Abstract
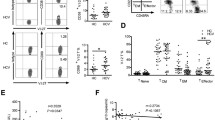
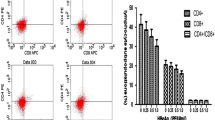
Chronic HBV infection is the leading cause of liver cirrhosis and hepatic cancer, but the individual responses toward HBV infection are highly variable, ranging from asymptomatic to chronic active hepatitis B inflammation. In this study, we hypothesized that the different individual responses to HBV infection was associated with differences in HBV-specific CD8+ T cell-mediated inflammation and cytotoxicity. Blood samples were collected from subjects with asymptomatic HBV-infection, subjects undergoing active chronic HBV flares (active CHB), and subjects with HBV-infected hepatocellular carcinoma (HBV-HCC). By tetramer staining, we found that all three groups had similar frequencies of HBVspecific CD8+ T cells. However, after HBV peptide stimulation, the HBV-specific CD8+ T cells in asymptomatic subjects had significantly stronger interferon gamma (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and CD107a expression than those in active CHB and HBV-HCC patients. Examination of surface marker expression revealed that the PD-1-Tim-3- double-negative cell population was the main contributor to HBV-specific inflammation. In active CHB patients and HBV-HCC patients, however, the frequencies of activated PD-1-Tim-3- cells were significantly reduced. Moreover, the serum HBV DNA titer was not correlated with the frequencies of HBV-specific CD8+ T cells but was inversely correlated with the frequencies of IFN-g-expressing and CD107a-express cells in response to HBV stimulation. Together, our data demonstrated that the status of HBVspecific CD8+ T cell exhaustion was associated with different clinical outcomes of chronic HBV infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alter, G., Malenfant, J.M., and Altfeld, M. 2004. CD107a as a functional marker for the identification of natural killer cell activity. J. Immunol. Methods 294, 15–22.
Altman, J.D., Moss, P.A.H., Goulder, P.J.R., Barouch, D.H., Mc-Heyzer-Williams, M.G., Bell, J.I., McMichael, A.J., and Davis, M.M. 1996. Phenotypic analysis of antigen-specific T lymphocytes. Science 274, 94–96.
Anderson, A.C. 2012. Tim-3, a negative regulator of anti-tumor immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 24, 213–216.
Betts, M.R., Brenchley, J.M., Price, D.A., De Rosa, S.C., Douek, D.C., Roederer, M., and Koup, R.A. 2003. Sensitive and viable identification of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells by a flow cytometric assay for degranulation. J. Immunol. Methods 281, 65–78.
Boni, C., Fisicaro, P., Valdatta, C., Amadei, B., Di Vincenzo, P., Giuberti, T., Laccabue, D., Zerbini, A., Cavalli, A., Missale, G., et al. 2007. Characterization of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific T-cell dysfunction in chronic HBV infection. J. Virol. 81, 4215–4225.
Boni, C., Penna, A., Bertoletti, A., Lamonaca, V., Rapti, I., Missale, G., Pilli, M., Urbani, S., Cavalli, A., Cerioni, S., et al. 2003. Transient restoration of anti-viral T cell responses induced by lamivudine therapy in chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 39, 595–605.
Chen, C.J. 2006. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 295, 65–73.
Diehl, L., Schurich, A., Grochtmann, R., Hegenbarth, S., Chen, L., and Knolle, P.A. 2007. Tolerogenic maturation of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells promotes B7-homolog 1-dependent CD8+ T cell tolerance. Hepatology 47, 296–305.
Ferrari, C., Penna, A., Bertoletti, A., and Fiaccadori, F. 1993. Cell mediated immune response to hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid antigen. Arch. Virol. Sup. 8, 91–101.
Fife, B.T. and Pauken, K.E. 2011. The role of the PD-1 pathway in autoimmunity and peripheral tolerance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1217, 45–59.
