Abstract
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is the leading cause of death from noncommunicable diseases worldwide. The pathological development of ASCVD begins with atherosclerosis, followed by the narrowing and occlusion of the vascular lumen and, subsequently, ischemic necrosis in coronary arteries. Preventing atherosclerosis development and delaying ischemia progression may be effective ways of pre-diagnosing and treating ASCVD. Studies have demonstrated that exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells play an increasingly important role in basic research on cardiovascular diseases in terms of the impact of macrophage polarization and the endothelial, anti-apoptosis, and angiogenesis effects. The related microRNAs play a significant role in ASCVD. This study was novel in reviewing the role of exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells and related microRNAs in ASCVD.
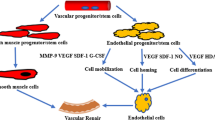
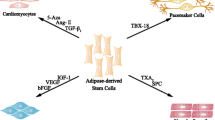
Graphical abstract
Therapeutic potentials of adipose-derived stem cell exosomes in terms of their impact on macrophage polarization, endothelial effect, anti-apoptosis intervention, and angiogenesis



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASCVD:
-
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
- AS:
-
Atherosclerosis
- MI:
-
Myocardial infarction
- ASCs:
-
Adipose-derived stem cells
- MSCs:
-
mesenchymal stem cells
- miRNAs:
-
microRNAs
- AMI:
-
acute myocardial infarction
- ECs:
-
endothelial cells
- I/R:
-
ischemia/reperfusion
References
Soehnlein O, Libby P. Targeting inflammation in atherosclerosis - from experimental insights to the clinic. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2021;20(8):589–610. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-021-00198-1.
Rosenblit PD. Extreme atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk recognition. Curr DiabRep. 2019;19(8):61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-019-1178-6.
Polonsky TS, Khera A, Miedema MD, Schocken DD, Wilson PWF. Highlights in ASCVD primary prevention for 2021. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022;11(13):e025973. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.122.025973.
Wang H, Xie Y, Salvador AM, Zhang Z, Chen K, Li G, Xiao J. Exosomes: multifaceted messengers in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2020;22(10):57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-020-00871-7.
Zhao L, Johnson T, Liu D. Therapeutic angiogenesis of adipose-derived stem cells for ischemic diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):125. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-017-0578-2.
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2020;367(6478). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6977
Pegtel DM, Gould SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88:487–514. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-111902.
Zhang H, Freitas D, Kim HS, Fabijanic K, Li Z, Chen H, Lyden D. Identification of distinct nanoparticles and subsets of extracellular vesicles by asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(3):332–43. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0040-4.
Lee B-C, Kang I, Yu K-R. Therapeutic features and updated clinical trials of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes. J Clin Med. 2021;10(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040711
Tran PHL, Xiang D, Tran TTD, Yin W, Zhang Y, Kong L, Duan W. Exosomes and nanoengineering: a match made for precision therapeutics. Adv Mater (Deerfield Beach Fla). 2020;32(18):e1904040. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201904040.
Sahoo S, Losordo DW. Exosomes and cardiac repair after myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 2014;114(2):333–44. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.300639.
Marbán E. The secret life of exosomes: what bees can teach us about next-generation therapeutics. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(2):193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2017.11.013.
Boon RA, Dimmeler S. MicroRNAs in myocardial infarction. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015;12(3):135–42. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2014.207.
Phinney DG, Pittenger MF. Concise review: MSC-derived exosomes for cell-free therapy. Stem cells (Dayton Ohio). 2017;35(4):851–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.2575.
Emanueli C, Shearn AIU, Angelini GD, Sahoo S. Exosomes and exosomal miRNAs in cardiovascular protection and repair. Vascul Pharmacol. 2015;71:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2015.02.008.
Lai RC, Arslan F, Lee MM, Sze NSK, Choo A, Chen TS, Lim SK. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem cell research. 2010;4(3):214–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scr.2009.12.003.
Arslan F, Lai RC, Smeets MB, Akeroyd L, Choo A, Aguor ENE, de Kleijn DP. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;10(3):301–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scr.2013.01.002.
