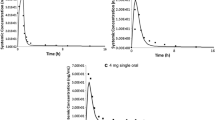
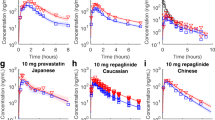
Abstract
Pitavastatin, a potent 3-hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor, is indicated for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia. Hepatic uptake of pitavastatin is predominantly occupied by the organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1) and solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B1 (SLCO1B1) gene, which is a polymorphic gene that encodes OATP1B1. SLCO1B1 genetic polymorphism significantly alters the pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin. This study aimed to establish the physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model to predict pitavastatin pharmacokinetics according to SLCO1B1 genetic polymorphism. PK-Sim® version 10.0 was used to establish the whole-body PBPK model of pitavastatin. Our pharmacogenomic data and a total of 27 clinical pharmacokinetic data with different dose administration and demographic properties were used to develop and validate the model, respectively. Physicochemical properties and disposition characteristics of pitavastatin were acquired from previously reported data or optimized to capture the plasma concentration–time profiles in different SLCO1B1 diplotypes. Model evaluation was performed by comparing the predicted pharmacokinetic parameters and profiles to the observed data. Predicted plasma concentration–time profiles were visually similar to the observed profiles in the non-genotyped populations and different SLCO1B1 diplotypes. All fold error values for AUC and Cmax were included in the two fold range of observed values. Thus, the PBPK model of pitavastatin in different SLCO1B1 diplotypes was properly established. The present study can be useful to individualize the dose administration strategy of pitavastatin in individuals with various ages, races, and SLCO1B1 diplotypes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abe T, Kakyo M, Tokui T, Nakagomi R, Nishio T, Nakai D, Nomura H, Unno M, Suzuki M, Naitoh T, Matsuno S, Yawo H (1999) Identification of a novel gene family encoding human liver-specific organic anion transporter LST-1. J Biol Chem 274(24):17159–17163. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.24.17159
Ando H, Tsuruoka S, Yanagihara H, Sugimoto K, Miyata M, Yamazoe Y, Takamura T, Kaneko S, Fujimura A (2005) Effects of grapefruit juice on the pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin and atorvastatin. Br J Clin Pharmacol 60(5):494–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02462.x
Bae JW, Oh KY, Yoon SJ, Shin HB, Jung EH, Cho CK, Lim CW, Kang P, Choi CI, Jang CG, Lee SY, Lee YJ (2020) Effects of CYP2D6 genetic polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of metoclopramide. Arch Pharm Res 43(11):1207–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-020-01293-4
Byeon JY, Lee CM, Lee YJ, Kim YH, Kim SH, Jung EH, Chae WK, Lee YJ, Jang CG, Lee SY (2019) Influence of CYP2D6 genetic polymorphism on pharmacokinetics of active moiety of tolterodine. Arch Pharm Res 42(2):182–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-018-1099-y
Byeon JY, Cho CK, Kang P, Kim SH, Jang CG, Lee SY, Lee YJ (2023) Effects of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms and cigarette smoking on the pharmacokinetics of tolperisone. Arch Pharm Res 46(8):713–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-023-01462-1
Chen Y, Zhang W, Huang WH, Tan ZR, Wang YC, Huang X, Zhou HH (2013) Effect of a single-dose rifampin on the pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 69(11):1933–1938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-013-1554-0
Cho CK, Kang P, Park HJ, Lee YJ, Bae JW, Jang CG, Lee SY (2021a) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modelling of tamsulosin related to CYP2D6*10 allele. Arch Pharm Res 44(11):1037–1049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01357-z
Cho CK, Park HJ, Kang P, Moon S, Lee YJ, Bae JW, Jang CG, Lee SY (2021b) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling of meloxicam in different CYP2C9 genotypes. Arch Pharm Res 44(12):1076–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01361-3
Cho CK, Kang P, Park HJ, Ko E, Mu CY, Lee YJ, Choi CI, Kim HS, Jang CG, Bae JW, Lee SY (2022) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling of piroxicam with regard to CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism. Arch Pharm Res 45(5):352–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-022-01388-0
Cho CK, Byeon JY, Kang P, Park HJ, Ko E, Mu CY, Jang CG, Lee SY, Lee YJ (2023a) Effects of CYP2C19 genetic polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of tolperisone in healthy subjects. Arch Pharm Res 46(2):111–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-022-01423-0
