Abstract
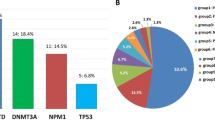
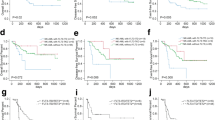
Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML) is one of the common forms of haematological malignancy in adults. We analysed the prevalence and clinical significance of FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) and Nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1) mutations in AML patients of North East India. Co-prevalence and clinical significance of three recurrent chromosomal translocations namely t(15; 17), t(8; 21), t(16; 16) and expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), flow markers were also documented and co-related with disease progress. We analysed bone marrow aspirates or peripheral blood samples from 165 newly diagnosed AML patients. All clinical samples were analysed by Real Time PCR and DNA sequencing based assays. NPM1 was the most frequently detected mutation in the study population (46/165 = 27.90%, 95% CI 20.75–35.05). FLT3 mutations were detected in 27/165 (16.40%, 95% CI 10.45–22.35) patients with internal tandem duplication (FLT3-ITD) in 24/165 (14.60%, 95% CI 8.91–20.29) and FLT3-D835 in 3/165 (1.80%, 95% CI 0–4.13) patients. NPM1 mutations were associated with a higher complete remission rate and longer overall survival (P < 0.01) compared to FLT3-ITD whereas FLT3-ITD showed adverse impact with poor survival rate (P < 0.01), leukocytosis (P < 0.01) and a packed bone marrow. EGFR expression was more in patients with NPM1 mutation compared to FLT3 mutation (P = 0.09). Patients with FLT3 and NPM1 mutations uniformly expressed CD13 and CD33 whereas CD34 was associated with poor prognosis (P ≤ 0.01) in patients with NPM1 mutation. FLT3-ITD was associated with inferior overall survival. However the clinical significance of FLT3-D835 was not clear due to small number of samples. NPM1 mutation showed better prognosis with increased response to treatment in the absence of FLT3-ITD.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FLT3:
-
FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3
- NPM1:
-
Nucleophosmin 1
References
Zhong L, Jia YQ, Meng WT, Ni X (2012) FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 internal tandem duplication and the patterns of its gene sequence in 207 Chinese patients with De novo acute myeloid leukemia. Arch Pathol Lab Med 136:84–89
Takahash S (2011) Current findings for recurring mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol 4:36
Chauhan PS, Ihsan R, Singh LC, Gupta DK, Mittal V, Kapur S (2013) Mutation of NPM1 and FLT3 genes in acute myeloid leukemia and their association with clinical and immunophenotypic features. Dis Mark 35:581–588
Kao HW, Liang DC, Wu JH, Kuo MC, Wang PN, Yang CP, Shih YS, Lin TH, Huang YH, Shih LY (2014) Gene mutation patterns in patients with minimally differentiated acute myeloid leukemia. Neoplasia 16:481–488
Levis M (2013) FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: what is the best approach in 2013? Hematology. Am Soc Hematol Educ Progr 2013:220–226
Elyamany G, Awad M, Fadalla K, Albalawi M, Shahrani MA, Abdulaaly AA (2014) Frequency and prognostic relevance of FLT3 mutations in saudi acute myeloid leukemia patients. Adv Hematol. doi:10.1155/2014/141360
Shamaa S, Laimon N, Aladle DA, Azmy E, Elghannam DM, Salem DA, Taalab MM (2014) Prognostic implications of NPM1 mutations and FLT3 internal tandem duplications in Egyptian patients with cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. Hematology 19:22–30
Licínio MA, Silva MCSD (2010) Importance of detecting FLT3 and NPM1 gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia—World Health Organization Classification 2008. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter 32:476–481
Wakim JJ, Tirado CA (2012) Acute promyelocytic leukemia lacking the classic translocation t(15; 17). In: Koschmieder S, Krug U (eds) Myeloid leukemia—clinical diagnosis and treatment. InTech, Shanghai, pp 219–234
Reikvam H, Hatfield KJ, Kittang AO, Hovland R, Bruserud Ø (2011) Acute myeloid leukemia with the t(8; 21) translocation: clinical consequences and biological implications. J Biomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1155/2011/104631
Schwind S, Edwards CG, Nicolet D, Mrózek K, Maharry K, Wu YZ, Paschka P, Eisfeld AK, Hoellerbauer P, Becker H, Metzeler KH, Curfman J, Kohlschmidt J, Prior TW, Kolitz JE, Blum W, Pettenati MJ, Dal Cin P, Carroll AJ, Caligiuri MA, Larson RA, Volinia S, Marcucci G, Bloomfield CD (2013) inv(16)/t(16;16) acute myeloid leukemia with non-type A CBFB-MYH11 fusions associate with distinct clinical and genetic features and lack KIT mutations. Blood 121:385–391
