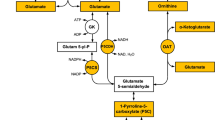
Abstract
Our study aimed to evaluate intraspecific variability of pea (Pisum sativum L.) in Al tolerance and to reveal mechanisms underlying genotypic differences in this trait. At the first stage, 106 pea genotypes were screened for Al tolerance using root re-elongation assay based on staining with eriochrome cyanine R. The root re-elongation zone varied from 0.5 mm to 14 mm and relationships between Al tolerance and provenance or phenotypic traits of genotypes were found. Tolerance index (TI), calculated as a biomass ratio of Al-treated and non-treated contrasting genotypes grown in hydroponics for 10 days, varied from 30% to 92% for roots and from 38% to 90% for shoots. TI did not correlate with root or shoot Al content, but correlated positively with increasing pH and negatively with residual Al concentration in nutrient solution in the end of experiments. Root exudation of organic acid anions (mostly acetate, citrate, lactate, pyroglutamate, pyruvate and succinate) significantly increased in several Al-treated genotypes, but did not correlate with TI. Al-treatment decreased Ca, Co, Cu, K, Mg, Mn, Mo, Ni, S and Zn contents in roots and/or shoots, whereas contents of several elements (P, B, Fe and Mo in roots and B and Fe in shoots) increased, suggesting that Al toxicity induced substantial disturbances in uptake and translocation of nutrients. Nutritional disturbances were more pronounced in Al sensitive genotypes. In conclusion, pea has a high intraspecific variability in Al tolerance and this trait is associated with provenance and phenotypic properties of plants. Transformation of Al to unavailable (insoluble) forms in the root zone and the ability to maintain nutrient uptake are considered to be important mechanisms of Al tolerance in this plant species.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhter A, Wagatsuma T, Khan MSH, Tawaraya K (2009) Comparative studies on aluminum tolerance screening techniques for sorghum, soybean and maize in simple solution culture. Am J Plant Physiol 4:1–8. doi:10.3923/ajpp.2009.1.8
Anas A, Yoshida T (2004) Heritability and genetic correlation of Al-tolerance with several agronomic characters in sorghum assessed by hematoxylin staining. Plant Prod Sci 7:280–282. doi:10.1626/pps.7.280
Aniol A, Gustafson P (1984) Chromosome location of genes controlling aluminum tolerance in wheat, rye and triticale. Can J Genet Cytol 26:701–705. doi:10.1139/g84-111
Baligar VC, Wright RJ, Kinraide TB, Foy CD, Elgin JH (1987) Aluminum effects on growth, mineral uptake, and efficiency ratios in red clover cultivars. Agron J 79:1038–1044. doi:10.2134/agronj1987.00021962007900060018x
Belimov AA, Safronova VI, Tsyganov VE, Borisov AY, Kozhemyakov AP, Stepanok VV, Martenson AM, Gianinazzi-Pearson V, Tikhonovich IA (2003) Genetic variability in tolerance to cadmium and accumulation of heavy metals in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Euphytica 131:25–35. doi:10.1023/A:1023048408148
Belimov AA, Dodd IC, Safronova VI, Malkov NV, Davies WJ, Tikhonovich IA (2015a) The cadmium tolerant pea (Pisum sativum L.) mutant SGECdt is more sensitive to mercury: assessing plant water relations. J Exp Bot 66:2359–2369. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru536
Belimov AA, Puhalsky IV, Safronova VI, Shaposhnikov AI, Vishnyakova MA, Semenova EV, Zinovkina NY, Makarova NM, Wenzel W, Tikhonovich IA (2015b) Role of plant genotype and soil conditions in symbiotic plant-microbe interactions for adaptation of plants to cadmium polluted soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:1–15. doi:10.1007/s11270-015-2537-9
Bernal JH, Clark RB (1997) Mineral acquisition of aluminum-tolerant and sensitive sorghum genotypes grown with varied aluminum. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 28:49–62. doi:10.1080/00103629709369771
Bose J, Babourina O, Rengel Z (2011) Role of magnesium in alleviation of aluminium toxicity in plants. J Exp Bot 62:2251–2264. doi:10.1093/jxb/erq456
Degenhardt J, Larsen PB, Howell SH, Kochian LV (1998) Aluminum resistance in the arabidopsis mutant alr-104 is caused by an aluminum-induced increase in rhizosphere pH. Plant Physiol 117:19–27. doi:10.1104/pp.117.1.19
