Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this work is to report mid- to long-term clinical results, recurrence rates and instability following surgery to repair anterior dislocation of the shoulder by the remplissage technique.
Methods
This was a retrospective case series at a single center with patients with anterior shoulder instability that received surgery using the remplissage technique. Rowe questionnaire, instability complaints, recurrence episodes and return to sport were analyzed.
Results
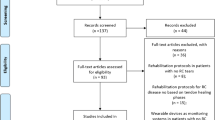
Of all patients screened, 21 (92.3%) were enrolled and only 2 patients were lost to follow-up. The mean age of the patients at the time of surgery was 27.8y.o., and the mean number of dislocations before surgery was 3.2 episodes. The follow-up average was 83.8 months (range 28–126). No case of postoperative infection was observed. Two patients (9.5%) had recurrent shoulder instability and required reintervention after 18 and 48 months. The average final Rowe score was 92.9 (range 75–100). All patients that played sports before surgery returned to the sport, and 73.7% of them returned to the same activity level.
Conclusion
The remplissage technique applied to repair anterior shoulder dislocation with humeral bone loss presents good results regarding clinical scores, shoulder stability and acceptable rates of return to sports, even in a mid- to long-term follow-up.
Level of evidence
IV.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hill HA, Sachs MD (1940) The grooved defect of the humeral head. Radiology 35:690–700. https://doi.org/10.1148/35.6.690
Armitage MS, Faber KJ, Drosdowech DS et al (2010) Humeral head bone defects: remplissage, allograft, and arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am 41:417–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocl.2010.03.004
Longo UG, Loppini M, Rizzello G et al (2014) Remplissage, humeral osteochondral grafts, weber osteotomy, and shoulder arthroplasty for the management of humeral bone defects in shoulder instability: systematic review and quantitative synthesis of the literature. Arthroscopy 30:1650–1666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2014.06.010
Wolf EM, Pollack ME (2004) Hill-Sachs “Remplissage”: an arthroscopic solution for the engaging Hill-Sachs lesion (SS-32). Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg 20:e14–e15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2004.02.033
Purchase RJ, Wolf EM, Hobgood ER et al (2008) Hill-sachs “remplissage”: an arthroscopic solution for the engaging Hill-Sachs lesion. Arthroscopy 24:723–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2008.03.015
Di Giacomo G, Itoi E, Burkhart SS (2014) Evolving concept of bipolar bone loss and the Hill-Sachs lesion: from “engaging/non-engaging” lesion to “on-track/off-track” lesion. Arthroscopy 30:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2013.10.004
Saliken D, Lavoué V, Trojani C et al (2017) Combined all-arthroscopic Hill-Sachs remplissage, Latarjet, and Bankart repair in patients with bipolar glenohumeral bone loss. Arthrosc Tech 6:e2031–e2037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eats.2017.08.001
Boileau P, O’Shea K, Vargas P et al (2012) Anatomical and functional results after arthroscopic Hill-Sachs remplissage. J Bone Jt Surg Am 94:618–626. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.K.00101
Bois AJ, Fening SD, Polster J et al (2012) Quantifying glenoid bone loss in anterior shoulder instability: reliability and accuracy of 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional computed tomography measurement techniques. Am J Sports Med 40:2569–2577. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546512458247
Bonnevialle N, Azoulay V, Faraud A et al (2017) Results of arthroscopic Bankart repair with Hill-Sachs remplissage for anterior shoulder instability. Int Orthop 41:2573–2580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-017-3491-5
Deutsch AA, Kroll DG (2008) Decreased range of motion following arthroscopic remplissage. Orthopedics 31:492
Garcia GH, Wu H-H, Liu JN et al (2016) Outcomes of the remplissage procedure and its effects on return to sports. Am J Sports Med 44:1124–1130. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546515626199
Gracitelli MEC, Helito CP, Malavolta EA et al (2011) Results from filling “remplissage” arthroscopic technique for recurrent anterior shoulder dislocation. Rev Bras Ortop 46:684–690. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-36162011000600010