Sun JZ, Lu Y, Xu Y, Liu F, Li FQ, Wang QL, Wu CT, Hu XW, Duan HF (2012) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in acute myelogenous leukaemia is associated with clinical prognosis. Hematol Oncol 30:89–97
Angelescu S, Berbec NM, Colita A, Barbu D, Lupu AR (2012) Value of multifaced approach diagnosis and classification of acute leukemias. Maedica (Buchar) 7:254–260
Selicean EC, Patiu M, Cucuianu A, Dima D, Dobreanu M (2013) Correlation of cytomorphology with flowcytometric immunophenotyping in acute myeloid leukemia. Rom J Lab Med 21:333–341
Mir Mazloumi SH, Appaji L, Madhumathi DS, Kumari P (2013) G-banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization in childhood acute myeloid leukemia from South India. Arch Iran Med 16:459–462
Dong HY, Kung JX, Bhardwaj V, McGill J (2011) Flow cytometry rapidly identifies all acute promyelocytic leukemias with high specificity independent of underlying cytogenetic abnormalities. Am J Clin Pathol 135:76–84
Pazhakh V, Zaker F, Alimoghaddam K, Atashrazm F (2011) Detection of nucleophosmin and FMS-like tyrosine kinase-3 gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Saudi Med 31:45–50
Kassem N, Hamid AA, Attia T, Baathallah S, Mahmoud S, Moemen E, Safwat E, Khalaf M, Shaker O (2011) Novel mutations of the nucleophosmin (NPM-1) gene in Egyptian patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a pilot study. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst 23:73–78
Wang W, Wang XQ, Xu XP, Lin GW (2010) Prevalence and prognostic significance of FLT3 gene mutations in patients with acute leukaemia: analysis of patients from the shanghai leukaemia co-operative group. J Int Med Res 38:432–442
Cuervo-Sierra J, Gómez-Almaguer D, Jaime-Pérez JC, Martínez-Hernández RA, Sepúlveda RDG, Sánchez-Cárdenas M, Ortiz-López R, Ignacio-Ibarra G, Muciño-Hernández G, Arana-Trejo RM, Ruiz-Arguelles GJ, Ruiz-Delgado GJ, Lutz-Prestno J, Jiménez-Mejía A, Vásquez-Palacio G, Camargo-Guerrero M (2013) Prevalence of FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: a multicenter Latin America study. Blood 122:4979
Dunna NR, Rajappa S, Digumarti R, Vure S, Kagita S, Damineni S, Rao VR, Yadav SK, Ravuri RR, Satti V (2010) Fms like tyrosine kinase (FLT3) and nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1) mutations in de novo normal karyotype acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 11:1811–1816
Park BG, Chi HS, Park SJ, Min SK, Jang S, Park CJ, Kim DY, Lee JH, Lee JH, Lee KH (2012) Clinical implications of non-A-type NPM1 and FLT3 mutations in patients with normal karyotype acute myeloid leukemia. Acta Haematol 127:63–71
Koczkodaj D, Zmorzyński S, Michalak-Wojnowska M, Wąsik-Szczepanek E, Filip AA (2016) Examination of the FLT3 and NPM1 mutational status in patients with acute myeloid leukemia from southeastern Poland. Arch Med Sci 12:120–128
Al-Mawali A, Gillis D, Lewis I (2013) Characteristics and prognosis of adult acute myeloid leukemia with internal tandem duplication in the FLT3 gene. Oman Med J 28:432–440
Gari M, Abuzenadah A, Chaudhary A, Al-Qahtani M, Banni H, Ahmad W, Al-Sayes F, Lary S, Damanhouri G (2008) Detection of FLT3 oncogene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia using conformation sensitive gel electrophoresis. Int J Mol Sci 9:2194–2204
Thiede C, Koch S, Creutzig E, Steudel C, Illmer T, Schaich M, Ehninger G (2006) Prevalence and prognostic impact of NPM1 mutations in 1485 adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood 107:4011–4020
Wei H, Zhang YQ, Lin D, Wang Y, Zhou CL, Liu BC, Li W, Rao Q, Wang M, Mi YC, Wang JX (2014) Clinical characteristics of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia patients with NPM1 mutation. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 22:11–15
Boonthimat C, Thongnoppakhun W, Auewarakul CU (2008) Nucleophosmin mutation in Southeast Asian acute myeloid leukemia: eight novel variants, FLT3 coexistence and prognostic impact of NPM1/FLT3 mutations. Haematologica 93:1565–1569
Marshall RC, Tlagadi A, Bronze M, Kana V, Naidoo S, Wiggill TM, Carmona SC (2014) Lower frequency of NPM1 and FLT3-ITD mutations in a South African adult de novo AML cohort. Int J Lab Hematol 36:656–664
Zidan M, Shaaban H, Ghannam DE (2013) Prognostic impact of nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1) gene mutations in Egyptian acute myeloid leukemia patients. Turk J Haematol 30:129–136
Mrózek K (2008) Acute myeloid leukemia with a complex karyotype. Semin Oncol 35:365–377
Stölzel F, Mohr B, Kramer M, Oelschlägel U, Bochtler T, Berdel WE, Kaufmann M, Baldus CD, Schäfer-Eckart K, Stuhlmann R, Einsele H, Krause SW, Serve H, Hänel M, Herbst R, Neubauer A, Sohlbach K, Mayer J, Middeke JM, Platzbecker U, Schaich M, Krämer A, Röllig C, Schetelig J, Bornhäuser M, Ehninger G (2016) Karyotype complexity and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J. doi:10.1038/bcj.2015.114