Suzuki E, Fujita D, Takahashi M, Oba S, Nishimatsu H. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells as a therapeutic tool for cardiovascular disease. World J Cardiol. 2015;7(8):454–65. https://doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v7.i8.454.
Gimble JM, Katz AJ, Bunnell BA. Adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine. Circ Res. 2007;100(9):1249–60. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000265074.83288.09.
Adolfsson E, Helenius G, Friberg Ö, Samano N, Frøbert O, Johansson K. Bone marrow- and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells from donors with coronary artery disease; growth, yield, gene expression and the effect of oxygen concentration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2020;80(4):318–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365513.2020.1741023.
Cai Y, Li J, Jia C, He Y, Deng C. Therapeutic applications of adipose cell-free derivatives: a review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):312. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01831-3.
Bourin P, Bunnell BA, Casteilla L, Dominici M, Katz AJ, March KL, Gimble JM. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: a joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International S. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(6):641–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2013.02.006.
Chen J, Ren S, Duscher D, Kang Y, Liu Y, Wang C, Chen Z. Exosomes from human adipose-derived stem cells promote sciatic nerve regeneration via optimizing Schwann cell function. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):23097–110. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28873.
Shao L, Zhang Y, Lan B, Wang J, Zhang Z, Zhang L, Li Y. MiRNA-sequence indicates that mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes have similar mechanism to enhance cardiac repair. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4150705. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4150705.
Mazini L, Rochette L, Admou B, Amal S, Malka G. Hopes and limits of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in wound healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041306
He C, Zheng S, Luo Y, Wang B. Exosome theranostics: biology and translational medicine. Theranostics. 2018;8(1):237–55. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.21945.
Modani S, Tomar D, Tangirala S, Sriram A, Mehra NK, Kumar R, Singh PK. An updated review on exosomes: biosynthesis to clinical applications. J Drug Target. 2021;29(9):925–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/1061186X.2021.1894436.
Chen W, Schilperoort M, Cao Y, Shi J, Tabas I, Tao W. Macrophage-targeted nanomedicine for the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022;19(4):228–49. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-021-00629-x.
Deng S, Zhou X, Ge Z, Song Y, Wang H, Liu X, Zhang D. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cardiac damage after myocardial infarction by activating S1P/SK1/S1PR1 signaling and promoting macrophage M2 polarization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;114:105564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2019.105564.
Zhao H, Shang Q, Pan Z, Bai Y, Li Z, Zhang H, Wang Q. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells attenuate adipose inflammation and obesity through polarizing M2 macrophages and Beiging in white adipose tissue. Diabetes. 2018;67(2):235–47. https://doi.org/10.2337/db17-0356.
Heo JS, Choi Y, Kim HO. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote M2 macrophage phenotype through exosomes. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:7921760. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7921760.
Zhu D, Johnson TK, Wang Y, Thomas M, Huynh K, Yang Q, Liu D. Macrophage M2 polarization induced by exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells contributes to the exosomal proangiogenic effect on mouse ischemic hindlimb. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):162. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01669-9.
Nayor M, Brown KJ, Vasan RS. The molecular basis of predicting atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk. Circ Res. 2021;128(2):287–303. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.315890.
Luo Q, Guo D, Liu G, Chen G, Hang M, Jin M. Exosomes from MiR-126-overexpressing Adscs are therapeutic in relieving acute myocardial ischaemic injury. Cell Physiol Biochem Int J Exp Cell Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2017;44(6):2105–16. https://doi.org/10.1159/000485949.
Huang H, Xu Z, Qi Y, Zhang W, Zhang C, Jiang M, Wang H. Exosomes from SIRT1-overexpressing ADSCs restore cardiac function by improving angiogenic function of EPCs. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;21:737–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.07.007.
Hong P, Yang H, Wu Y, Li K, Tang Z. The functions and clinical application potential of exosomes derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):242. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1358-y.
Guduric-Fuchs J, Pedrini E, Lechner J, Chambers SEJ, O’Neill CL, Lopes M, de Melo J, Medina RJ. miR-130a activates the VEGFR2/STAT3/HIF1α axis to potentiate the vasoregenerative capacity of endothelial colony-forming cells in hypoxia. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;23:968–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2021.01.015.
