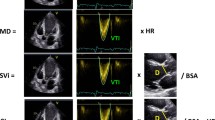
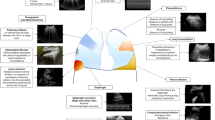
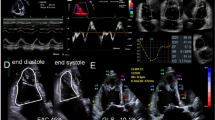
Abstract
Little data is available about the pathophysiological mechanisms of unexplained dyspnea and their clinical meaning. Consecutive patients with unexplained dyspnea underwent prospective standardized cardiopulmonary exercise testing with echocardiography (CPETecho). Patients were grouped as having normal exercise capacity (peak VO2 > 80% with respiratory exchange [RER] > 1.05), reduced exercise capacity (peak VO2 ≤ 80% with RER > 1.05), or a submaximal exercise test (RER ≤ 1.05). From 307 patients, 144 (47%) had normal and 116 (38%) reduced exercise capacity, and 47 (15%) had a submaximal exercise test. Patients with reduced versus normal exercise capacity had significantly more mechanisms for unexplained dyspnea (2.3±1.0 vs 1.5±1.0, respectively; p<0.001). Exercise PH (42%), low heart rate reserve (51%), low stroke volume reserve (38%), low diastolic reserve (18%), and peripheral muscle limitation (17%) were most common. Patients with more mechanisms for dyspnea displayed poorer peak VO2 and had an increased risk for cardiovascular hospitalization (p=0.002). Patients with unexplained dyspnea display multiple coexisting mechanisms for exercise intolerance, which relate to the severity of exercise limitation and risk of subsequent cardiovascular hospitalizations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarkar, S., & Amelung, P. J. (2006). Evaluation of the dyspneic patient in the office. Primary Care, 33(3), 643–657.
Shiber, J. R., & Santana, J. (2006). Dyspnea. The Medical Clinics of North America, 90(3), 453–479.
Martinez, F. J., Stanopoulos, I., Acero, R., Becker, F. S., Pickering, R., & Beamis, J. F. (1994). Graded comprehensive cardiopulmonary exercise testing in the evaluation of dyspnea unexplained by routine evaluation. Chest, 105(1), 168–174.
Gillespie, D. J., & Staats, B. A. (1994). Unexplained dyspnea. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 69(7), 657–663.
Borlaug BA. (2020). Evaluation and management of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nature Reviews. Cardiology
Huang, W., Resch, S., Oliveira, R. K., Cockrill, B. A., Systrom, D. M., & Waxman, A. B. (2017). Invasive cardiopulmonary exercise testing in the evaluation of unexplained dyspnea: Insights from a multidisciplinary dyspnea center. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, 24(11), 1190–1199.
Obokata, M., Kane, G. C., Reddy, Y. N., Olson, T. P., Melenovsky, V., & Borlaug, B. A. (2017). Role of diastolic stress testing in the evaluation for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A simultaneous invasive-echocardiographic study. Circulation, 135(9), 825–838.
Borlaug, B. A., Nishimura, R. A., Sorajja, P., Lam, C. S., & Redfield, M. M. (2010). Exercise hemodynamics enhance diagnosis of early heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation. Heart Failure, 3(5), 588–595.
Martens, P., Verbrugge, F. H., Bertrand, P. B., Verhaert, D., Vandervoort, P., Dupont, M., Tang, W. H. W., Janssens, S., & Mullens, W. (2018). Effect of cardiac resynchronization therapy on exercise-induced pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular-arterial coupling. Circulation. Cardiovascular Imaging, 11(9), e007813.
Guazzi, M., Bandera, F., Ozemek, C., Systrom, D., & Arena, R. (2017). Cardiopulmonary exercise testing: What is its value? Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 70(13), 1618–1636.
Obokata, M., Reddy, Y. N. V., & Borlaug, B. A. (2020). Diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Understanding mechanisms by using noninvasive methods. JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging, 13(1 Pt 2), 245–257.
Pugliese, N. R., De, B. N., Conte, L., Gargani, L., Mazzola, M., Fabiani, I., Natali, A., Dini, F. L., Frumento, P., Rosada, J., Taddei, S., Borlaug, B. A., & Masi, S. (2021). Cardiac reserve and exercise capacity: Insights from combined cardiopulmonary and exercise echocardiography stress testing. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography, 34(1), 38–50.