Delhaize E, Ma JF, Ryan PR (2012) Transcriptional regulation of aluminium tolerance genes. Trends Plant Sci 17:341–348. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2012.02.008
Foy CD (1996) Tolerance of durum wheat lines to an acid, aluminum toxic subsoil. J Plant Nutr 19:1381–1394. doi:10.1080/01904169609365206
Guinel FC, LaRue TA (1993) Excessive aluminium accumulation in the pea mutant El07 (brz). Plant Soil 157:75–82. doi:10.1007/BF02390229
Gupta N, Gaurav SS, Kumar A (2013) Molecular basis of aluminium toxicity in plants: a review. Am J Plant Sci 4:21–37. doi:10.4236/ajps.2013.412A3004
Horst WJ (1987) Aluminium tolerance and calcium efficiency in cowpea genotypes. J Plant Nutr 10:1121–1129. doi:10.1080/01904168709363640
Huang JW, Grunes DL, Kochian LV (1995) Aluminium and calcium transport interactions in intact roots and root plasmalemma vesicles from aluminium-sensitive and tolerant wheat cultivars. Plant Soil 171:131–135. doi:10.1007/BF00009575
Jan F, Pettersson S (1989) Varietal diversity of upland rice in sensitivity to aluminium. J Plant Nutr 12:973–993. doi:10.1080/01904168909364017
Jemo MR, Abaidoo C, Nolte C, Horst WJ (2007) Aluminum resistance of cowpea as affected by phosphorus-deficiency stress. J Plant Physiol 164:442–451. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2005.12.010
Khabaz-Saberi H, Rengel Z (2010) Aluminum, manganese, and iron tolerance improves performance of wheat genotypes in waterlogged acidic soils. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 173:461–468. doi:10.1002/jpln.200900316
Kidd PS, Llugany M, Poschenrieder C, Gunse B, Barcelo J (2001) The role of root exudates in aluminium resistance and silicon-induced amelioration of aluminium toxicity in three varieties of maize (Zea mays L.). J Exp Bot 52:1339–1352. doi:10.1093/jexbot/52.359.1339
Kikui S, Sasaki T, Osawa H, Matsumoto H, Yamamoto Y (2007) Malate enhances recovery from aluminum-caused inhibition of root elongation in wheat. Plant Soil 290:1–15. doi:10.1007/s11104-006-9068-5
Kinraide TB (1998) Three mechanisms for the calcium alleviation of mineral toxicities. Plant Physiol 118:513–520
Kinraide TB, Pedler JF, Parker DR (2004) Relative effectiveness of calcium and magnesium in the alleviation of rhizotoxicity in wheat induced by copper, zinc, aluminum, sodium, and low pH. Plant Soil 259:201–208. doi:10.1023/B:PLSO.0000020972.18777.99
Klimashevsky EL, Markova YA, Malysheva AS (1972) Genotypic specify in localization of Al3+ in cells of pea roots. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 203:711–713
Kobayashi Y, Kobayashi Y, Watanabe T, Shaff JF, Ohta H, Kochian LV, Wagatsuma T, Kinraide TB, Koyama Y (2013) Molecular and physiological analysis of Al3+ and H+ rhizotoxicities at moderately acidic conditions. Plant Physiol 163:180–192. doi:10.1104/pp.113.222893
Kochian LV (1995) Cellular mechanisms of aluminum toxicity and resistance in plants. Annu Rev Plant Phys 46:237–260. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.46.060195.001321
Kochian LV, Hoekenga OA, Pineros MA (2004) How do crop plants tolerate acid soils? mechanisms of aluminum tolerance and phosphorous efficiency. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:459–493. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141655
Kolawole GO, Tian G, Singh BB (2000) Differential response of cowpea lines to aluminum and phosphorus application. J Plant Nutr 23:731–740. doi:10.1080/01904160009382055
Kuzmicheva YV, Shaposhnikov AI, Azarova NS, Petrova SN, Naumkina TS, Borisov AY, Belimov AA, Kravchenko LV, Parakhin NV, Tikhonovich IA (2014) Composition of root exometabolites of the symbiotically effective pea cultivar triumph and its parental forms. Russ J Plant Physiol 61:112–118. doi:10.1134/S1021443714010087
Lazof DB, Holland MJ (1999) Evaluation of the aluminium-induced root growth inhibition in isolation from low pH effects in Glycine max, Pisum sativum and Phaseolus vulgaris. Aust J Plant Physiol 26:147–157. doi:10.1071/PP98072
Liang C, Piñeros MA, Tian J, Yao Z, Sun L, Liu J, Shaff J, Coluccio A, Kochian LV, Liao H (2013) Low pH, aluminum, and phosphorus coordinately regulate malate exudation through GmALMT1 to improve soybean adaptation to acid soils. Plant Physiol 161:1347–1361. doi:10.1104/pp.112.208934
