Abstract
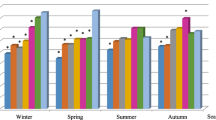
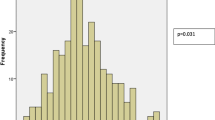
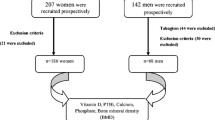
Many studies showed Vitamin D deficiency is highly prevalent in healthy individuals. We planned to study the normal levels of Vitamin D in healthy individuals and make recommendation for defining deficiency of 25(OH)D in Indian population. Normal healthy subjects 18 to 60 years of age were included. Estimation of serum calcium, serum phosphorus, iPTH and bone alkaline phosphatase levels with vitamin D (25(OH)D) levels were done to study the normal 25(OH)D levels and make recommendation for defining deficiency of 25(OH)D in Indian population. Meta-analysis was performed of studies which estimated the mean vitamin D levels in healthy individuals. There was significant positive correlation of serum 25(OH)D levels with calcium levels (r = 0.148; p-value = 0.003). The normal mean values of 25(OH)D levels in total population was 13.5 ± 7.83 ng/ml, iPTH was 59.8 ± 28.84 pg/ml, bone ALP was 14.6 ± 6.66 microg/ml. The normal upper bound of 25(OH)D in 97.5% of total population in our study is less than 33.19 ng/ml. The normal upper bound of iPTH and bone ALP in 97.5% of total population in our study was less than 123.97 pg/ml and 32.19 microg/ml, respectively. Pooled analysis of 33 studies revealed overall mean 25(OH)D levels in total population to be 13.95 ng/ml (95%CI – 12.37–15.54). The concept of initializing treatment based on serum Vitamin D levels using the RDA (20ng/ml) and EAR (16ng/ml) values as “cutoff-points” is not recommended as per Institute of Medicine Committee on Dietary Reference Intakes, Washington DC. Vitamin D levels less than 12.5ng/ml in a symptomatic individual should be the sole criteria for treatment rather than Vitamin D levels alone.
Trial Registration: CTRI/2018/02/011820; CTRI/2018/02/011913.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mithal A, Wahl DA, Bonjour JP, Burckhardt P, Dawson-Hughes B, Eisman JA, et al. Global vitamin D status and determinants of hypovitaminosis D. Osteoporos Int. 2009 Nov;20(11):1807–20.
van Schoor NM, Lips P. Worldwide vitamin D status. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Aug;25(4):671–80.
Aparna P, Muthathal S, Nongkynrih B, Gupta SK. Vitamin D deficiency in India. J Family Med Prim Care. 2018 Mar-Apr;7(2):324–30.
Institute of Medicine. Dietary reference intakes: calcium and vitamin D. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2011.
Manson JE, Brannon PM, Rosen CJ, Taylor CL. Vitamin D Deficiency - Is There Really a Pandemic? N Engl J Med. 2016 Nov;10(19):1817–20. 375(.
R Core Team. (2013). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL http://www.R-project.org/.
Marwaha RK, Tandon N, Reddy DR, Aggarwal R, Singh R, Sawhney RC, et al. Vitamin D and bone mineral density status of healthy schoolchildren in northern India. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005 Aug;82(2):477–82.
Tandon N, Marwaha RK, Kalra S, Gupta N, Dudha A, Kochupillai N. Bone mineral parameters in healthy young Indian adults with optimal vitamin D availability. Natl Med J India. 2003 Nov-Dec;16(6):298–302.
Marwaha RK, Tandon N, Reddy DH, Mani K, Puri S, Aggarwal N, et al. Peripheral bone mineral density and its predictors in healthy school girls from two different socioeconomic groups in Delhi. Osteoporos Int. 2007 Mar;18(3):375–83.
Marwaha RK, Puri S, Tandon N, Dhir S, Agarwal N, Bhadra K, et al. Effects of sports training & nutrition on bone mineral density in young Indian healthy females. Indian J Med Res. 2011 Sep;134:307–13.
Marwaha RK, Tandon N, Garg MK, Kanwar R, Narang A, Sastry A, et al. Bone health in healthy Indian population aged 50 years and above. Osteoporos Int. 2011 Nov;22(11):2829–36.
Shah S, Chiang C, Sikaris K, Lu Z, Bui M, Zebaze R, et al. Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Insufficiency in Search of a Bone Disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Jul 1;102(7):2321-8.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
All India Institute of Medical Sciences Jodhpur sponsored all the investigations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study design and planning of Study - All of the authors. Literature search - DJ, SS. Figures – SS, DJ. Tables – AE, DJ, SS. Data collection and analysis - SS, DJ. Data interpretation -, SS, DJ, AE. Writing - SS, AE, DJ. Corrections and Final approval of Manuscript - All of the authors. The corresponding author attests that all listed authors meet authorship criteria as per ICJME and that the manuscript is an honest, accurate, and transparent account of the study being reported.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval taken for study from All India Institute of Medical Sciences Jodhpur Ethics Committee - (IEC AIIMS/IEC/2017/737 and IEC AIIMS/IEC/2017/738).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of supporting data
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
Competing Interests
Dr. SINGH has nothing to disclose. Dr Jalan D has nothing to disclose. Dr Bhardwaj P has nothing to disclose. Dr. Sharma P has nothing to disclose. Dr. Elhence A has nothing to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Jalan, D., Bhardwaj, P. et al. Cross Sectional Study of Vitamin D Levels in Western Rajasthan and Meta-Analysis for Estimation of Vitamin D LevelsIn the PDF, in Header of all pages, Journal title should be abbreviated as "Ind J Clin Biochem". Ind J Clin Biochem (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-022-01074-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-022-01074-4