Cho CK, Byeon JY, Kang P, Park JI, Jang CG, Lee SY, Choi CI, Bae JW, Lee YJ (2023b) Effects of CYP2D6*10 allele on the pharmacokinetics of tolperisone. Arch Pharm Res 46(1):59–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-022-01422-1
Choi CI, Lee YJ, Lee HI, Kim BH, Kim MJ, Jang CG, Bae JW, Lee SY (2012) Effects of the SLCO1B1*15 allele on the pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin. Xenobiotica 42(5):496–501. https://doi.org/10.3109/00498254.2011.632030
Chung JY, Cho JY, Yu KS, Kim JR, Oh DS, Jung HR, Lim KS, Moon KH, Shin SG, Jang IJ (2005) Effect of OATP1B1 (SLCO1B1) variant alleles on the pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 78(4):342–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clpt.2005.07.003
Cooper-DeHoff RM, Niemi M, Ramsey LB, Luzum JA, Tarkiainen EK, Straka RJ, Gong L, Tuteja S, Wilke RA, Wadelius M, Larson EA, Roden DM, Klein TE, Yee SW, Krauss RM, Turner RM, Palaniappan L, Gaedigk A, Giacomini KM, Caudle KE, Voora D (2022) The clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and statin-associated musculoskeletal symptoms. Clin Pharmacol Ther 111(5):1007–1021. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.2557
Cui Y, König J, Leier I, Buchholz U, Keppler D (2001) Hepatic uptake of bilirubin and its conjugates by the human organic anion transporter SLC21A6. J Biol Chem 276(13):9626–9630. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M004968200
Deng JW, Song IS, Shin HJ, Yeo CW, Cho DY, Shon JH, Shin JG (2008) The effect of SLCO1B1*15 on the disposition of pravastatin and pitavastatin is substrate dependent: the contribution of transporting activity changes by SLCO1B1*15. Pharmacogenet Genomics 18(5):424–433. https://doi.org/10.1097/FPC.0b013e3282fb02a3
Duan P, Zhao P, Zhang L (2017) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling of pitavastatin and atorvastatin to predict drug-drug interactions (DDIs). Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 42(4):689–705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-016-0383-9
Fujino H, Yamada I, Shimada S, Yoneda M, Kojima J (2003) Metabolic fate of pitavastatin, a new inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase: human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes involved in lactonization. Xenobiotica 33(1):27–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/0049825021000017957
Fujino H, Nakai D, Nakagomi R, Saito M, Tokui T, Kojima J (2004) Metabolic stability and uptake by human hepatocytes of pitavastatin, a new inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase. Arzneimittelforschung 54(7):382–388. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1296988
Hirano M, Maeda K, Shitara Y, Sugiyama Y (2004) Contribution of OATP2 (OATP1B1) and OATP8 (OATP1B3) to the hepatic uptake of pitavastatin in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 311(1):139–146. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.104.068056
Hirano M, Maeda K, Matsushima S, Nozaki Y, Kusuhara H, Sugiyama Y (2005) Involvement of BCRP (ABCG2) in the biliary excretion of pitavastatin. Mol Pharmacol 68(3):800–807. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.105.014019
Hu M, Mak VW, Yin OQ, Chu TT, Tomlinson B (2013) Effects of grapefruit juice and SLCO1B1 388A>G polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 28(2):104–108. https://doi.org/10.2133/dmpk.dmpk-12-rg-067
Hui CK, Cheung BM, Lau GK (2005) Pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin in subjects with Child-Pugh A and B cirrhosis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 59(3):291–297. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.02251.x
Ieiri I, Suwannakul S, Maeda K, Uchimaru H, Hashimoto K, Kimura M, Fujino H, Hirano M, Kusuhara H, Irie S, Higuchi S, Sugiyama Y (2007) SLCO1B1 (OATP1B1, an uptake transporter) and ABCG2 (BCRP, an efflux transporter) variant alleles and pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 82(5):541–547. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.clpt.6100190
Jung JA, Noh YH, Jin S, Kim MJ, Kim YH, Jung JA, Lim HS, Bae KS (2012) Pharmacokinetic interaction between pitavastatin and valsartan: a randomized, open-labeled crossover study in healthy male Korean volunteers. Clin Ther 34(4):958–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.01.026
Jung EH, Cho CK, Kang P, Park HJ, Lee YJ, Bae JW, Choi CI, Jang CG, Lee SY (2021) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling of candesartan related to CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism in adult and pediatric patients. Arch Pharm Res 44(12):1109–1119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01363-1
Kalliokoski A, Niemi M (2009) Impact of OATP transporters on pharmacokinetics. Br J Pharmacol 158(3):693–705. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00430.x