Xing X, Li Z, Yang X, Li M, Liu C, Pang Y, Xiao Y. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosome-mediated microRNA-342-5p protects endothelial cells against atherosclerosis. Aging. 2020;12(4):3880–98. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102857.
Liu K, Shi H, Peng Z, Wu X, Li W, Lu X. Exosomes from adipose mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing stanniocalcin-1 promote reendothelialization after carotid endarterium mechanical injury. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(3):1041–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-021-10180-4.
Zhu D, Wang Y, Thomas M, McLaughlin K, Oguljahan B, Henderson J, Liu D. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells alleviate myocardial infarction via microRNA-31/FIH1/HIF-1α pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022;162:10–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.08.010.
Cui X, He Z, Liang Z, Chen Z, Wang H, Zhang J. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect the myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2017;70(4):225–31. https://doi.org/10.1097/FJC.0000000000000507.
Xu H, Wang Z, Liu L, Zhang B, Li B. Exosomes derived from adipose tissue, bone marrow, and umbilical cord blood for cardioprotection after myocardial infarction. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(3):2089–102. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27399.
Liu L, Zhang H, Mao H, Li X, Hu Y. Exosomal miR-320d derived from adipose tissue-derived MSCs inhibits apoptosis in cardiomyocytes with atrial fibrillation (AF). Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):3976–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1671432.
Liu Z, Xu Y, Wan Y, Gao J, Chu Y, Li J. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by oxidative stress. Cell death Discov. 2019;5:79. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-019-0159-5.
Kang T, Jones TM, Naddell C, Bacanamwo M, Calvert JW, Thompson WE, Liu D. Adipose-derived stem cells induce angiogenesis via microvesicle transport of miRNA-31. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(4):440–50. https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2015-0177.
Pu C-M, Liu C-W, Liang C-J, Yen Y-H, Chen S-H, Jiang-Shieh Y-F, Chen Y-L. Adipose-derived stem cells protect skin flaps against ischemia/reperfusion injury via IL-6 expression. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137(6):1353–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2016.12.030.
Xue C, Shen Y, Li X, Li B, Zhao S, Gu J, Zhao RC. Exosomes derived from hypoxia-treated human adipose mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis through the PKA signaling pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2018;27(7):456–65. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2017.0296.
Chen B, Cai J, Wei Y, Jiang Z, Desjardins HE, Adams AE, Guo L. Exosomes are comparable to source adipose stem cells in fat graft retention with up-regulating early inflammation and angiogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144(5):816e–27e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000006175.
Gao L, Mei S, Zhang S, Qin Q, Li H, Liao Y, Zhu H. Cardio-renal exosomes in myocardial infarction serum regulate proangiogenic paracrine signaling in adipose mesenchymal stem cells. Theranostics. 2020;10(3):1060–73. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.37678.
Isaac R, Reis FCG, Ying W, Olefsky JM. Exosomes as mediators of intercellular crosstalk in metabolism. Cell Metab. 2021;33(9):1744–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2021.08.006.
Hoefer IE, Steffens S, Ala-Korpela M, Bäck M, Badimon L, Bochaton-Piallat M-L, Weber C. Novel methodologies for biomarker discovery in atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(39):2635–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehv236.
Wang L, Jia Q, Xinnong C, Xie Y, Yang Y, Zhang A, Zhang J. Role of cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosome-mediated microRNA-210 in cardiovascular disease. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(11):7124–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14562.
Zheng D, Huo M, Li B, Wang W, Piao H, Wang Y, Liu K. The role of exosomes and exosomal microRNA in cardiovascular disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:616161. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.616161.
Hong Y, Sun Y, Rong X, Li D, Lu Y, Ji Y. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells attenuate UVB-induced apoptosis, ROS, and the Ca(2+) level in HLEC cells. Exp Cell Res. 2020;396(2):112321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112321.
