Abstract
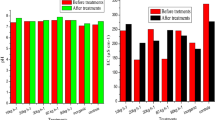
A field experiment was conducted for three consecutive seasons on sugarcane plant–ratoon system during years 2008–2014 at crop research farm, Dr. Rajendra Prasad Central Agricultural University, Pusa, Bihar to evaluate the integrated effect of bio-compost and nitrogen on productivity and soil properties in calcareous soil. The distribution of different fractions of soil nitrogen viz. exchangeable NH4 +–N, hydrolysable NH4 +–N, hexoseamine-N, amino acid-N, unidentified-N and status of total-N were determined. The significant increase in number of millable cane (NMC) and cane yield was recorded in the treatments receiving bio-compost in combination with fertilizer-N over control both in plant and ratoon crops. The highest number of NMC (90.7 × 103/ha), cane yield (74.14 t/ha) and sugar yield (7.72 t/ha) of plant was recorded in treatments receiving 50% N through bio-compost +50% N through inorganic fertilizer. The residual effect of treatment receiving 50% N through bio-compost and 50% N through inorganic fertilizer was also pronounced on NMC (83.90 × 103/ha), yield (69.70 t/ha) and sugar yield (7.42 t/ha). Further, application of 100, 125 and 150% N through bio-compost resulted in gradual decrease in yield of plant, but on the contrary, it increased by 6–7% in ratoon crop as compared to plant cane. The uptake of nutrients varied significantly. The highest sugar yield (plant and ratoon) was recorded in treatment receiving 50% N through bio-compost +50% N through inorganic fertilizer. Addition of bio-compost either alone or in combination with inorganic fertilizer-N significantly improved organic carbon and availability of nutrients (N, P, K and S) with reduction in bulk density of post-harvest soil over control. The highest organic carbon (6.2 g/kg) and N (281.6 kg/ha), P2O5 (26.3 kg/ha), K2O (129.5 kg/ha) and S (33.6 kg/ha) was recorded in treatment receiving 150% N through bio-compost. The bulk density varied from 1.33 to 1.42 g/cm3. The EC increased while pH decreased with increasing levels of bio-compost. The significant improvement in microbial population was also recorded in bio-compost treated plots. After third crop cycle of sugarcane cropping system, application of bio-compost either alone or in combination with fertilizer significantly increased all the forms of N-fraction over control. Among the various N-fractions, non-hydrolysable-N was the dominant N-fraction.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhalerao, V.P., M.B. Jadhav, and P.G. Bhoi. 2006. Effect of spent wash, press mud and compost on soil properties, yield and quality of seasonal sugarcane. Indian Sugar 6(9): 57–65.
Black, C.A. 1965. Methods of soil analysis. Physical Properties, vol. 1, 1–768. Madison, WI: American Society of Agronomy.
Bremner, J.M. 1965a. Total nitrogen. In Methods of soil analysis, vol. 2, ed. C.A. Black, 1149–1178. Madison, WI: Amertican Society of Agronomy.
Bremner, J.M. 1965b. Organic forms of nitrogen. In Methods of soil analysis, vol. 2, ed. C.A. Black, 1238–1255. Madison, WI: Amertican Society of Agronomy.
Heluf, G. 2002. Soil and water management research program summary report of 2000/2001. In Research Activity, 95. Dire Dawa: Alemaya Research Center, Alemaya University.
Jackson, M.L. 1973. Soil chemical analysis, 498. New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd.
Jadhav, M.B., V.A. Joshi, P.B. Jagtap, and S.B. Jadhav. 1992. Effect of spent wash press mud cake compost on soil physico-chemical, biological properties, yield and quality of adsali sugarcane. Proceedings Annual Covention Deccan Sugar Technologists Association 2: 119–134.
Jha, C.K., S.K. Sinha, M. Alam, and S.S. Pandey. 2015. Effect of bio-compost and zinc application on sugarcane (Saccharum species hybrid complex) productivity, quality and soil health. Indian Journal of Agronomy 60(30): 450–456.
Kamat, V.N., S.T. Mahankar, R.B. Puranik, W.S. Kohadkar, and R.P. Joshi. 1982. Effect of long term application of FYM and NPK on nitrogen fractions in vertisol. Journal of Indian Society of Soil Science 30: 381–383.
Kumar, Vipin. 2003. Integrated effect of chemical fertilizers and green manure on forms of nitrogen and their availability under rice-wheat cropping system in calciorthents. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science 51: 561–564.
Lal, M., and A.K. Singh. 2008. The influence of depth and method of cane planting on stool tipping and yield on a red ferrosol at Bunddaberg. In: Proceedings of the 2008 Conference of the Australlian Society of Sugar Cane Technologists held at Townsville, Queensland, Australlia, 29 April–02 May 2008, pp. 241–50.