Pratcorona M, Brunet S, Nomdedéu J, Ribera JM, Tormo M, Duarte R, Escoda L, Guàrdia R, Queipo de Llano MP, Salamero O, Bargay J, Pedro C, Martí JM, Torrebadell M, Díaz-Beyá M, Camós M, Colomer D, Hoyos M, Sierra J, Esteve J (2013) Favorable outcome of patients with acute myeloid leukemia harboring a low-allelic burden FLT3-ITD mutation and concomitant NPM1 mutation: relevance to post-remission therapy. Blood 121:2734–2738
Wu DP, Yan LZ, Yang L, Chen SN, Wu XJ, Liang JY (2007) A study of NPM1 and FLT3 gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. J Intern Med 46:907–910
Mały E, Przyborsk M, Nowak T, Nowak J, Januszkiewicz D (2010) FLT3 internal tandem duplication and FLT3-D835 mutation in 80 AML patients categorized into cytogenetic risk groups. Postepy Hig Med Dosw 64:466–470 (online)
Molica M, Breccia M (2015) FLT3-ITD in acute promyelocytic leukemia: clinical distinct profile but still controversial prognosis. Leuk Res 39:397–399
Breccia M, Loglisci G, Loglisci MG, Ricci R, Diverio D, Latagliata R, Foà R, Lo-Coco F (2013) FLT3-ITD confers poor prognosis in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with AIDA protocols: long-term follow-up analysis. Haematologica 98:161–163
Schnittger S, Bacher U, Haferlach C, Kern W, Alpermann T, Haferlach T (2011) Clinical impact of FLT3 mutation load in acute promyelocytic leukemia with t(15; 17)/PML–RARA. Haematologica 96:1799–1807
Kim YK, Kim HN, Lee IK, Bang SM, Jo DY, Won JH, Yim CY, Yang DH, Lee JJ, Kim HJ (2007) Prognostic significance of FLT3/ITD mutation in AML1/ETO-associated acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 110:3493
Bacher U, Haferlach C, Kern W, Haferlach T, Schnittger S (2008) Prognostic relevance of FLT3-TKD mutations in AML: the combination matters-an analysis of 3082 patients. Blood 111:2527–2537
Roti G, Rosati R, Bonasso R, Gorello P, Diverio D, Martelli MF, Falini B, Mecucci C (2006) Denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography: a valid approach for identifying NPM1 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. J Mol Diagn 8:254–259
Swaminathan S, Garg S, Madkaikar M, Gupta M, Jijina F, Ghosh K (2014) FLT3 and NPM-1 mutations in a cohort of acute promyelocytic leukemia patients from India. Indian J Hum Genet 20:160–165
Alpermann T, Schnittger S, Eder C, Dicker F, Meggendorfer M, Kern W, Schmid C, Aul C, Staib P, Wendtner CM, Schmitz N, Haferlach C, Haferlach T (2016) Molecular subtypes of NPM1 mutations have different clinical profiles, specific patterns of accompanying molecular mutations and varying outcomes in intermediate risk acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 101:55–58
Suzuki T, Kiyoi H, Ozeki K, Tomita A, Yamaji S, Suzuki R, Kodera Y, Miyawaki S, Asou N, Kuriyama K, Yagasaki F, Shimazaki C, Akiyama H, Nishimura M, Motoji T, Shinagawa K, Takeshita A, Ueda R, Kinoshita T, Emi N, Naoe T (2005) Clinical characteristics and prognostic implications of NPM1 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 106:2854–2861
Dang H, Chen Y, Kamel-Reid S, Brandwein J, Chang H (2013) CD34 expression predicts an adverse outcome in patients with NPM1-positive acute myeloid leukemia. Hum Pathol 44:2038–2046
Chen CY, Chou WC, Tsay W, Tang JL, Yao M, Huang SY, Tien HF (2013) Hierarchical cluster analysis of immunophenotype classify AML patients with NPM1 gene mutation into two groups with distinct prognosis. BMC Cancer 13:107
Stegmaie K, Corsello SM, Ross KN, Wong JS, Deangelo DJ, Golub TR (2005) Gefitinib induces myeloid differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 106:2841–2848
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India for their financial assistance for this project.
Funding
This study was financially supported by a grant from Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India (Grant Number BT/348/NE/TBP/2012).
Author Contributions
All authors listed have contributed to the work and agreed to submit the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
This study involves blood and bone marrow aspirates from AML patients. Ethical approval was obtained from institutional ethics committee (GUEC-12/2015) to conduct the study.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharyya, J., Nath, S., Saikia, K.K. et al. Prevalence and Clinical Significance of FLT3 and NPM1 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Patients of Assam, India. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 34, 32–42 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-017-0821-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-017-0821-0