Liao H, Wan H, Shaff J, Wang X, Yan X, Kochian LV (2006) Phosphorus and aluminum interactions in soybean in relation to aluminum tolerance. Exudation of specific organic acids from different regions of the intact root system. Plant Physiol 141:674–684. doi:10.1104/pp.105.076497
Liu J, Piñeros MA, Kochian LV (2014) The role of aluminum sensing and signaling in plant aluminum resistance. J Int Plant Biol 56:221–230. doi:10.1111/jipb.12162
Ma JF, Ryan PR, Delhaize E (2001) Aluminium tolerance in plants and the complexing role of organic acids. Trends Plant Sci 6:273–278. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(01)01961-6
Matsumoto H, Motoda H (2012) Review: aluminum toxicity recovery processes in root apexes. Possible association with oxidative stress. Plant Sci 185–186:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.07.019
Matsumoto H, Yamaya T (1986) Inhibition of potassium uptake and regulation of membrane-associated Mg2+-ATPase activity of pea roots by aluminium. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 32:179–188. doi:10.1080/00380768.1986.10557495
Metwally A, Safronova VI, Belimov AA, Dietz KJ (2005) Genotypic variation of the response to cadmium toxicity in Pisum sativum L. J Exp Bot 56:167–178. doi:10.1093/jxb/eri017
Mimmo T, Ghizzi M, Cesco S, Tomasi N, Pinton R, Puschenreiter M (2013) Aluminium–phosphate interactions in the rhizosphere of two bean species: Phaseolus lunatus L. and Phaseolus vulgaris L. J Sci Food Agric 93:3891–3896. doi:10.1002/jsfa.6392
Miyasaka SC, Kochian LV, Shaff JE, Foy CD (1989) Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance in wheat: an investigation of genotypic differences in rhizosphere pH, K+, and H+ transport, and root-cell membrane potentials. Plant Physiol 91:1188–1196. doi:10.1104/pp.91.3.1188
Motoda H, Kano Y, Hiragami F, Kawamura K, Matsumoto H (2010) Morphological changes in the apex of pea roots during and after recovery from aluminium treatment. Plant Soil 333:49–58. doi:10.1007/s11104-010-0318-1
Panda SK, Matsumoto H (2010) Changes in antioxidant gene expression and induction of oxidative stress in pea (Pisum sativum L.) under Al stress. Biometals 23:753–762. doi:10.1007/s10534-010-9342-0
Pandey P, Srivastava RK, Dubey RS (2013) Salicylic acid alleviates aluminum toxicity in rice seedlings better than magnesium and calcium by reducing aluminum uptake, suppressing oxidative damage and increasing antioxidative defense. Ecotoxicology 22:656–670. doi:10.1007/s10646-013-1058-9
Pellet DM, Grunes DL, Kochian LV (1995) Organic acid exudation as an aluminum-tolerance mechanism in maize (Zea mays L.). Planta 196:788–795. doi:10.1007/BF01106775
Pellet DM, Papernik LA, Kochian LV (1996) Multiple aluminum-resistance mechanisms in wheat: roles of root apical phosphate and malate exudation. Plant Physiol 112:591–597. doi:10.1104/pp.112.2.591
Pineros MA, Magalhaes JV, Alves VMC, Kochian LV (2002) The physiology and biophysics of an aluminum tolerance mechanism based on root citrate exudation in maize. Plant Physiol 129:1194–1206. doi:10.1104/pp.002295
Pineros MA, Shaff JE, Manslank HS, Carvalho AVM, Kochian LV (2005) Aluminum resistance in maize cannot be solely explained by root organic acid exudation. A comparative physiological study. Plant Physiol 137:231–241. doi:10.1104/pp.104.047357
Rengel Z (1992) Role of calcium in aluminium toxicity. New Phytol 121:499–513. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1992.tb01120.x
Rengel Z, Robinson DL (1989) Competitive A13+ inhibition of net Mg2+ uptake by intact Lolium multiflorum roots. Plant Physiol 91:1407–1413. doi:10.1104/pp.91.4.1407
Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Randall PJ (1995) Malate efflux from root apices and tolerance to aluminium are highly correlated in wheat. Aust J Plant Physiol 22:531–653
Shen H, Yan XL, Wang XR, Zheng SL (2002) Exudation of citrate in common bean in response to aluminum stress. J Plant Nutr 25:1921–1932. doi:10.1081/PLN-120013284
Silva IR, Smyth TJ, Israel DW, Raper CD, Rufty TW (2001) Magnesium ameliorates aluminum rhizotoxicity in soybean by increasing citric acid production and exudation by roots. Plant Cell Physiol 42:546–554. doi:10.1093/pcp/pce067
Stass A, Wang Y, Eticha D, Horst WJ (2006) Aluminium rhizotoxicity in maize grown in solutions with Al3+ or Al(OH) −4 as predominant solution Al species. J Exp Bot 57:4033–4042. doi:10.1093/jxb/erl174