Li, Z.G., Y.M. Luo, and Y. Teng. 2008. Research methods of soil and environmental microbe. Beijing: Science Press.
Nagaraju, M.S., C. Shankuriah, and V. Ravindra. 2000. Effect of integrated use of fertilizer with sulphitation pressmud and Azotobacter on growth and yield of sugarcane. Co-operative Sugar 3(5): 391–395.
Olsen, S.R., C.V. Coles., F.S. Watanble., and L.N. Dean. 1954. Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate, United States Department of Agriculture Circular 939.
Pandey, D.K., S. Kumar, P.K. Singh, and J. Singh. 2012. Interpreting phenotypic stability in sugarcane using different parametric models. Indian Journal of Sugarcane Technology 27(1): 48–53.
Panse, V.G., and P.V. Sukhatme. 1967. Statistical methods for agricultural workers. New Delhi: Indian Council Agricultural Research.
Patel, K.P., and J.M. Jain. 1994. Effect of some organic chemicals on soil organic nitrogen fractions and their availability in a rice- wheat sequence. Journal of Indian Society of Soil Science 42: 50–54.
Prasad, B., and M.K. Sinha. 1984. Structural characteristics of humic and fulvic acids isolated from soil and poultry litter. Journal of Indian Society of Soil Science 32: 165–167.
Prasad, B., and J. Rokima. 1991. Integrated nutrient management on nitrogen fractions and their availability in calcareous soil. Journal of Indian Society of Soil Science 39: 693–698.
Prasad, R.K. 2005. Studies on microbial activities and micro nutrient availability in long term experiment on crop residue and Zn application under Rice-Wheat System. M.Sc. Thesis RAU, Pusa, Samastipur, Bihar.
Santhy, P., S. Jayasree Shankar, P. Muthuvel, and D. Selvi. 1998. Long- term fertilizer experiments status of N, P and K fractions in soil. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science 46: 395–398.
Sharma, B.L., P.K. Singh, S. Sharma, and S.D. Singh. 1999. Sulphitation pressmud cake in sugarcane. Integrated approach with inorganic nitrogen. Indian Journal of Agricultural Chemistry 32(1, 2): 1–5.
Sharma, R.P., and T.S. Verma. 2001. Dynamics of nitrogen fractions with long term addition of Lantana Camara biomass in rice wheat cropping sequences. Journal of Indian Society of Soil Science 49: 407–412.
Sharma, D.K., R.S., Kaushik, S. Tripathi., and H.C. Joshi. 2006. Distillary effluent based pressmud compost for nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition in rice wheat cropping system. In 2nd International Rice Conference held during 9–13 October, 2006 at New Delhi, 341.
Sihag, D., J.P. Singh, D.S. Mehta, and K.K. Bhardwaj. 2005. Effect of integrated use of inorganic fertilizers and organic materials on the distribution of different forms of nitrogen and phosphorous in soil. Journal of Indian Society of Soil Science 53: 80–84.
Singh, K.P., A. Suman, P.N. Singh, and M. Lal. 2007. Yield and nutrient balance of a sugarcane plant–ratoon system with conventional and organic nutrient management in sub-tropical India. Nutrient cycling in Agro ecosystems. 79: 209–219.
Sinha, S.K., C.K. Jha, V. Kumar, G. Kumara, and M. Alam. 2014. Integrated effect of bio-methanated distillery effluent and bio-compost on soil properties, juice quality and yield of sugarcane in Entisol. Sugar Tech 16(1): 75–79.
Solomon, S. 2011. Sugarcane by- products based industries in India. Sugar Tech. 13(4): 408–416.
Spencer, E.F. and G.P. Meade. 1964. Cane sugar hand book, 9th Ed. Library of Congress Catalog No. 63-18029, USA.
Subbiah, B.V., and G.L. Asija. 1956. A rapid method procedure for the determination of available nitrogen in soil. Current Science 25: 259–260.
Umesh, U.N., R.K. Prasad, K.D.N. Singh, and A.K. Singh. 2014. Effect of integrated use of inorganic and organic materials on the distribution of different forms of nitrogen on soil and their influence on sugarcane yield and nutrient uptake. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science 62: 209–215.
Virdia, H.M., and C.L. Patel. 2010. Integrated nutrient management for sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrid complex) plant- ratoon system. Indian Journal of Agronomy 55(2): 147–151.
Walkley, A., and C.A. Black. 1934. An examination of degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science 37: 29–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The all authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, S.K., Kumar, V. & Jha, C.K. Effect of Integrated use of Bio-Compost and Nitrogen on Productivity and Soil Properties of Sugarcane Plant–Ratoon System in Calcareous Soil. Sugar Tech 19, 485–491 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-016-0501-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-016-0501-7