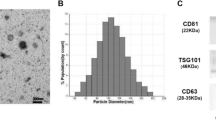
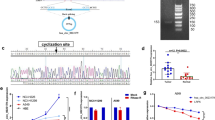
Abstract
Due to the lack of efficient diagnosis techniques, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) continues to be the main contributor to global death from cancer. Consequently, our research aims to identify reliable biomarkers for diagnosing non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by using serum exosomal short nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs). Based on the databases, we selected SNORD60 and further verified it in 48 paired FFPE tissues. To define exosomes isolated from the serum, we conducted transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and qNano besides western blots. qRT-PCR helped further verify SNORD60 in exosomal serum from 132 NSCLC patients and 143 participants in good health. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) was employed to estimate the diagnostic efficacy of SNORD60, both alone and in combination with carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and cytokeratin 19 fragment (CYFRA21-1). SNORD60 was significantly overexpressed in tissues and serum exosomes of NSCLC patients compared to those of good-health individuals. To evaluate the effectiveness of diagnostic biomarkers for NSCLC and its early stage, serum exosomal SNORD60 was found to have the ability to be a diagnostic biomarker, as well as CEA or CYFRA21-1 with an exosomal combination of SNORD60. The exosomal level of SNORD60 is significantly overexpressed in patients with NSCLC, which offers a promising diagnostic biomarker of NSCLC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The author can provide original data supporting the conclusion of this investigation without reservation.
References
Gridelli C, Rossi A, Carbone DP, Guarize J, Karachaliou N, Mok T, et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1:15009. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.9.
Brody H. Lung cancer. Nature. 2020;587(7834):S7. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03152-0.
Jin G, Miao R, Hu Z, Xu L, Huang X, Chen Y, et al. Putative functional polymorphisms of MMP9 predict survival of NSCLC in a Chinese population. Int J Cancer. 2009;124(9):2172–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24190.
Evison M, AstraZeneca UKL. The current treatment landscape in the UK for stage III NSCLC. Br J Cancer. 2020;123(Suppl 1):3–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-020-01069-z.
Wortzel I, Dror S, Kenific CM, Lyden D. Exosome-mediated metastasis: communication from a distance. Dev Cell. 2019;49(3):347–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.04.011.
Zhang J, Li S, Li L, Li M, Guo C, Yao J, et al. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: trafficking, sorting, and function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinform. 2015;13(1):17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2015.02.001.
Zhuo C, Yi T, Pu J, Cen X, Zhou Y, Feng S, et al. Exosomal linc-FAM138B from cancer cells alleviates hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulating miR-765. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(24):26236–47. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202430.
Wang Y, Liu J, Ma J, Sun T, Zhou Q, Wang W, et al. Exosomal circRNAs: biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):116. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1041-z.
Dupuis-Sandoval F, Poirier M, Scott MS. The emerging landscape of small nucleolar RNAs in cell biology. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2015;6(4):381–97. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1284.
Wajahat M, Bracken CP, Orang A. Emerging functions for snoRNAs and snoRNA-derived fragments. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(19):10193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910193.
Ding Y, Sun Z, Zhang S, Zhou L, Xu Q, Zhou D, et al. Identification of snoRNA SNORA71A as a novel biomarker in prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dis Markers. 2020;2020:8879944. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8879944.
Shen L, Lin C, Lu W, He J, Wang Q, Huang Y, et al. Involvement of the oncogenic small nucleolar RNA SNORA24 in regulation of p53 stability in colorectal cancer. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023;39(4):1377–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-022-09765-7.
Gong J, Li Y, Liu CJ, Xiang Y, Li C, Ye Y, et al. A pan-cancer analysis of the expression and clinical relevance of small nucleolar rnas in human cancer. Cell Rep. 2017;21(7):1968–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.070.
Zhang Z, Tang Y, Song X, Xie L, Zhao S, Song X. Tumor-derived exosomal miRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. 2020;10: 560025. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.560025.
Yu M, Song XG, Zhao YJ, Dong XH, Niu LM, Zhang ZJ, et al. Circulating serum exosomal long noncoding RNAs FOXD2-AS1, NRIR, and XLOC_009459 as diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11: 618967. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.618967.
Trummer A, Bethge A, Dickgreber N, Dittrich I, Golpon H, Hoffknecht P, et al. NSCLC with uncommon EGFR mutations treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy. Lung Cancer. 2022;174:141–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2022.11.006.
Pasello G, Lorenzi M, Pretelli G, Comacchio GM, Pezzuto F, Schiavon M, et al. Diagnostic-therapeutic pathway and outcomes of early stage NSCLC: a focus on EGFR testing in the real-world. Front Oncol. 2022;12: 909064. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.909064.
Chen H, Rong Z, Ge L, Yu H, Li C, Xu M, et al. Leader gene identification for digestive system cancers based on human subcellular location and cancer-related characteristics in protein-protein interaction networks. Front Genet. 2022;13: 919210. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.919210.