Taylor GJ (1988) Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance in Triticum aestivum (wheat). V. Nitrogen nutrition, plant-induced pH, and tolerance to aluminum; correlation without causality? Can J Bot 66:694–699. doi:10.1139/b88-100
Taylor GJ (1991) Current views of the aluminum stress response: the physiological basis of tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 10:57–93
Taylor GJ, Foy CD (1985a) Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance in Triticum aestivum L. (wheat). I. Differential pH induced by winter cultivars in nutrient solutions. Am J Bot 72:695–701
Taylor GJ, Foy CD (1985b) Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance in Triticum aestivum L. (wheat). II. Differential pH induced by spring cultivars in nutrient solutions. Am J Bot 72:702–706
Tsyganov VE, Belimov AA, Borisov AY, Safronova VI, Georgi M, Dietz KJ, Tikhonovich IA (2007) A chemically induced new pea (Pisum sativum L.) mutant SGECdt with increased tolerance to and accumulation of cadmium. Ann Bot 99:227–237. doi:10.1093/aob/mcl261
Villagarcia MR, Carter TEJ, Rufty TW, Niewoehner AS, Jennette MV, Arrellano C (2001) Genotypic rankings for aluminum tolerance of soybean roots grown in hydroponics and sand culture. Crop Sci 41:1499–1507. doi:10.2135/cropsci2001.4151499x
Vishnyakova MA, Semenova EV, Kosareva IA, Kravchuk ND, Loskutov SI, Puhalsky IV, Shaposhnikov AI, Sazanova AL, Belimov AA (2015) Method for rapid assessment of aluminum tolerance of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Agric Biol 50:353–360. doi:10.15389/agrobiology.2015.3.353eng
Vorobyev NI, Provorov NA, Sviridova OV (2013) Program for ANOVA randomized biological data. The official e-newsletter of the Federal Service for Intellectual Property “Computer programs, databases, integrated circuits”, 2, State registration certificate 2013615092, Mascow.
Wagatsuma T, Yamasaku K (1985) Relationship between differential aluminum tolerance and plant-induced pH change of medium among barley cultivars. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 31:521–535. doi:10.1080/00380768.1985.10557461
Wenzl P, Patiño GM, Chaves AL, Mayer JE, Rao IM (2001) The high level of aluminum resistance in signalgrass is not associated with known mechanisms of external aluminum detoxification in root apices. Plant Physiol 125:1473–1484. doi:10.1104/pp.125.3.1473
Yamamoto Y, Kobayashi Y, Matsumoto H (2001) Lipid peroxidation is an early symptom triggered by aluminum, but not the primary cause of elongation inhibition in pea roots. Plant Physiol 125:199–208. doi:10.1104/pp.125.1.199
Yu M, Shen R, Liu J, Chen R, Xu M, Yang Y, Xiao H, Wang HD, Wang HZ, Wang C (2009a) The role of root border cells in aluminum resistance of pea (Pisum sativum) grown in mist culture. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 172:528–534. doi:10.1002/jpln.200800039
Yu M, Shen RF, Xiao HD, Xu MM, Wang HZ (2009b) Boron alleviates aluminium toxicity in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Plant Soil 314:87–98. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0115485
Zheng SJ, Ma JF, Matsumoto H (1998) Continuous secretion of organic acids is related to aluminum resistance during relatively long-term exposure to aluminum stress. Physiol Plant 103:209–214. doi:10.1034/j.1399-3054.1998.1030208.x
Zhou XX, Yang LT, Qi YP, Guo P, Chen SL (2015) Mechanisms on boron-induced alleviation of aluminum-toxicity in Citrus grandis seedlings at a transcriptional level revealed by cDNA-AFLP analysis. PLoS ONE 10:e0115485. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0115485
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Dodd I.C. for critically reading the manuscript and help in improving the English language. This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (14-16-00137 and only for UPLC analysis 14-26-0094).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kichigina, N.E., Puhalsky, J.V., Shaposhnikov, A.I. et al. Aluminum exclusion from root zone and maintenance of nutrient uptake are principal mechanisms of Al tolerance in Pisum sativum L.. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23, 851–863 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-017-0469-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-017-0469-0