Haviv B, Mayo L, Biggs D (2011) Outcomes of arthroscopic “remplissage”: capsulotenodesis of the engaging large Hill-Sachs lesion. J Orthop Surg Res 6:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-799X-6-29
McCabe MP, Weinberg D, Field LD et al (2014) Primary versus revision arthroscopic reconstruction with remplissage for shoulder instability with moderate bone loss. Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg 30:444–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2013.12.015
Merolla G, Paladini P, Di Napoli G et al (2015) Outcomes of arthroscopic Hill-Sachs remplissage and anterior bankart repair. Am J Sports Med 43:407–414. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546514559706
Morsy MG (2017) Arthroscopic remplissage. EFORT Open Rev 2:478–483. https://doi.org/10.1302/2058-5241.2.160070
Park MJ, Tjoumakaris FP, Garcia G et al (2011) Arthroscopic remplissage with Bankart repair for the treatment of glenohumeral instability with Hill-Sachs defects. Arthroscopy 27:1187–1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2011.05.010
Sood M, Ghai A (2018) Functional outcome after arthroscopic management of traumatic recurrent dislocation shoulder using Bankart repair and Remplissage techniques. Med J Armed Forces India 74:51–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mjafi.2017.05.004
Zhu Y-M, Lu Y, Zhang J et al (2011) Arthroscopic bankart repair combined with remplissage technique for the treatment of anterior shoulder instability with engaging Hill-Sachs lesion. Am J Sports Med 39:1640–1648. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546511400018
Buza JA, Iyengar JJ, Anakwenze OA et al (2014) Arthroscopic Hill-Sachs remplissage: a systematic review. J Bone Jt Surg Am 96:549–555. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.L.01760
Rashid MS, Crichton J, Butt U et al (2016) Arthroscopic “Remplissage” for shoulder instability: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sport Traumatol Arthrosc 24:578–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-2881-0
Consigliere P, Morrissey N, Imam M, Narvani AA (2017) The tripod-pulley technique for arthroscopic remplissage in engaging Hill-Sachs lesions. Arthrosc Tech 6:e1675–e1684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eats.2017.06.038
Garcia GH, Degen RM, Liu JN et al (2017) The “Safe Zone” technique improves suture placement and accuracy during arthroscopic remplissage. Orthopedics 40:e598–e603. https://doi.org/10.3928/01477447-20170411-05
Kahlenberg CA, Garcia GH, Degen RM et al (2017) The intra-articular “Wave Sign” as a landmark for suture anchor placement in arthroscopic remplissage. Orthopedics 40:e831–e835. https://doi.org/10.3928/01477447-20170619-03
Koo SS, Burkhart SS, Ochoa E (2009) Arthroscopic double-pulley remplissage technique for engaging Hill-Sachs lesions in anterior shoulder instability repairs. Arthroscopy 25:1343–1348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2009.06.011
Luedke C, Tokish JM (2017) Arthroscopic panlabral repair with remplissage of Hill-Sachs Lesion. Arthrosc Tech 6:e743–e749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eats.2017.02.004
Werner BC, Chen X, Camp CL et al (2017) Medial posterior capsular plication reduces anterior shoulder instability similar to remplissage without restricting motion in the setting of an engaging hill-sachs defect. Am J Sports Med 45:1982–1989. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546517700860
Wolf EM, Arianjam A (2014) Hill-Sachs remplissage, an arthroscopic solution for the engaging Hill-Sachs lesion: 2- to 10-year follow-up and incidence of recurrence. J Shoulder Elb Surg 23:814–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2013.09.009
Gyftopoulos S, Beltran LS, Yemin A et al (2014) Use of 3D MR reconstructions in the evaluation of glenoid bone loss: a clinical study. Skeletal Radiol 43:213–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-013-1774-5
Cho SH, Cho NS, Rhee YG (2011) Preoperative analysis of the hill-sachs lesion in anterior shoulder instability: How to predict engagement of the lesion. Am J Sports Med 37:2389–2395. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546511398644
Rowe C (1988) Evaluation of the shoulder. In: Mackenzie M (ed) the shoulder. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 631–637
Rowe CR, Zarins B, Ciullo JV (1984) Recurrent anterior dislocation of the shoulder after surgical repair. Apparent causes of failure and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 66:159–168
Marcondes FB, de Vasconcelos RA, Marchetto A et al (2012) Translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the rowe score for portuguese. Acta Ortopédica Bras 20:346–350. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-78522012000600007