Tikhomirov R, Donnell BR-O, Catapano F, Faggian G, Gorelik J, Martelli F, Emanueli C. Exosomes: from potential culprits to new therapeutic promise in the setting of cardiac fibrosis. Cells. 2020;9(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030592
Xu F, Xiang Q, Huang J, Chen Q, Yu N, Long X, Zhou Z. Exosomal miR-423-5p mediates the proangiogenic activity of human adipose-derived stem cells by targeting Sufu. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):106. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1196-y.
Chen C, Wang Y, Yang S, Li H, Zhao G, Wang F, Wang DW. MiR-320a contributes to atherogenesis by augmenting multiple risk factors and down-regulating SRF. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(5):970–85. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12483.
Li C, Li J, Xue K, Zhang J, Wang C, Zhang Q, Sun L. MicroRNA-143-3p promotes human cardiac fibrosis via targeting sprouty3 after myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;129:281–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.03.005.
Nakamura Y, Kita S, Tanaka Y, Fukuda S, Obata Y, Okita T, Shimomura I. Adiponectin stimulates exosome release to enhance mesenchymal stem-cell-driven therapy of heart failure in mice. Mol Ther J Am Soc Gene Ther. 2020;28(10):2203–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.06.026.
Schober A, Blay RM, Saboor Maleki S, Zahedi F, Winklmaier AE, Kakar MY, Nazari-Jahantigh M. MicroRNA-21 Controls circadian regulation of apoptosis in atherosclerotic lesions. Circulation. 2021;144(13):1059–73. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.051614.
Yu C, Tang W, Lu R, Tao Y, Ren T, Gao Y. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote lymphocyte apoptosis and alleviate atherosclerosis via miR-125b-1-3p/BCL11B signal axis. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10(2):2123–33. https://doi.org/10.21037/apm-21-49.
Liu J, Jiang M, Deng S, Lu J, Huang H, Zhang Y, Wang H. miR-93-5p-containing exosomes treatment attenuates acute myocardial infarction-induced myocardial damage. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;11:103–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2018.01.010.
Zhao Z, Du S, Shen S, Wang L. microRNA-132 inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis and myocardial remodeling in myocardial infarction by targeting IL-1β. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(3):2710–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29175.
Li C, Chen X, Huang J, Sun Q, Wang L. Clinical impact of circulating miR-26a, miR-191, and miR-208b in plasma of patients with acute myocardial infarction. Eur J Med Res. 2015;20(1):58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-015-0148-y.
Zhang C, Wang P, Mohammed A, Zhou Z, Zhang S, Ni S, Tang Z. Function of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension through miR-191 via regulation of BMPR2. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:2858750. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2858750.
Pan J, Alimujiang M, Chen Q, Shi H, Luo X. Exosomes derived from miR-146a-modified adipose-derived stem cells attenuate acute myocardial infarction-induced myocardial damage via downregulation of early growth response factor 1. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(3):4433–43. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27731.
Lai T-C, Lee T-L, Chang Y-C, Chen Y-C, Lin S-R, Lin S-W, Chen Y-L. MicroRNA-221/222 mediates ADSC-exosome-induced cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion by targeting PUMA and ETS-1. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:569150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.569150.
Wang X, Zhu Y, Wu C, Liu W, He Y, Yang Q. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes carry MicroRNA-671 to alleviate myocardial infarction through inactivating the TGFBR2/Smad2 axis. Inflammation. 2021;44(5):1815–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01460-9.
Xia W, Chen H, Xie C, Hou M. Long-noncoding RNA MALAT1 sponges microRNA-92a-3p to inhibit doxorubicin-induced cardiac senescence by targeting ATG4a. Aging. 2020;12(9):8241–60. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103136.
Waters R, Alam P, Pacelli S, Chakravarti AR, Ahmed RPH, Paul A. Stem cell-inspired secretome-rich injectable hydrogel to repair injured cardiac tissue. Acta Biomater. 2018;69:95–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2017.12.025.
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the language edit service from Medsci. Fan Zhou and Ke Li contribute to this work equally.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This study does not contain any experimentation with human participants or animals by any of the authors.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Associate Editor Junjie Xiao oversaw the review of this article
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, F., Li, K. & Yang, K. Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes and Related microRNAs in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. J. of Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 16, 453–462 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-022-10329-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-022-10329-7