Liu Y, Ruan H, Li S, Ye Y, Hong W, Gong J, et al. The genetic and pharmacogenomic landscape of snoRNAs in human cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):108. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01228-z.
Cavaillé J. Box C/D small nucleolar RNA genes and the Prader-Willi syndrome: a complex interplay. Wiley Interdiscip Rev: RNA. 2017;8(4):e1417. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1417.
Warner WA, Spencer DH, Trissal M, White BS, Helton N, Ley TJ, et al. Expression profiling of snoRNAs in normal hematopoiesis and AML. Blood Adv. 2018;2(2):151–63. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2017006668.
Han C, Sun LY, Luo XQ, Pan Q, Sun YM, Zeng ZC, et al. Chromatin-associated orphan snoRNA regulates DNA damage-mediated differentiation via a non-canonical complex. Cell Rep. 2022;38(13): 110421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110421.
Sletten AC, Davidson JW, Yagabasan B, Moores S, Schwaiger-Haber M, Fujiwara H, et al. Loss of SNORA73 reprograms cellular metabolism and protects against steatohepatitis. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):5214. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25457-y.
Cui C, Liu Y, Gerloff D, Rohde C, Pauli C, Kohn M, et al. NOP10 predicts lung cancer prognosis and its associated small nucleolar RNAs drive proliferation and migration. Oncogene. 2021;40(5):909–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01570-y.
van der Werf J, Chin CV, Fleming NI. SnoRNA in cancer progression, metastasis and immunotherapy response. Biology. 2021;10(8):809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080809.
Shen L, Lin C, Lu W, He J, Wang Q, Huang Y, et al. Involvement of the oncogenic small nucleolar RNA SNORA24 in regulation of p53 stability in colorectal cancer. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-022-09765-7.
Chen S, Blank MF, Iyer A, Huang B, Wang L, Grummt I, et al. SIRT7-dependent deacetylation of the U3–55k protein controls pre-rRNA processing. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10734. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10734.
Zhou H, Yao Y, Li Y, Guo N, Zhang H, Wang Z, et al. Identification of small nucleolar RNA SNORD60 as a potential biomarker and its clinical significance in lung adenocarcinoma. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:5501171. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5501171.
Zhang Y, Shang X, Yu M, Bi Z, Wang K, Zhang Q, et al. A three-snoRNA signature: SNORD15A, SNORD35B and SNORD60 as novel biomarker for renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2023;23(1):136. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-023-02978-8.
Wu W, Chen X, Liu X, Bao HJ, Li QH, Xian JY, Chen S. SNORD60 promotes the tumorigenesis and progression of endometrial cancer through binding PIK3CA and regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol Carcinog. 2023;62(4):413–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.23495.
Kitagawa T, Taniuchi K, Tsuboi M, Sakaguchi M, Kohsaki T, Okabayashi T, et al. Circulating pancreatic cancer exosomal RNAs for detection of pancreatic cancer. Mol Oncol. 2019;13(2):212–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12398.
Song J, Zheng A, Li S, Zhang W, Zhang M, Li X, et al. Clinical significance and prognostic value of small nucleolar RNA SNORA38 in breast cancer. Front Oncol. 2022;12: 930024. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.930024.
Liu J, Liao X, Zhu X, Lv P, Li R. Identification of potential prognostic small nucleolar RNA biomarkers for predicting overall survival in patients with sarcoma. Cancer Med. 2020;9(19):7018–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.3361.
Ding Y, Sun Z, Zhang S, Xu Q, Zhou L, Zhou D, Wang W. Revealing the clinical significance and prognostic value of small nucleolar RNA SNORD31 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(7):BSR20201479.
Sun Y, Chen E, Li Y, Ye D, Cai Y, Wang Q, et al. H/ACA box small nucleolar RNA 7B acts as an oncogene and a potential prognostic biomarker in breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:125. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0830-1.
Wang K, Song X, Li X, Zhang Z, Xie L, Song X. Plasma SNORD83A as a potential biomarker for early diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2022;18(7):821–32. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2021-1278.
Funding
This work was funded via the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (no. ZR2023QH096), the Tai’an City Science and Technology Development Plan Project (2022NS332, 2022NS212) and the Nursery Project of the Affiliated Tai’an City Central Hospital of Qingdao University (no.2022MPM01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors participated in the project design, interpretation of results, data analysis, and manuscript review; ZJZ and XML designed the experiments; LL and QZ conducted the experiments; NY performed the statistical analysis; KYW and NY wrote the article. All authors have accepted the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The research conducted with human subjects underwent a thorough evaluation and received clearance from the Affiliated Taian City Central Hospital Committee of Qingdao University (approval number: 2023–05-10). Each participant provided their informed permission in compliance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Wang, K., Yuan, N. et al. Advancing NSCLC Diagnosis: The Role of Tumor-Derived Serum Exosomal SNORD60 as a Novel Biomarker. Ind J Clin Biochem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-024-01230-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-024-01230-y