Abstract
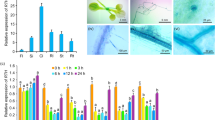
The halotolerance protein HAL3, also known as SIS2, is a yeast protein that regulates the cell cycle and tolerance to salt stress through inhibition of the Ppz1 type 1 protein phosphatase. Although the roles of HAL3 have been demonstrated during the growth, development, and stress adaptation of Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana tabacum, the function of HAL3 in other plant species, including soybean (Glycine max), has not been elucidated. In this study, GmHAL3a and GmHAL3b were isolated from Glycine max, and their roles were analyzed. GmHAL3a and GmHAL3b transcripts were detected in the roots, stems, leaves and seeds, with higher levels in the roots, and were induced by sodium chloride (NaCl), lithium chloride (LiCl), sorbitol, cold and ABA treatment. Overexpression of GmHAL3a or GmHAL3b in Arabidopsis accelerated the onset of flowering and resulted in more vigorous seed germination and increased tolerance to NaCl, LiCl, and sorbitol stress in seedlings, compared with wild type (WT) and empty vector control (VC) plants. Transgenic Arabidopsis plants accumulated proline and eliminated superoxide radical (O2 −) in response to the stress. In addition, transcription levels of the stress-related genes RD22 and P5CS1 were substantially higher in transgenic Arabidopsis than in WT and VC plants. Taken together, the data indicate that GmHAL functions as a positive regulator of the response to salt, lithium cations and sorbitol stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrie JA, Gonzalez A, Strauss E, Arino J (2012) Functional mapping of the disparate activities of the yeast moonlighting protein Hal3. Biochem J 442:357–368
Albert A, Martinez-Ripoll M, Espinosa-Ruiz A, Yenush L, Culianez-Macia FA, Serrano R (2000) The X-ray structure of the FMNbinding protein AtHal3 provides the structural basis for the activity of a regulatory subunit involved in signal transduction. Structure 8:961–969
Bates L, Waldren R, Teare I (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–20
Chen M, Xu Z, Xia L, Li L, Cheng X, Dong J, Wang Q, Ma Y (2009) Cold-induced modulation and functional analyses of the DREbinding transcription factor gene, GmDREB3, in soybean (Glycine max L.). J Exp Bot 60:121–135
Chen X, Chen Z, Zhao H, Zhao Y, Cheng B, Xiang Y (2014) Genome-wide analysis of soybean HD-Zip gene family and expression profiling under salinity and drought treatments. PloS one 9:e87156
Clotet J, Gari E, Aldea M, Arino J (1999) The yeast ser/thr phosphatases sit4 and ppz1 play opposite roles in regulation of the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol 19:2408–2415
De Nadal E, Calero F, Ramos J, Arino J (1999) Biochemical and genetic analyses of the role of yeast casein kinase 2 in salt tolerance. J Bacteriol 181:6456–6462
De Nadal E, Clotet J, Posas F, Serrano R, Gomez N, Arino J (1998) The yeast halotolerance determinant Hal3p is an inhibitory subunit of the Ppz1p Ser/Thr protein phosphatase. P Natl Acad Sci USA 95:7357–7362
Di-Como CJ, Bose R, and Arndt KT (1995) Overexpression of Sis2, Which Contains an Extremely Acidic Region, Increases the Expression of Swi4, Cln1 and Cln2 in Sit4 Mutants. Genetics 139:95–107
Elstner EF, Heupel A (1976) Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammoniumchloride: a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Anal Biochem 70:616–620
Espinosa-Ruiz A, Belles JM, Serrano R, Culianez-MacIa FA (1999) Arabidopsis thaliana AtHAL3: a flavoprotein related to salt and osmotic tolerance and plant growth. Plant J 20:529–539
Fernandez-Sarabia MJ, Sutton A, Zhong T, Arndt KT (1992) SIT4 protein phosphatase is required for the normal accumulation of SWI4, CLN1, CLN2, and HCS26 RNAs during late G1. Gene Dev 6:2417–2428.
