Abstract
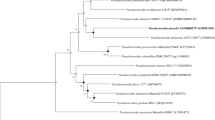
Two unknown Gram-stain-positive, catalase- and oxidasenegative, non-motile, and coccus-shaped bacteria, designated MN-17T and MN-09, were isolated from yaks faeces (Bos grunniens) in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China. 16S rRNA gene sequence-based comparative analyses revealed that the two strains were grouped within the genus Vagococcus, displaying the highest similarity with Vagococcus xieshaowenii CGMCC 1.16436T (98.6%) and Vagococcus elongatus CCUG 51432T (96.4%). Both strains grew optimally at 37°C and pH 7.0 in the presence of 0.5% (w/v) NaCl. The complete genome of MN-17T comprises 2,085 putative genes with a total of 2,190,262 bp and an average G + C content of 36.7 mol%. The major fatty acids were C16:0 (31.2%), C14:0 (28.5%), and C18:1ω9c (13.0%); the predominant respiratory quinone was MK-7 (68.8%); the peptidoglycan type was A4α(l-Lys-d-Asp); and the major polar lipid was diphosphatidylglycerol. Together, these supported the affiliation of strain MN-17T to the genus Vagococcus. In silico DNA-DNA hybridization and the average nucleotide identity values between MN-17T and all recognized species in the genus were 21.6–26.1% and 70.7–83.0%, respectively. MN-17T produced acid from d-cellobiose, d-fructose, glycerol, d-glucose, N-acetyl-glucosamine, gentiobiose, d-mannose, d-maltose, d-ribose, d-saccharose, salicin, d-trehalose, and d-xylose. These results distinguished MN-17T and MN-09 from closely related species in Vagococcus. Thus, we propose that strains MN-17T and MN-09 represent a novel species in the genus Vagococcus, with the name Vagococcus zengguangii sp. The type strain is MN-17T (= CGMCC 1.16726T = GDMCC 1.1589T = JCM 33478T).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W., and Lipman, D.J. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403–410.
Auch, A.F., von Jan, M., Klenk, H.P., and Göker, M. 2010. Digital DNA-DNA hybridization for microbial species delineation by means of genome-to-genome sequence comparison. Stand. Genomic Sci. 2, 117–134.
Austrian, R. 1960. The Gram stain and the etiology of lobar pneumonia, an historical note. Bacteriol. Rev. 24, 261–265.
Bai, X., Zhao, A., Lan, R., Xin, Y., Xie, H., Meng, Q., Jin, D., Yu, B., Sun, H., Lu, S., et al. 2013. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in yaks (Bos grunniens) from the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. PLoS ONE 8, e65537.
Bauer, A.W., Kirby, W.M., Sherris, J.C., and Turck, M. 1966. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 45, 493–496.
Berlin, K., Koren, S., Chin, C.S., Drake, J.P., Landolin, J.M., and Phillippy, A.M. 2015. Assembling large genomes with single-molecule sequencing and locality-sensitive hashing. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 623–630.
Chaudhari, N.M., Gupta, V.K., and Dutta, C. 2016. BPGA- an ultra-fast pan-genome analysis pipeline. Sci. Rep. 6, 24373.
Chen, C., Zhang, W., Zheng, H., Lan, R., Wang, H., Du, P., Bai, X., Ji, S., Meng, Q., Jin, D., et al. 2013. Minimum core genome sequence typing of bacterial pathogens: a unified approach for clinical and public health microbiology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 51, 2582–2591.
Collins, M.D., Ash, C., Farrow, J.A., Wallbanks, S., and Williams, A.M. 1989. 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid sequence analyses of lactococci and related taxa. Description of Vagococcus fluvialis gen. nov., sp. nov. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 67, 453–460.
Collins, M.D. and Jones, D. 1981. Distribution of isoprenoid quinone structural types in bacteria and their taxonomic implication. Microbiol. Rev. 45, 316–354.
Drancourt, M., Roux, V., Fournier, P.E., and Raoult, D. 2004. rpoB gene sequence-based identification of aerobic Gram-positive cocci of the genera Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Gemella, Abiotrophia, and Granulicatella. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42, 497–504.
Felsenstein, J. 1981. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 17, 368–376.
Felsenstein, J. 1985. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39, 783–791.
