Abstract
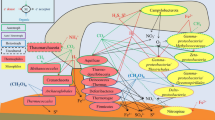
Methanogens are an important biogenic source of methane, especially in estuarine waters across a river-to-sea gradient. However, the diversity and trophic strategy of methanogens in this gradient are not clear. In this study, the diversity and trophic strategy of methanogens in sediments across the Yellow River (YR) to the Bohai Sea (BS) gradient were investigated by high-throughput sequencing based on the 16S rRNA gene. The results showed that the diversity of methanogens in sediments varied from multitrophic communities in YR samples to specific methylotrophic communities in BS samples. The methanogenic community in YR samples was dominated by Methanosarcina, while that of BS samples was dominated by methylotrophic Methanococcoides. The distinct methanogens suggested that the methanogenic community of BS sediments did not originate from YR sediment input. High-throughput sequencing of the mcrA gene revealed that active Methanococcoides dominated in the BS enrichment cultures with trimethylamine as the substrate, and methylotrophic Methanolobus dominated in the YR enrichment cultures, as detected to a limited amount in in situ sediment samples. Methanosarcina were also detected in this gradient sample. Furthermore, the same species of Methanosarcina mazei, which was widely distributed, was isolated from the area across a river-to-sea gradient by the culture-dependent method. In summary, our results showed that a distribution of diverse methanogens across a river-to-sea gradient may shed light on adaption strategies and survival mechanisms in methanogens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai, H., Yoshioka, R., Hanazawa, S., Minh, V.Q., Tuan, V.Q., Tinh, T.K., Phu, T.Q., Jha, C.S., Rodda, S.R., and Dadhwal, V.K. 2016. Function of the methanogenic community in mangrove soils as influenced by the chemical properties of the hydrosphere. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 62, 150–163.
Bagnara, C., Toci, R., Gaudin, C., and Belaich, J.P. 1985. Isolation and characterization of a cellulolytic microorganism, Cellulomonas fermentans sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 35, 502–507.
Capone, D.G. and Kiene, R.P. 1988. Comparison of microbial dynamics in marine and fresh-water sediments — contrasts in anaerobic carbon catabolism. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33, 725–749.
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Pena, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., and Gordon, J.I. 2010. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 7, 335–336.
Cauwet, G. and Mackenzie, F.T. 1993. Carbon inputs and distribution in estuaries of turbid rivers: the Yang Tze and Yellow Rivers (China). Mar. Chem. 43, 235–246.
Cavicchioli, R. 2007. Archaea: Molecular and cellular biology. ASM Press, USA.
Comte, J., Eiler, A., and Langenheder, S. 2014. Can marine bacteria be recruited from freshwater sources and the air? ISME J. 8, 2423–2430.
Conrad, R. 2009. The global methane cycle: recent advances in understanding the microbial processes involved. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 1, 285–292.
Crutzen, P.J. 1991. Methane’s sinks and sources. Nature 350, 380–381.
Dridi, B., Raoult, D., and Drancourt, M. 2012. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry identification of Archaea: towards the universal identification of living organisms. APMIS 120, 85–91.
Elberson, M.A. and Sowers, K.R. 1997. Isolation of an aceticlastic strain of Methanosarcina siciliae from marine canyon sediments and emendation of the species description for Methanosarcina siciliae. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47, 1258–1261.
Fan, X., Liang, Q., Niu, M., Yu, T., Wang, Y., and Wang, F. 2017. The diversity and richness of archaea in the northern continental slope of South China Sea. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 44, 1589–1601.
Fang, Q., Zhang, C.S., and Wang, X.L. 2010. Spatial distribution and influential factors for COD in the high frequency red tide area of the East China Sea. Periodical of Ocean University of China.
Gao, L., Yao, P., Wang, J., and Zhao, B. 2016. Distribution and sources of organic carbon in surface sediments from the Bohai Sea. Hai Yang Xue Bao 38, 8–20.
Großkopf, R., Stubner, S., and Liesack, W. 1998. Novel euryarchaeotal lineages detected on rice roots and in the anoxic bulk soil of flooded rice microcosms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 4983–4989.
Heděnec, P., Rui, J., Lin, Q., Yao, M., Li, J., Li, H., Frouz, J., and Li, X. 2017. Functional and phylogenetic response of soil prokaryotic community under an artificial moisture gradient. Appl. Soil Ecol. 124, 372–378.
Hedges, J.I. 2002. Why dissolved organics matter-chapter 1, pp. 1–33. In Biogeochemistry of marine dissolved organic matter. Elsevier Science, USA.
Hu, L., Shi, X., Bai, Y., Qiao, S., Li, L., Yu, Y., Yang, G., Ma, D., and Guo, Z. 2016. Recent organic carbon sequestration in the shelf sediments of the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea, China. J. Mar. Syst. 155, 50–58.
Jetten, M.S.M., Stams, A.J.M., and Zehnder, A.J.B. 1992. Methanogenesis from acetate: a comparison of the acetate metabolism in Methanothrix-soehngenii and Methanosarcina spp. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 88, 181–197.
