Abstract
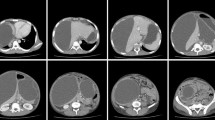
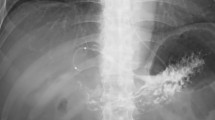
Pancreatic pseudocysts (PPs) can be accompanied by infection, pseudoaneurysm ruptures, and fistulae to other organs, which can be fatal without appropriate treatment. Herein, we present the case of an 82-year-old man with PPs accompanied by infection, pseudoaneurysm rupture, and pseudocystocolonic fistula that were managed via multidisciplinary treatment. Computed tomography (CT) revealed two inflamed PPs, one each in the pancreatic head and tail. He was, therefore, diagnosed with infectious PPs. The pancreatic head PP shrunk on endoscopic nasopancreatic drainage (ENPD), but the pancreatic tail PP did not. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided transluminal drainage was performed to treat the pancreatic tail PP; his symptoms improved. However, he vomited blood at 14 day post-drainage. Angiography revealed pseudoaneurysm rupture in a left gastric artery branch. After successful angioembolization, he developed hematochezia 2 days later. We suspected re-bleeding of the pseudoaneurysm. The bleeding stopped spontaneously, but CT and radiography revealed the presence of a pseudocystocolonic fistula. Careful follow-up was performed, and he has not had any symptoms at 9 month post-discharge. We managed PP-related complications via ENPD, EUS-guided transluminal drainage, angioembolization, and careful follow-up. Infection, pseudoaneurysm rupture, and pseudocystocolonic fistula are rare, but can occur simultaneously. Therefore, clinicians should consider these complications when treating patients with PPs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarr MG. 2012 revision of the Atlanta classification of acute pancreatitis. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2013;123:118–24.
Baillie J. Pancreatic pseudocysts (Part I). Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59:873–9.
Ramsey ML, Conwell DL, Hart PA. Complications of chronic pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62:1745–50.
Tan J, Zhou L, Cao R, et al. Identification of risk factors for pancreatic pseudocysts formation, intervention and recurrence: a 15-year retrospective analysis in a tertiary hospital in China. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018;18:143.
Agalianos C, Passas I, Sideris I, et al. Review of management options for pancreatic pseudocysts. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3:18.
Andrén-Sandberg A, Dervenis C. Pancreatic pseudocysts in the 21st century. Part II: Natural history. JOP. 2004;5:64–70.
Melman L, Azar R, Beddow K, et al. Primary and overall success rates for clinical outcomes after laparoscopic, endoscopic, and open pancreatic cystgastrostomy for pancreatic pseudocysts. Surg Endosc. 2009;23:267–71.
Wiersema MJ. Endosonography-guided cystoduodenostomy with a therapeutic ultrasound endoscope. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996;44:614–7.
Azar RR, Oh YS, Janec EM, et al. Wire-guided pancreatic pseudocyst drainage by using a modified needle knife and therapeutic echoendoscope. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:688–92.
Varadarajulu S, Wilcox CM, Tamhane A, et al. Role of EUS in drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections not amenable for endoscopic transmural drainage. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;66:1107–19.
Subtil Iñigo JC, Muñoz-Navas M. Endoscopic ultrasonographic drainage of pancreatic fluid collections. Interv Ther Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;27:485–500.
Tyberg A, Karia K, Gabr M, et al. Management of pancreatic fluid collections: a comprehensive review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:2256–70.
Sadik R, Kalaitzakis E, Thune A, et al. EUS-guided drainage is more successful in pancreatic pseudocysts compared with abscesses. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:499–505.
Varadarajulu S, Bang JY, Phadnis MA, et al. Endoscopic transmural drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections: outcomes and predictors of treatment success in 211 consecutive patients. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011;15:2080–8.
Varadarajulu S, Christein JD, Tamhane A, et al. Prospective randomized trial comparing EUS and EGD for transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68:1102–11.
Chiang KC, Chen TH, Te Hsu J. Management of chronic pancreatitis complicated with a bleeding pseudoaneurysm. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:16132–7.
Udd M, Leppäniemi AK, Bidel S, et al. Treatment of bleeding pseudoaneurysms in patients with chronic pancreatitis. World J Surg. 2007;31:504–10.
Carr JA, Cho JS, Shepard AD, et al. Visceral pseudoaneurysms due to pancreatic pseudocysts: rare but lethal complications of pancreatitis. J Vasc Surg. 2000;32:722–30.
Cui B, Zhou L, Khan S, et al. Role of enteral nutrition in pancreaticocolonic fistulas secondary to severe acute pancreatitis: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:e9054.
Kwon JC, Kim BY, Kim AL, et al. Pancreatic pseudocystocolonic fistula treated without surgical or endoscopic intervention. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:1882–6.
Suzuki A, Suzuki S, Sakaguchi T, et al. Colonic fistula associated with severe acute pancreatitis: report of two cases. Surg Today. 2008;38:178–83.
Shatney CH, Sosin H. Spontaneous perforation of a pancreatic pseudocyst into the colon and duodenum. Am J Surg. 1973;126:433–8.
Will U, Meyer F, Hartmeier S, et al. Endoscopic treatment of a pseudocystocolonic fistula by band ligation and endoloop application: case report. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59:581–3.
Karvonen J, Gullichsen R, Salminen P, et al. Endoscopic treatment of pseudocystocolonic fistula with fibrin glue. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:664–5.
Koike Y, Kudo T, Shigesawa T, et al. Pancreatic pseudocyst with complicating colonic fistula successfully closed using the over-the-scope-clip system. Endoscopy. 2014;46:178–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Yoshinori Kihara and Dr. Yuzuru Okuizumi in the department of radiology, Niigata Prefectural Central Hospital for a technical support.
Funding
No funding to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Drafting of the paper: KS; critical revision of the manuscript: KT; revision of the manuscript: YA and ST; and technical support: FY, DK, MY, MH, and KF.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have a conflict of interest.
Human/animal rights
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008(5).
Ethics approval
Ethical approval was not required.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, K., Takahashi, K., Aruga, Y. et al. A case of pancreatic pseudocysts accompanied by infection, pseudoaneurysm ruptures, and pseudocystocolonic fistulae. Clin J Gastroenterol 12, 615–620 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-019-00986-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-019-00986-8