Garcia, V., Abat, C., and Rolain, J.M. 2016. Report of the first Vagococcus lutrae human infection, Marseille, France. New Microbes New Infect. 9, 56–57.
Ge, Y., Yang, J., Lai, X.H., Zhang, G., Jin, D., Lu, S., Wang, B., Huang, Y., Huang, Y., Ren, Z., et al. 2020. Vagococcus xieshaowenii sp. nov., isolated from snow finch (Montifringilla taczanowskii) cloacal content. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 70, 2493–2498.
Hoyles, L., Lawson, P.A., Foster, G., Falsen, E., Ohlén, M., Grainger, J.M., and Collins, M.D. 2000. Vagococcus fessus sp. nov., isolated from a seal and a harbour porpoise. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50, 1151–1154.
Jaffrès, E., Prévost, H., Rossero, A., Joffraud, J.J., and Dousset, X. 2010. Vagococcus penaei sp. nov., isolated from spoilage microbiota of cooked shrimp (Penaeus vannamei). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 60, 2159–2164.
Jin, D., Yang, J., Lu, S., Lai, X.H., Xiong, Y., and Xu, J. 2017. Enterococcus wangshanyuanii sp. nov., isolated from faeces of yaks (Bos grunniens). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 67, 5216–5221.
Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Hattori, M., Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F., Itoh, M., Kawashima, S., Katayama, T., Araki, M., and Hirakawa, M. 2006. From genomics to chemical genomics: new developments in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, D354–D357.
Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Kawashima, S., Okuno, Y., and Hattori, M. 2004. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, D277–D280.
Killer, J., Švec, P., Sedláček, I., Černohlávková, J., Benada, O., Hroncová, Z., Havlík, J., Vlková, E., Rada, V., Kopečný, J., et al. 2014. Vagococcus entomophilus sp. nov., from the digestive tract of a wasp (Vespula vulgaris). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64, 731–737.
Kimura, M. 1980. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotidesequences. J. Mol. Evol. 16, 111–120.
Kolaczkowski, B. and Thornton, J.W. 2004. Performance of maximum parsimony and likelihood phylogenetics when evolution is heterogeneous. Nature 431, 980–984.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., and Tamura, K. 2016. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33, 1870–1874.
Larkin, M.A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N.P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P.A., McWilliam, H., Valentin, F., Wallace, I.M., Wilm, A., Lopez, R., et al. 2007. Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23, 2947–2948.
Lawson, P.A., Falsen, E., Cotta, M.A., and Whitehead, T.R. 2007. Vagococcus elongatus sp. nov., isolated from a swine-manure storage pit. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 751–754.
Lawson, P.A., Foster, G., Falsen, E., Ohlén, M., and Collins, M.D. 1999. Vagococcus lutrae sp. nov., isolated from the common otter (Lutra lutra). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49, 1251–1254.
Li, D., Liu, C.M., Luo, R., Sadakane, K., and Lam, T.W. 2015. MEGAHIT: an ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 31, 1674–1676.
McLaughlin, R.W., Shewmaker, P.L., Whitney, A.M., Humrighouse, B.W., Lauer, A.C., Loparev, V.N., Gulvik, C.A., Cochran, P.A., and Dowd, S.E. 2017. Enterococcus crotali sp. nov., isolated from faecal material of a timber rattlesnake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 67, 1984–1989.
Meier-Kolthoff, J.P., Auch, A.F., Klenk, H.P., and Göker, M. 2013. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinformatics 14, 60.
Nahaie, M.R., Goodfellow, M., Minnikin, D.E., and Hájek, V. 1984. Polar lipid and isoprenoid quinone composition in the classification of Staphylococcus. J. Gen. Microbiol. 130, 2427–2437.
Naser, S.M., Thompson, F.L., Hoste, B., Gevers, D., Dawyndt, P., Vancanneyt, M., and Swings, J. 2005. Application of multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) for rapid identification of Enterococcus species based on rpoA and pheS genes. Microbiology 151, 2141–2150.
Price, M.N., Dehal, P.S., and Arkin, A.P. 2009. FastTree: computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 26, 1641–1650.
Rosselló-Móra, R. and Amann, R. 2015. Past and future species definitions for Bacteria and Archaea. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 38, 209–216.
Saitou, N. and Nei, M. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425.
Sasser, M. 1990. Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc., Newark, Delaware, USA.
Schleifer, K.H. and Kandler, O. 1972. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol. Rev. 36, 407–477.
