assess 137:427–439
Turgut C (2003) The contamination with organochlorine pesticides and heavy metals in surface water in Küçük Menderes River in Turkey, 2000–2002. Environ Int 29:29–32
USEPA (1989) United States Environment Protection Agency. Risk assessment guidance for Superfund, vol 1, Human health evaluation manual, part A. EPA/540/1-89/ 002. Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, Washington, D.C. http://www.epa.gov/oswer/riskassessment/ragsa/index.htm. Accessed December 1989
USEPA (2012) United States Environment Protection Agency, Integrated risk information system (IRIS). http://www.epa.gov/oswer/riskassessment/ragsa/index.htm. Accessed June 2012
Walker K, Vallero DA, Lewis RG (1999) Factors influencing the distribution of lindane and other hexachlorocyclohexanes in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 33:4373–4378
Wan YW, Kang TF, Zhou ZL, Li PN, Zhang Y (2009) Health risk assessment of volatile organic compounds in water of beijing Guanting Reservoir. Res of Environ Sci (China) 22:150–154
Wang ZS, Duan XL, Liu P, Nie J, Huang N, Zhang JL (2009) Human exposure factors of Chinese people in environmental health risk assessment. Res of Environ Sci (China) 22:1164–1170
Xia F, Hu XX, Han ZH, Wang WH (2006) Distributi on characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in surface water from the Huangpu River. Res of Environ Sci (China) 19:11–15
Xu XQ, Yang HH, Li QL, Yang BJ, Wang XR, Lee FS (2007) Residues of organochlorine pesticides in near shore waters of LaiZhou Bay and JiaoZhou Bay, Shandong Peninsula, China. Chemosphere 68:126–139
Yang QS, Mai BX, Luo XJ, Fu JM, Sheng GY, Lin Z (2004b) Vertical distribution of organochlorine pesticites (OCPs) in Macau coastal waters. J Environ Sci (China) 24:428–434
Yang YY, Yun XY, Liu MX, Jiang Y, Li QX, Wang J (2013) Concentrations, distributions, sources, and risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in surface water of the East Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21(4):3041–3050
Acknowledgments
This project was supported in part by Open Funding Project of the Key Laboratory of Aquatic Botany and Watershed Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Open Funding Project of The State Key Laboratory of Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering Science (2013B115), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China (No. 2012FFB07301), and the Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Y329671K01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, L., Yang, Y., Li, Q.X. et al. Composition, Distribution, and Risk Assessment of Organochlorine Pesticides in Drinking Water Sources in South China. Water Qual Expo Health 7, 89–97 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-014-0147-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-014-0147-1