Kantachote, D., Nunkaew, T., Kantha, T., and Chaiprapat, S. 2016. Biofertilizers from Rhodopseudomonas palustris strains to enhance rice yields and reduce methane emissions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 100, 154–161.
Kendall, M.M. and Boone, D.R. 2006. Cultivation of methanogens from shallow marine sediments at Hydrate Ridge, Oregon. Archaea 2, 31–38.
Kim, J., Yoo, G., Kim, D., Ding, W., and Kang, H. 2017. Combined application of biochar and slow-release fertilizer reduces methane emission but enhances rice yield by different mechanisms. Appl. Soil Ecol. 117–118, 57–62.
Lang, K., Schuldes, J., Klingl, A., Poehlein, A., Daniel, R., and Brune, A. 2014. Comparative genome analysis of “candidatus Methanoplasma termitum” indicates a new mode of energy metabolism in the seventh order of methanogens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81, 1338–1352.
Li, T., Wang, P., and Wang, P. 2008. Bacterial and archaeal diversity in surface sediment from the south slope of the South China Sea. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 48, 323–329.
Li, B., Yang, Y., Chen, J., Wu, Z., Liu, Y., and Xie, S. 2018. Nitrifying activity and ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in a constructed wetland treating polluted surface water. Sci. Total Environ. 628–629, 310–318.
Li, Y., Zhan, L., Zhang, J., Chen, L., Chen, J., and Zhuang, Y. 2017. A significant methane source over the Chukchi Sea shelf and its sources. Cont. Shelf Res. 148, 150–158.
Li, X., Zhang, W., Liu, T., Chen, L., Chen, P., and Li, F. 2016. Changes in the composition and diversity of microbial communities during anaerobic nitrate reduction and Fe(II) oxidation at circumneutral pH in paddy soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 94, 70–79.
Li, P., Zhang, G., Zhao, Y., and Liu, S. 2010. Study on distributions and flux of methane dissolved in the Bohai Sea in summer. Adv. Mar. Sci. 28, 478–488.
Liu, F. and Conrad, R. 2010. Thermoanaerobacteriaceae oxidize acetate in methanogenic rice field soil at 50°C. Environ. Microbiol. 12, 2341–2354.
Liu, F., Rotaru, A.E., Shrestha, P.M., Malvankar, N.S., Nevin, K.P., and Lovley, D.R. 2012. Promoting direct interspecies electron transfer with activated carbon. Energ. Environ. Sci. 5, 8982–8989.
Lueders, T., Chin, K.J., Conrad, R., and Friedrich, M. 2001. Molecular analyses of methyl-coenzyme M reductase a-subunit (mcrA) genes in rice field soil and enrichment cultures reveal the methanogenic phenotype of a novel archaeal lineage. Environ. Microbiol. 3, 194–204.
Maltby, J., Sommer, S., Dale, A.W., and Treude, T. 2016. Microbial methanogenesis in the sulfate-reducing zone of surface sediments traversing the Peruvian margin. Biogeosciences 13, 283–299.
Marmur, J. 1961. A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J. Mol. Biol. 3, 208–218.
Martin, J.M., Zhang, J., Shi, M.C., and Zhou, Q. 1993. Actual flux of the Huanghe (Yellow-River) sediment to the western pacificocean. Netherlands J. Sea Res. 31, 243–254.
Mckay, L.J., Hatzenpichler, R., Inskeep, W.P., and Fields, M.W. 2017. Occurrence and expression of novel methyl-coenzyme M reductase gene (mcrA) variants in hot spring sediments. Sci. Rep. 7, 7252.
Miller, T.L., Wolin, M.J., Conway, D.M.E., and Macario, A.J. 1982. Isolation of Methanobrevibacter smithii from human feces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 43, 227–232.
Moraes, L.E., Strathe, A.B., Fadel, J.G., Casper, D.P., and Kebreab, E. 2014. Prediction of enteric methane emissions from cattle. Glob. Chang. Biol. 20, 2140.
Oremland, R.S. and Polcin, S. 1982. Methanogenesis and sulfate reduction — competitive and noncompetitive substrates in estuarine sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 44, 1270–1276.
Pinto, A.J. and Raskin, L. 2012. PCR biases distort bacterial and archaeal community structure in pyrosequencing datasets. PLoS One 7, e43093.
Purdy, K.J., Munson, M.A., Cresswell-Maynard, T., Nedwell, D.B., and Embley, T.M. 2003. Use of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes to investigate function and phylogeny of sulphate-reducing bacteria and methanogenic archaea in a UK estuary. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 44, 361–371.
Qiao, S., Shi, X., Wang, G., Yang, G., Hu, N., Liu, S., Liu, Y., Zhu, A., and Li, C. 2010. Discussion on grain-size characteristics of sea-floor sediment and trasport pattern in the Bohai Sea. Hai Yang Xue Bao 32, 139–147.