Lynch JR, Clinton JM, Dewing CB et al (2009) Treatment of osseous defects associated with anterior shoulder instability. J Shoulder Elb Surg 18:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2008.10.013
Maffulli N, Longo UG, Gougoulias N et al (2011) Sport injuries: a review of outcomes. Br Med Bull 97:47–80. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldq026
Balg F, Boileau P (2007) The instability severity index score: a simple pre-operative score to select patients for arthroscopic or open shoulder stabilisation. J Bone Jt Surg Br 89:1470–1477
Burkhart SS, De Beer JF (2000) Traumatic glenohumeral bone defects and their relationship to failure of arthroscopic Bankart repairs: significance of the inverted-pear glenoid and the humeral engaging Hill-Sachs lesion. Arthroscopy 16:677–694. https://doi.org/10.1053/jars.2000.17715
Ko S-H, Cha J-R, Lee C-C et al (2016) The influence of arthroscopic remplissage for engaging Hill-Sachs lesions combined with Bankart repair on redislocation and shoulder function compared with bankart repair alone. Clin Orthop Surg 8:428–436. https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.428
Momaya AM, Tokish JM (2017) Applying the glenoid track concept in the management of patients with anterior shoulder instability. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 10:463–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-017-9436-1
Nourissat G, Kilinc AS, Werther JR, Doursounian L (2011) A prospective, comparative, radiological, and clinical study of the influence of the “remplissage” procedure on shoulder range of motion after stabilization by arthroscopic Bankart repair. Am J Sports Med 39:2147–2152. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546511416315
Yamamoto N, Itoi E, Abe H et al (2007) Contact between the glenoid and the humeral head in abduction, external rotation, and horizontal extension: a new concept of glenoid track. J Shoulder Elb Surg 16:649–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2006.12.012
Brilakis E, Mataragas E, Deligeorgis A et al (2016) Midterm outcomes of arthroscopic remplissage for the management of recurrent anterior shoulder instability. Knee Surg Sport Traumatol Arthrosc 24:593–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-2848-1
Brilakis E, Avramidis G, Malahias M-A et al (2018) Long-term outcome of arthroscopic remplissage in addition to the classic Bankart repair for the management of recurrent anterior shoulder instability with engaging Hill-Sachs lesions. Knee Surg Sport Traumatol Arthrosc 27:305–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-5261-3
Acknowledgments
The authors want to acknowledge the assistance received from Luis Marchi, PhD, in the preparation of the manuscript and submission process.
Funding
No author has financial relations to disclose regarding this work. The Fellowship program in Instituto Vita receives financial support from DePuy Synthes; however, the study did not receive support in the form of grants, equipment or other items.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ACB contributed to conceptualization, data curation, funding acquisition, methodology, project administration, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing; MCF contributed to data curation, formal analysis, methodology, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing; DGF contributed to data curation, formal analysis, methodology, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing; AGPG contributed to formal analysis, methodology, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing; BS contributed to conceptualization, investigation, methodology, project administration, writing—review and editing; FOZ contributed to data curation, formal analysis, methodology, writing—review and editing; MN contributed to conceptualization, supervision, writing—review and editing, ARHS contributed to data curation, formal analysis, methodology, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing; WC contributed to conceptualization, investigation, project administration, supervision, validation, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bitar, A.C., Fabiani, M.C., Ferrari, D.G. et al. Clinical and functional outcomes of the remplissage technique to repair anterior shoulder dislocation: average 7 years of follow-up. Musculoskelet Surg 105, 61–67 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-019-00630-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-019-00630-1