Abstract
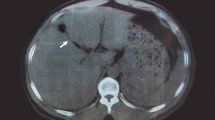
This study aimed to demonstrate the effect of transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) on hepatic segmental arterial mediolysis (SAM). The patient, a 68-year-old female, suddenly developed right upper abdominal pain in October 2021, which was initially relieved. However, she was rushed to a local hospital the next day when her abdominal pain recurred. An abdominal computed tomography scan suggested a ruptured hepatic aneurysm; therefore, she was transferred to our hospital and admitted on the same day. On the first day after admission, she underwent emergency catheterization and N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate (NBCA)/lipiodol embolization for an aneurysm in the hepatic S6. A multi-detector computed tomography on hospital day 8 to probe for extrahepatic lesions revealed multiple beaded irregularities in the superior mesenteric and bilateral renal arteries. A head magnetic resonance angiography performed on the ninth day showed no aneurysms or irregularities. She did well after TAE, did not have rebleeding, and was discharged on hospital day 16. Rupture of an aneurysm associated with SAM occurs frequently in the colonic and gastroepiploic arteries, and rupture of a hepatic aneurysm is relatively rare. TAE hemostasis was able to save the patient by preventing intraperitoneal bleeding caused by hepatic segmental arterial mediolysis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SAM:
-
Segmental arterial mediolysis
- TAE:
-
Transcatheter arterial embolization
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- Hb:
-
Hemoglobin
- CA:
-
Celiac artery
References
Slavin RE, Gonzalez-Vitale JC. Segmental mediolytic arteritis: a clinical pathologic study. Lab Invest. 1976;35:23–9.
Slavin RE, Saeki K, Bhagavan B, et al. Segmental arterial mediolysis: a precursor to fibromuscular dysplasia? Mod Pathol. 1995;8:287–94.
Slavin RE, Cafferty L, Cartwright J Jr. Segmental mediolytic arteritis. A clinicopathologic and ultrastructural study of two cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1989;13:558–68.
Peng KX, Davila VJ, Stone WM, et al. Natural history and management outcomes of segmental arterial mediolysis. J Vasc Surg. 2019;70:1877–86.
Ko M, Kamimura K, Ogawa K, et al. Diagnosis and management of fibromuscular dysplasia and segmental arterial mediolysis in gastroenterology field: a mini-review. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24:3637–49.
Michael M, Widmer U, Wildermuth S, et al. Segmental arterial mediolysis: CTA findings at presentation and follow-up. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;187:1463–9.
Kalva SP, Somarouthu B, Jaff MR, et al. Segmental arterial mediolysis: clinical and imaging features at presentation and during follow-up. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011;22:1380–7.
Baker-LePain JC, Stone DH, Mattis AN, et al. Clinical diagnosis of segmental arterial mediolysis: differentiation from vasculitis and other mimics. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010;62:1655–60.
Shenouda M, Riga C, Naji Y, et al. Segmental arterial mediolysis: a systematic review of 85 cases. Ann Vasc Surg. 2014;28:269–77.
Inada K, Maeda M, Ikeda T. Segmental arterial mediolysis: unrecognized cases culled from cases of ruptured aneurysm of abdominal visceral arteries reported in the Japanese literature [published correction appears in Pathol Res Pract. 2008;204(2):147]. Pathol Res Pract. 2007;203:771–8.
Tabassum A, Sasani S, Majid AJ, et al. Segmental arterial mediolysis of left gastric artery: a case report and review of pathology. BMC Clin Pathol. 2013;13:26.
Shimohira M, Kondo H, Ogawa Y, et al. Natural history of unruptured visceral artery aneurysms due to segmental arterial mediolysis and efficacy of transcatheter arterial embolization: a retrospective multiinstitutional study in Japan. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216:691–7.
Slavin RE. Segmental arterial mediolysis: course, sequelae, prognosis, and pathologic-radiologic correlation. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2009;18:352–60.
Chao CP. Segmental arterial mediolysis. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2009;26:224–32.
Skeik N, Olson SL, Hari G, et al. Segmental arterial mediolysis (SAM): systematic review and analysis of 143 cases. Vasc Med. 2019;24:549–63.
Srinivasan A, Olowofela A, Rothstein A, et al. A single center 8 year experience of segmental arterial mediolysis management. Ann Vasc Surg. 2022;81:273–82.
Pillai AK, Iqbal SI, Liu RW, et al. Segmental arterial mediolysis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2014;37:604–12.
Nagamura N, Higuchi H. Segmental arterial mediolysis with preceding symptoms resembling viral infection hampers the differentiation from Polyarteritis nodosa. Intern Med. 2019;58:2721–6.
Zhakubayev M, Maruya Y, Takatsuki M, et al. Stent treatment for huge aneurysm of the common hepatic artery: a case report. Radiol Case Rep. 2018;14:44–7.
Olivares E, Vingan H, Zhou Q. Spontaneous hemoperitoneum resulting from segmental arterial mediolysis. Radiol Case Rep. 2018;13:732–5.
Beerle C, Soll C, Breitenstein S, et al. Spontaneous rupture of an intrahepatic aneurysm of the right hepatic artery caused by segmental arterial mediolysis. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:bcr2015214109.
Ashfaq A. Money SR biopsy proven hepatic segmental arteriolar mediolysis successfully treated with coil embolization. Circulation. 2015;132:2265–6.
Marshall L, O’Rourke T, McCann A, et al. Spontaneous intrahepatic haemorrhage: two cases of segmental arterial mediolysis. ANZ J Surg. 2015;85:49–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained in from the patient.
Human rights
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Animal studies
Not applicable.
Approval of the research protocol
Not applicable.
Registry and the registration no. of the study/trial
Not applicable.
Research involving recombinant DNA
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kato, H., Hagiwara, S., Nishida, N. et al. A case of transcatheter arterial embolization for intraperitoneal hemorrhage due to giant hepatic segmental arterial mediolysis. Clin J Gastroenterol 16, 397–401 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-023-01766-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-023-01766-1