Francisco, L.M., Sage, P.T., and Sharpe, A.H. 2010. The PD-1 pathway in tolerance and autoimmunity. Immunol. Rev. 236, 219–242.
Golden-Mason, L., Palmer, B.E., Kassam, N., Townshend-Bulson, L., Livingston, S., McMahon, B.J., Castelblanco, N., Kuchroo, V., Gretch, D.R., and Rosen, H.R. 2009. Negative immune regulator Tim-3 is overexpressed on T cells in hepatitis C virus infection and its blockade rescues dysfunctional CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. J. Virol. 83, 9122–9130.
Ha, S.J., West, E.E., Araki, K., Smith, K.A., and Ahmed, R. 2008. Manipulating both the inhibitory and stimulatory immune system towards the success of therapeutic vaccination against chronic viral infections. Immunol. Rev. 223, 317–333.
Iwai, Y., Terawaki, S., Ikegawa, M., Okazaki, T., and Honjo, T. 2003. PD-1 inhibits antiviral immunity at the effector phase in the liver. J. Exp. Med. 198, 39–50.
Jones, R.B., Ndhlovu, L.C., Barbour, J.D., Sheth, P.M., Jha, A.R., Long, B.R., Wong, J.C., Satkunarajah, M., Schweneker, M., Chapman, J.M., et al. 2008. Tim-3 expression defines a novel population of dysfunctional T cells with highly elevated frequencies in progressive HIV-1 infection. J. Exp. Med. 205, 2763–2779.
Kao, J.H. and Chen, D.S. 2002. Global control of hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2, 395–403.
Knolle, P., Schlaak, J., Uhrig, A., Kempf, P., zum B- schenfelde, K.H.M., and Gerken, G. 1995. Human Kupffer cells secrete IL-10 in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge. J. Hepatol. 22, 226–229.
Kremsdorf, D., Soussan, P., Paterlini-Brechot, P., and Brechot, C. 2006. Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: paradigms for viral-related human carcinogenesis. Oncogene 25, 3823–3833.
Li, H., Wu, K., Tao, K., Chen, L., Zheng, Q., Lu, X., Liu, J., Shi, L., Liu, C., Wang, G., et al. 2012. Tim-3/galectin-9 signaling pathway mediates T-cell dysfunction and predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 56, 1342–1351.
Lok, A.S.F. and McMahon, B.J. 2007. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 45, 507–539.
Maini, M.K., Boni, C., Lee, C.K., Larrubia, J.R., Reignat, S., Ogg, G.S., King, A.S., Herberg, J., Gilson, R., Alisa, A., et al. 2000. The role of virus-specific CD8+ cells in liver damage and viral control during persistent hepatitis B virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 191, 1269–1280.
McMahan, R.H., Golden-Mason, L., Nishimura, M.I., McMahon, B.J., Kemper, M., Allen, T.M., Gretch, D.R., and Rosen, H.R. 2010. Tim-3 expression on PD-1+ HCV-specific human CTLs is associated with viral persistence, and its blockade restores hepatocyte-directed in vitro cytotoxicity. J. Clin. Invest. 120, 4546–4557.
Mengshol, J.A., Golden-Mason, L., Arikawa, T., Smith, M., Niki, T., McWilliams, R., Randall, J.A., McMahan, R., Zimmerman, M.A., Rangachari, M., et al. 2010. A crucial role for kupffer cell-derived galectin-9 in regulation of T cell immunity in hepatitis C infection. PLoS One 5, e9504.
Moorman, J.P., Wang, J.M., Zhang, Y., Ji, X.J., Ma, C.J., Wu, X.Y., Jia, Z.S., Wang, K.S., and Yao, Z.Q. 2012. Tim-3 pathway controls regulatory and effector T cell balance during hepatitis C virus infection. J. Immunol. 189, 755–766.