Kameyama Y, Yamashita K, Kobayashi K, Hosokawa M, Chiba K (2005) Functional characterization of SLCO1B1 (OATP-C) variants, SLCO1B1*5, SLCO1B1*15 and SLCO1B1*15+ C1007G, by using transient expression systems of HeLa and HEK293 cells. Pharmacogenet Genomics 15(7):513–522. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.fpc.0000170913.73780.5f
Kamiya Y, Omura A, Hayasaka R, Saito R, Sano I, Handa K, Ohori J, Kitajima M, Shono F, Funatsu K, Yamazaki H (2021) Prediction of permeability across intestinal cell monolayers for 219 disparate chemicals using in vitro experimental coefficients in a pH gradient system and in silico analyses by trivariate linear regressions and machine learning. Biochem Pharmacol 192:114749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114749
Kang P, Cho CK, Jang CG, Lee SY, Lee YJ, Choi CI, Bae JW (2023) Effects of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of gliclazide in healthy subjects. Arch Pharm Res 46(5):438–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-023-01448-z
Kim EY, Cho DY, Shin HJ, Lee SS, Shon JH, Shin JG, Shin SG (2008) Duplex pyrosequencing assay of the 388A>G and 521T>C SLCO1B1 polymorphisms in three Asian populations. Clin Chim Acta 388(1–2):68–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2007.10.010
Kim SH, Byeon JY, Kim YH, Lee CM, Lee YJ, Jang CG, Lee SY (2018) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling of atomoxetine with regard to CYP2D6 genotypes. Sci Rep 8(1):12405. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30841-8
Kim YH, Kang P, Cho CK, Jung EH, Park HJ, Lee YJ, Bae JW, Jang CG, Lee SY (2021) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling for prediction of celecoxib pharmacokinetics according to CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism. Arch Pharm Res 44(7):713–724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01346-2
Kim NT, Cho CK, Kang P, Park HJ, Lee YJ, Bae JW, Jang CG, Lee SY (2022) Effects of CYP2C9*3 and *13 alleles on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of glipizide in healthy Korean subjects. Arch Pharm Res 45(2):114–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01366-y
Kolesnikov N, Hastings E, Keays M, Melnichuk O, Tang YA, Williams E, Dylag M, Kurbatova N, Brandizi M, Burdett T, Megy K, Pilicheva E, Rustici G, Tikhonov A, Parkinson H, Petryszak R, Sarkans U, Brazma A (2015) ArrayExpress update–simplifying data submissions. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D1113–D1116. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1057
König J, Cui Y, Nies AT, Keppler D (2000) A novel human organic anion transporting polypeptide localized to the basolateral hepatocyte membrane. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 278(1):G156–G164. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.2000.278.1.G156
Kuepfer L, Niederalt C, Wendl T, Schlender JF, Willmann S, Lippert J, Block M, Eissing T, Teutonico D (2016) Applied concepts in PBPK modeling: how to build a PBPK/PD model. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol 5(10):516–531. https://doi.org/10.1002/psp4.12134
Lee CM, Kang P, Cho CK, Park HJ, Lee YJ, Bae JW, Choi CI, Kim HS, Jang CG, Lee SY (2022) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling to predict the pharmacokinetics of metoprolol in different CYP2D6 genotypes. Arch Pharm Res 45(6):433–445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-022-01394-2
Li R, Barton HA (2018) Explaining ethnic variability of transporter substrate pharmacokinetics in healthy Asian and Caucasian subjects with allele frequencies of OATP1B1 and BCRP: a mechanistic modeling analysis. Clin Pharmacokinet 57(4):491–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-017-0568-7
Link E, Parish S, Armitage J, Bowman L, Heath S, Matsuda F, Gut I, Lathrop M, Collins R (2008) SLCO1B1 variants and statin-induced myopathy–a genomewide study. N Engl J Med 359(8):789–799. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0801936
Liu JE, Liu XY, Chen S, Zhang Y, Cai LY, Yang M, Lai WH, Ren B, Zhong SL (2017) SLCO1B1 521T> C polymorphism associated with rosuvastatin-induced myotoxicity in Chinese coronary artery disease patients: a nested case–control study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 73(11):1409–1416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-017-2318-z
Lu B, Sun L, Seraydarian M, Hoffmann TJ, Medina MW, Risch N, Iribarren C, Krauss RM, Oni-Orisan A (2021) Effect of SLCO1B1 T521C on statin-related myotoxicity with use of lovastatin and atorvastatin. Clin Pharmacol Ther 110(3):733–740. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.2337