Ferrando A, Kron SJ, Rios G, Fink GR, Serrano R (1995) Regulation of cation transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by the salt tolerance gene HAL3. Mol Cell Biol 15:5470–5481
Hernandez Torres J, Chatellard P, Stutz E (1995) Isolation and characterization of gmsti, a stress-inducible gene from soybean (Glycine max) coding for a protein belonging to the TPR (tetratricopeptide repeats) family. Plant Mol Biol 27:1221–1226
Hoque MA, Banu MN, Nakamura Y, Shimoishi Y, Murata Y (2008) Proline and glycinebetaine enhance antioxidant defense and methylglyoxal detoxification systems and reduce NaCl-induced damage in cultured tobacco cells. J Plant Physiol 165:813–824
Khedr AH, Abbas MA, Wahid AA, Quick WP, Abogadallah GM (2003) Proline induces the expression of salt-stress-responsive proteins and may improve the adaptation of Pancratium maritimum L. to salt-stress. J Exp Bot 54:2553–2562
Kidokoro S, Watanabe K, Ohori T, Moriwaki T, Maruyama K, Mizoi J, Myint Phyu Sin Htwe N, Fujita Y, Sekita S, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2015) Soybean DREB1/CBF-type transcription factors function in heat and drought as well as cold stress-responsive gene expression. Plant J 81:505–518
Kumar AA, Mishra P, Kumari K, Panigrahi KC (2012) Environmental stress influencing plant development and flowering. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 4:1315–1324
Lee KS, Hines LK, Levin DE (1993) A pair of functionally redundant yeast genes (PPZ1 and PPZ2) encoding type 1-related protein phosphatases function within the PKC1-mediated pathway. Mol Cell Biol 13:5843–5853
Liu JP, and Zhu JK (1997) Proline accumulation and salt-stress-induced gene expression in a salt-hypersensitive mutant of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 114:591–596
Posas F, Camps M, Arino J (1995) The PPZ protein phosphatases are important determinants of salt tolerance in yeast cells. J Biol Chem 270:13036–13041
Rentsch D, Hirner B, Schmelzer E, Frommer WB (1996) Salt stressinduced proline transporters and salt stress-repressed broad specificity amino acid permeases identified by suppression of a yeast amino acid permease-targeting mutant. Plant cell 8:1437–1446
Ruiz A, Gonzalez A, Munoz I, Serrano R, Abrie JA, Strauss E, Arino J (2009) Moonlighting proteins Hal3 and Vhs3 form a heteromeric PPCDC with Ykl088w in yeast CoA biosynthesis. Nat Chem Biol 5:920–928
Savouré A, Hua XJ, Bertauche N, Van Montagu M, Verbruggen N (1997) Abscisic acid-independent and abscisic acid-dependent regulation of proline biosynthesis following cold and osmotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Genet Genomics 254:104–109.
Silveira JA, Viegas Rde A, da Rocha IM, Moreira AC, Moreira Rde A, Oliveira JT (2003) Proline accumulation and glutamine synthetase activity are increased by salt-induced proteolysis in cashew leaves. J Plant Physiol 160:115–123
Su L, Shan JX, Gao JP, Lin HX (2016) OsHAL3, a Blue Light responsive Protein, Interacts with the Floral Regulator Hd1 to Activate Flowering in Rice. Mol Plant 9:233–244
Sun SY, Chao DY, Li XM, Shi M, Gao JP, Zhu MZ, Yang HQ, Luan S, Lin HX (2009) OsHAL3 mediates a new pathway in the lightregulated growth of rice. Nat Cell Biol 11:845–851
Tran LS, Quach TN, Guttikonda SK, Aldrich DL, Kumar R, Neelakandan A, Valliyodan B, Nguyen HT (2009) Molecular characterization of stress-inducible GmNAC genes in soybean. Mol Genet Genomics 281:647–664
Wang H, Zhou L, Fu Y, Cheung MY, Wong FL, Phang TH, Sun Z, Lam HM (2012) Expression of an apoplast-localized BURPdomain protein from soybean (GmRD22) enhances tolerance towards abiotic stress. Plant Cell Environ 35:1932–1947
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14
Wu T, Pi EX, Tsai SN, Lam HM, Sun SM, Kwan YW, Ngai SM (2011) GmPHD5 acts as an important regulator for crosstalk between histone H3K4 di-methylation and H3K14 acetylation in response to salinity stress in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 11:178
Xu J, Xue C, Xue D, Zhao J, Gai J, Guo N, Xing H (2013) Overexpression of GmHsp90s, a heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) gene family cloning from soybean, decrease damage of abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. PloS one 8:e69810
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1993) The plant hormone abscisic acid mediates the drought-induced expression but not the seed-specific expression of rd22, a gene responsive to dehydration stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Genet Genomics 238:17–25
Yenush L, Merchan S, Holmes J, Serrano R (2005) pH-Responsive, posttranslational regulation of the Trk1 potassium transporter by the type 1-related Ppz1 phosphatase. Mol Cell Biol 25:8683–8692
Yenush L, Mulet JM, Arino J, Serrano R (2002) The Ppz protein phosphatases are key regulators of K+ and pH homeostasis: implications for salt tolerance, cell wall integrity and cell cycle progression. EMBO J 21:920–929
Yonamine I, Yoshida K, Kido K, Nakagawa A, Nakayama H, Shinmyo A (2004) Overexpression of NtHAL3 genes confers increased levels of proline biosynthesis and the enhancement of salt tolerance in cultured tobacco cells. J Exp Bot 55:387–395
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, N., Wang, Mx., Xue, Cc. et al. Over-expression of GmHAL3 modulates salt stresses tolerance in transgenic arabidopsis. J. Plant Biol. 59, 444–455 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-016-0005-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-016-0005-8