Qu, X. and Chen, J. 2009. Analysis of the content of methylamine in DMF-recovered tannery wastewater. Ying Yong Hua Gong 38, 906–907, 910.
Ruf, T. and Emmerling, C. 2017. Impact of premature harvest of Miscanthus x giganteus for biogas production on organic residues, microbial parameters and earthworm community in soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 114, 74–81.
Sang, Y.K., Jeong, S.T., Ho, A., Chang, O.H., Chang, H.L., and Kim, P.J. 2017. Cattle manure composting: Shifts in the methanogenic community structure, chemical composition, and consequences on methane production potential in a rice paddy. Appl. Soil Ecol. 124, 344–350.
Shi, X.F. 2014. China ocean offshore-ocean bottom material. China Ocean Press. China.
Shrestha, P.M., Kube, M., Reinhardt, R., and Liesack, W. 2009. Transcriptional activity of paddy soil bacterial communities. Environ. Microbiol. 11, 960–970.
Smith, D.R., DoucetteStamm, L.A., Deloughery, C., Lee, H.M., Dubois, J., Aldredge, T., Bashirzadeh, R., Blakely, D., Cook, R., Gilbert, K., et al. 1997. Complete genome sequence of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum Delta H: Functional analysis and comparative genomics. J. Bacteriol. 179, 7135–7155.
Sprenger, W.W., Belzen, M.C.V., Rosenberg, J., Hackstein, J.H.P., and Keltjens, J.T. 2000. Methanomicrococcus blatticola gen. nov., sp. nov., a methanol- and methylamine-reducing methanogen from the hindgut of the cockroach Periplaneta americana. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50, 1989–1999.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., and Kumar, S. 2013. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 2725–2729.
Ticak, T., Hariraju, D., Arcelay, M.B., Arivett, B.A., Fiester, S.E., and Ferguson, D.J. 2015. Isolation and characterization of a tetramethylammonium-degrading Methanococcoides strain and a novel glycine betaine-utilizing Methanolobus strain. Arch. Microbiol. 197, 197–209.
van Lingen, H.J., Edwards, J.E., Vaidya, J.D., van Gastelen, S., Saccenti, E., van den Bogert, B., Bannink, A., Smidt, H., Plugge, C.M., and Dijkstra, J. 2017. Diurnal dynamics of gaseous and dissolved metabolites and microbiota composition in the bovine rumen. Front. Microbiol. 8, 425.
Vizza, C., West, W.E., Jones, S.E., Hart, J.A., and Lamberti, G.A. 2017. Regulators of coastal wetland methane production and responses to simulated global change. Biogeosciences 14, 431–446.
Waarde, A.V. 1988. Biochemistry of non-protein nitrogenous compounds in fish including the use of amino acids for anaerobic energy production. Comp. Biochem. Phys. 91, 207–228.
Wang, R., Tang, J., Xie, Z., Mi, W., Chen, Y., Wolschke, H., Tian, C., Pan, X., Luo, Y., and Ebinghaus, R. 2015. Occurrence and spatial distribution of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in 40 rivers draining into the Bohai Sea, North China. Environ. Pollut. 198, 172–178.
Wang, B., Zheng, S., Zhang, H., Wei, W., Wang, O., and Liu, F. 2017. Diversity of archaea in the sediments from different areas of the Bohai Sea. Hai Yang Xue Bao 41, 8–16.
Xiao, L., Liu, F., Liu, J., Li, J., Zhang, Y., Yu, J., and Wang, O. 2017. Nano-Fe3O4 particles accelerating electromethanogenesis on an hour-long timescale in wetland soil. Environ. Sci. Nano 5, 436–445.
Xing, L., Yang, S., Yin, Q., Xie, S., Strong, P.J., and Wu, G. 2017. Effects of carbon source on methanogenic activities and pathways incorporating metagenomic analysis of microbial community. Bioresour. Technol. 244, 982–988.
Yuan, J., Ding, W., Liu, D., Xiang, J., and Lin, Y. 2014. Methane production potential and methanogenic archaea community dynamics along the Spartina alterniflora invasion chronosequence in a coastal salt marsh. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98, 1817–1829.
Zehnder, A.J.B. and Wuhrmann, K. 1977. Physiology of a Methanobacterium strain AZ. Arch. Microbiol. 111, 199–205.
Zeikus, J.G., Ben-Bassat, A., and Hegge, P.W. 1980. Microbiology of methanogenesis in thermal, volcanic environments. J. Bacteriol. 143, 432–440.
Zheng, S., Zhang, H., Li, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, O., Zhang, J., and Liu, F. 2015. Co-occurrence of Methanosarcina mazei and Geobacteraceae in an iron (III)-reducing enrichment culture. Front. Microbiol. 6, 941.
Zinder, S.H. 1993. Physiological ecology of methanogens. Springer, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Liu, F., Zheng, S. et al. Trophic strategy of diverse methanogens across a river-to-sea gradient. J Microbiol. 57, 470–478 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-019-8482-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-019-8482-3