Shewmaker, P.L., Steigerwalt, A.G., Morey, R.E., Carvalho, M.D.G.S., Elliott, J.A., Joyce, K., Barrett, T.J., Teixeira, L.M., and Facklam, R.R. 2004. Vagococcus carniphilus sp. nov., isolated from ground beef. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 54, 1505–1510.
Shewmaker, P.L., Whitney, A.M., Gulvik, C.A., Humrighouse, B.W., Gartin, J., Moura, H., Barr, J.R., Moore, E.R.B., Karlsson, R., Pinto, T.C.A., et al. 2019. Vagococcus bubulae sp. nov., isolated from ground beef, and Vagococcus vulneris sp. nov., isolated from a human foot wound. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 69, 2268–2276.
Sorroza, L., Padilla, D., Acosta, F., Román, L., Grasso, V., Vega, J., and Real, F. 2012. Characterization of the probiotic strain Vagococcus fluvialis in the protection of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) against vibriosis by Vibrio anguillarum. Vet. Microbiol. 155, 369–373.
Sundararaman, A., Srinivasan, S., and Lee, S.S. 2017. Vagococcus humatus sp. nov., isolated from soil beneath a decomposing pig carcass. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 67, 330–335.
Tak, E.J., Kim, H.S., Lee, J.Y., Kang, W., Hyun, D.W., Kim, P.S., Shin, N.R., and Bae, J.W. 2017. Vagococcus martis sp. nov., isolated from the small intestine of a marten, Martes flavigula. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 67, 3398–3402.
Teixeira, L.M., Carvalho, M.G., Merquior, V.L., Steigerwalt, A.G., Brenner, D.J., and Facklam, R.R. 1997. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Vagococcus fluvialis, including strains isolated from human sources. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35, 2778–2781.
Wallbanks, S., Martinez-Murcia, A.J., Fryer, J.L., Phillips, B.A., and Collins, M.D. 1990. 16S rRNA sequence determination for members of the genus Carnobacterium and related lactic acid bacteria and description of Vagococcus salmoninarum sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 40, 224–230.
Wang, L., Cui, Y.S., Kwon, C.S., Lee, S.T., Lee, J.S., and Im, W.T. 2011. Vagococcus acidifermentans sp. nov., isolated from an acidogenic fermentation bioreactor. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 61, 1123–1126.
Wu, Y.C., Lin, S.T., Guu, J.R., Tamura, T., Mori, K., Wang, L.T., Huang, L., and Watanabe, K. 2020. Vagococcus silagei sp. nov., isolated from brewer’s grain used to make silage in Taiwan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 70, 1953–1960.
Wullschleger, S., Jans, C., Seifert, C., Baumgartner, S., Lacroix, C., Bonfoh, B., Stevens, M.J.A., and Meile, L. 2018. Vagococcus teuberi sp. nov., isolated from the Malian artisanal sour milk fènè. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 41, 65–72.
Xu, Y., Xu, X., Lan, R., Xong, Y., Ye, C., Ren, Z., Liu, L., Zhao, A., Wu, L.F., and Xu, J. 2013. An O island 172 encoded RNA helicase regulates the motility of Escherichia coli O157:H7. PLoS ONE 8, e64211.
Yoon, S.H., Ha, S.M., Kwon, S., Lim, J., Kim, Y., Seo, H., and Chun, J. 2017a. Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 67, 1613–1617.
Yoon, S.H., Ha, S.M., Lim, J., Kwon, S., and Chun, J. 2017b. A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 110, 1281–1286.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Science and Technology Major Project of China (2018ZX10712001-018, 2017ZX10303405-002, 2017ZX10303405-002-005), National Science and Technology of China (2017FY101202), National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFC1200500 and 2019YFC1200505), Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (SZSM201811071) and Research Units of Discovery of Unknown Bacteria and Function (2018RU010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The ethical practice was approved by Ethical Committee of the National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (# ICDC-2016004).
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956. Copyright © 2021, The Microbiological Society of Korea
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that therd are no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
12275_2021_406_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary data Table S1. Characteristics that differentiate V. zengguangii sp. from other species in the genus Vagococcus
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, Y., Jin, D., Lai, XH. et al. Vagococcus zengguangii sp. nov., isolated from yak faeces. J Microbiol. 59, 1–9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-021-0406-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-021-0406-3