Luo Z, Zhang Y, Gu J, Feng P, Wang Y (2015) Pharmacokinetic properties of single- and multiple-dose pitavastatin calcium tablets in healthy Chinese volunteers. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp 77:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.curtheres.2015.02.001
Michalski C, Cui Y, Nies AT, Nuessler AK, Neuhaus P, Zanger UM, Klein K, Eichelbaum M, Keppler D, Konig J (2002) A naturally occurring mutation in the SLC21A6 gene causing impaired membrane localization of the hepatocyte uptake transporter. J Biol Chem 277(45):43058–43063. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M207735200
Morgan RE, Campbell SE, Yu CY, Sponseller CA, Muster HA (2012) Comparison of the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetic profile of a single oral dose of pitavastatin 4 mg in adult subjects with severe renal impairment not on hemodialysis versus healthy adult subjects. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 60(1):42–48. https://doi.org/10.1097/FJC.0b013e318256cdf0
Mori D, Kashihara Y, Yoshikado T, Kimura M, Hirota T, Matsuki S, Maeda K, Irie S, Ieiri I, Sugiyama Y, Kusuhara H (2019) Effect of OATP1B1 genotypes on plasma concentrations of endogenous OATP1B1 substrates and drugs, and their association in healthy volunteers. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 34(1):78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dmpk.2018.09.003
Mukhtar R, Reid J, Reckless J (2005) Pitavastatin. Int J Clin Pract 59(2):239–252. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2005.00461.x
National Center for Biotechnology Information (2010) Expressed sequence tags (EST) from UniGene. https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/repository/UniGene/. Accessed 03 Apr 2023
Nishimura M, Naito S (2005) Tissue-specific mRNA expression profiles of human ATP-binding cassette and solute carrier transporter superfamilies. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 20(6):452–477. https://doi.org/10.2133/dmpk.20.452
Nishimura M, Naito S (2006) Tissue-specific mRNA expression profiles of human phase I metabolizing enzymes except for cytochrome P450 and phase II metabolizing enzymes. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 21(5):357–374. https://doi.org/10.2133/dmpk.21.357
Nishimura M, Yaguti H, Yoshitsugu H, Naito S, Satoh T (2003) Tissue distribution of mRNA expression of human cytochrome P450 isoforms assessedby high-sensitivity real-time reverse transcription PCR. Yakugaku Zasshi 123(5):369–375. https://doi.org/10.1248/yakushi.123.369
Nozawa T, Nakajima M, Tamai I, Noda K, Nezu J, Sai Y, Tsuji A, Yokoi T (2002) Genetic polymorphisms of human organic anion transporters OATP-C (SLC21A6) and OATP-B (SLC21A9): allele frequencies in the Japanese population and functional analysis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302(2):804–813. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.302.2.804
Oh ES, Kim CO, Cho SK, Park MS, Chung JY (2013) Impact of ABCC2, ABCG2 and SLCO1B1 polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin in humans. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 28(3):196–202. https://doi.org/10.2133/dmpk.dmpk-12-rg-068
Parashar P, Mangla B, Joshi SK (2016) Design and development of novel lipid based carrier system for delivery of pitavastatin calcium. IJPSR 7(12):5030–5038. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.7(12).5030-38
Pasanen MK, Neuvonen PJ, Niemi M (2008) Global analysis of genetic variation in SLCO1B1. Pharmacogenomics 9(1):19–33. https://doi.org/10.2217/14622416.9.1.19
Prueksaritanont T, Chu X, Evers R, Klopfer SO, Caro L, Kothare PA, Dempsey C, Rasmussen S, Houle R, Chan G, Cai X, Valesky R, Fraser IP, Stoch SA (2014) Pitavastatin is a more sensitive and selective organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B clinical probe than rosuvastatin. Br J Clin Pharmacol 78(3):587–598. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.12377
Qi X, Ding L, Wen A, Zhou N, Du X, Shakya S (2013) Simple LC-MS/MS methods for simultaneous determination of pitavastatin and its lactone metabolite in human plasma and urine involving a procedure for inhibiting the conversion of pitavastatin lactone to pitavastatin in plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Pharm Biomed Anal 72:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2012.09.026
Ramsey LB, Gong L, Lee SB, Wagner JB, Zhou X, Sangkuhl K, Adams SM, Straka RJ, Empey PE, Boone EC, Klein TE, Niemi M, Gaedigk A (2023) PharmVar GeneFocus: SLCO1B1. Clin Pharmacol Ther 113(4):782–793. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.2705
Rüdesheim S, Selzer D, Fuhr U, Schwab M, Lehr T (2022a) Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling of dextromethorphan to investigate interindividual variability within CYP2D6 activity score groups. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol 11(4):494–511. https://doi.org/10.1002/psp4.12776