Nebbia, G., Peppa, D., Schurich, A., Khanna, P., Singh, H.D., Cheng, Y., Rosenberg, W., Dusheiko, G., Gilson, R., ChinAleong, J., et al. 2012. Upregulation of the Tim-3/Galectin-9 pathway of T cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. PLoS One 7, e47648.
Phillips, S., Chokshi, S., Riva, A., Evans, A., Williams, R., and Naoumov, N.V. 2010. CD8(+) T cell control of hepatitis B virus replication: Direct comparison between cytolytic and noncytolytic functions. J. Immunol. 184, 287–295.
Popov, A., Abdullah, Z., Wickenhauser, C., Saric, T., Driesen, J., Hanisch, F.G., Domann, E., Raven, E.L., Dehus, O., Hermann, C., et al. 2006. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing dendritic cells form suppurative granulomas following Listeria monocytogenes infection. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 3160–3170.
Protzer, U., Maini, M.K., and Knolle, P.A. 2012. Living in the liver: hepatic infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 12, 201–213.
Publicover, J., Goodsell, A., Nishimura, S., Vilarinho, S., Wang, Z.e., Avanesyan, L., Spolski, R., Leonard, W.J., Cooper, S., and Baron, J.L. 2011. IL-21 is pivotal in determining age-dependent effectiveness of immune responses in a mouse model of human hepatitis B. J. Clin. Invest. 121, 1154–1162.
Rehermann, B., Ferrari, C., Pasquinelli, C., and Chisari, F.V. 1996. The hepatitis B virus persists for decades after patients- recovery from acute viral hepatitis despite active maintenance of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response. Nat. Med. 2, 1104–1108.
Rehermann, B., Fowler, P., Sidney, J., Person, J., Redeker, A., Brown, M., Moss, B., Sette, A., and Chisari, F.V. 1995. The cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to multiple hepatitis B virus polymerase epitopes during and after acute viral hepatitis. J. Exp. Med. 181, 1047–1058.
Rehermann, B. and Nascimbeni, M. 2005. Immunology of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5, 215–229.
Thimme, R., Wieland, S., Steiger, C., Ghrayeb, J., Reimann, K.A., Purcell, R.H., and Chisari, F.V. 2003. CD8+ T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 77, 68–76.
Thomson, A.W. and Knolle, P.A. 2010. Antigen-presenting cell function in the tolerogenic liver environment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 10, 753–766.
Virgin, H.W., Wherry, E.J., and Ahmed, R. 2009. Redefining chronic viral infection. Cell 138, 30–50.
Wang, L.I.N., Zhao, C., Peng, Q., Shi, J., and Gu, G. 2014. Expression levels of CD28, CTLA-4, PD-1 and Tim-3 as novel indicators of T-cell immune function in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Biomed. Rep. 2, 270–274.
Wherry, E.J. 2011. T cell exhaustion. Nat. Immunol. 131, 492–499.
Wherry, E.J., Ha, S.J., Kaech, S.M., Haining, W.N., Sarkar, S., Kalia, V., Subramaniam, S., Blattman, J.N., Barber, D.L., and Ahmed, R. 2007. Molecular signature of CD8+ T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection. Immunity 27, 670–684.
Wirth, T.C., Xue, H.H., Rai, D., Sabel, J.T., Bair, T., Harty, J.T., and Badovinac, V.P. 2010. Repetitive antigen stimulation induces stepwise transcriptome diversification but preserves a core signature of memory CD8+ T cell differentiation. Immunity 33, 128–140.
Wu, W., Shi, Y., Li, J., Chen, F., Chen, Z., and Zheng, M. 2011. Tim-3 expression on peripheral T cell subsets correlates with disease progression in hepatitis B infection. Virol. J. 8, 113.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinney, C.M., Zhao, LD., Conrad, C.D. et al. Regulation of HBV-specific CD8+ T cell-mediated inflammation is diversified in different clinical presentations of HBV infection. J Microbiol. 53, 718–724 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-015-5314-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-015-5314-y