Rüdesheim S, Selzer D, Mürdter T, Igel S, Kerb R, Schwab M, Lehr T (2022b) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling to describe the CYP2D6 activity score-dependent metabolism of paroxetine, atomoxetine and risperidone. Pharmaceutics 14(8):1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081734
Saito Y, Yamada N, Teramoto T, Itakura H, Hata Y, Nakaya N, Mabuchi H, Tushima M, Sasaki J, Ogawa N, Goto Y (2002) A randomized, double-blind trial comparing the efficacy and safety of pitavastatin versus pravastatin in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 162(2):373–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9150(01)00712-2
Schirris TJ, Ritschel T, Bilos A, Smeitink JA, Russel FG (2015) Statin lactonization by uridine 5′-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs). Mol Pharm 12(11):4048–4055. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00474
Shen H, Dai J, Liu T, Cheng Y, Chen W, Freeden C, Zhang Y, Humphreys WG, Marathe P, Lai Y (2016) Coproporphyrins I and III as functional markers of OATP1B activity: in vitro and in vivo evaluation in preclinical species. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 357(2):382–393. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.116.232066
Shin HB, Jung EH, Kang P, Lim CW, Oh KY, Cho CK, Lee YJ, Choi CI, Jang CG, Lee SY, Bae JW (2020) ABCB1 c.2677G>T/c.3435C>T diplotype increases the early-phase oral absorption of losartan. Arch Pharm Res 43(11):1187–1196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-020-01294-3
Tan ML, Zhao P, Zhang L, Ho YF, Varma MVS, Neuhoff S, Nolin TD, Galetin A, Huang SM (2019) Use of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling to evaluate the effect of chronic kidney disease on the disposition of hepatic CYP2C8 and OATP1B drug substrates. Clin Pharmacol Ther 105(3):719–729. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.1205
Vildhede A, Mateus A, Khan EK, Lai Y, Karlgren M, Artursson P, Kjellsson MC (2016) Mechanistic modeling of pitavastatin disposition in sandwich-cultured human hepatocytes: a proteomics-informed bottom-up approach. Drug Metab Dispos 44(4):505–516. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.115.066746
Wang J, Chen J, Wang L, Yang D, Shao R, Lou H, Ruan Z, Jiang B (2023) Evaluating the bioequivalence of two pitavastatin calcium formulations based on IVIVC modeling and clinical study. Clin Transl Sci 16(1):85–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/cts.13426
Wen J, Xiong Y (2010) OATP1B1 388A>G polymorphism and pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin in Chinese healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharm Ther 35(1):99–104. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01071.x
Whang SS, Cho CK, Jung EH, Kang P, Park HJ, Lee YJ, Choi CI, Bae JW, Kim HS, Jang CG, Lee SY (2022) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling of flurbiprofen in different CYP2C9 genotypes. Arch Pharm Res 45(8):584–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-022-01403-4
Yang GP, Yuan H, Tang B, Zhang W, Wang LS, Huang ZJ, Ou-Yang DS, Zhang GX, Zhou HH (2010) Lack of effect of genetic polymorphisms of SLCO1B1 on the lipid-lowering response to pitavastatin in Chinese patients. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31(3):382–386. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.203
Yu CY, Campbell SE, Sponseller CA, Small DS, Medlock MM, Morgan RE (2014) Steady-state pharmacokinetics of darunavir/ritonavir and pitavastatin when co-administered to healthy adult volunteers. Clin Drug Investig 34(7):475–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-014-0198-x
Zhou Q, Chen QX, Ruan ZR, Yuan H, Xu HM, Zeng S (2013) CYP2C9*3 (1075A > C), ABCB1 and SLCO1B1 genetic polymorphisms and gender are determinants of inter-subject variability in pitavastatin pharmacokinetics. Pharmazie 68(3):187–194. https://doi.org/10.1691/ph.2013.2742
Zhuang X, Lu C (2016) PBPK modeling and simulation in drug research and development. Acta Pharm Sin B 6(5):430–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2016.04.004
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2019R1A2C1004582 and NRF-2919R1C1C1006213).
Funding
Funding was provided by National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant No. NRF-2019R1A2C1004582 and NRF-2919R1C1C1006213).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, CK., Mo, J.Y., Ko, E. et al. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling of pitavastatin in relation to SLCO1B1 genetic polymorphism. Arch. Pharm. Res. 47, 95–110 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-023-01476-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-023-01476-9