Pugliese, N. R., Mazzola, M., Fabiani, I., Gargani, L., De, B. N., Pedrinelli, R., Natali, A., & Dini, F. L. (2020). Haemodynamic and metabolic phenotyping of hypertensive patients with and without heart failure by combining cardiopulmonary and echocardiographic stress test. European Journal of Heart Failure, 22(3), 458–468.
Elliott, P. M., Anastasakis, A., Borger, M. A., Borggrefe, M., Cecchi, F., Charron, P., Hagege, A. A., Lafont, A., Limongelli, G., Mahrholdt, H., McKenna, W. J., Mogensen, J., Nihoyannopoulos, P., Nistri, S., Pieper, P. G., Pieske, B., Rapezzi, C., Rutten, F. H., Tillmanns, C., & Watkins, H. (2014). 2014 ESC Guidelines on diagnosis and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal, 35(39), 2733–2779.
von EE Altman, D. G., Egger, M., Pocock, S. J., Gotzsche, P. C., & Vandenbroucke, J. P. (2007). The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet, 370(9596), 1453–1457.
Chemla, D., Castelain, V., Humbert, M., Hebert, J. L., Simonneau, G., Lecarpentier, Y., & Herve, P. (2004). New formula for predicting mean pulmonary artery pressure using systolic pulmonary artery pressure. Chest, 126(4), 1313–1317.
Obokata M, Kane GC, Sorimachi H, Reddy YNV, Olson TP, Egbe AC, Melenovsky V, Borlaug BA. (2020) Noninvasive evaluation of pulmonary artery pressure during exercise: The importance of right atrial hypertension. The European Respiratory Journal 55(2)
Ross, R. M. (2003). ATS/ACCP statement on cardiopulmonary exercise testing. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 167(10), 1451.
Brubaker, P. H., & Kitzman, D. W. (2011). Chronotropic incompetence: Causes, consequences, and management. Circulation, 123(9), 1010–1020.
Higginbotham, M. B., Morris, K. G., Williams, R. S., McHale, P. A., Coleman, R. E., & Cobb, F. R. (1986). Regulation of stroke volume during submaximal and maximal upright exercise in normal man. Circulation Research, 58(2), 281–291.
Lancellotti, P., Pellikka, P. A., Budts, W., Chaudhry, F. A., Donal, E., Dulgheru, R., Edvardsen, T., Garbi, M., Ha, J. W., Kane, G. C., Kreeger, J., Mertens, L., Pibarot, P., Picano, E., Ryan, T., Tsutsui, J. M., & Varga, A. (2017). The clinical use of stress echocardiography in non-ischaemic heart disease: Recommendations from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging and the American Society of Echocardiography. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography, 30(2), 101–138.
Kovacs G, Herve P, Barbera JA, Chaouat A, Chemla D, Condliffe R, Garcia G, Grunig E, Howard L, Humbert M, Lau E, Laveneziana P, Lewis GD, Naeije R, Peacock A, Rosenkranz S, Saggar R, Ulrich S, Vizza D, Vonk NA, Olschewski H. (2017) An official European Respiratory Society statement: Pulmonary haemodynamics during exercise. The European Respiratory Journal ;50(5).
Guazzi, M., Adams, V., Conraads, V., Halle, M., Mezzani, A., Vanhees, L., Arena, R., Fletcher, G. F., Forman, D. E., Kitzman, D. W., Lavie, C. J., & Myers, J. (2012). EACPR/AHA Joint Scientific Statement. Clinical recommendations for cardiopulmonary exercise testing data assessment in specific patient populations. European Heart Journal, 33(23), 2917–2927.
Knuuti, J., Wijns, W., Saraste, A., Capodanno, D., Barbato, E., Funck-Brentano, C., Prescott, E., Storey, R. F., Deaton, C., Cuisset, T., Agewall, S., Dickstein, K., Edvardsen, T., Escaned, J., Gersh, B. J., Svitil, P., Gilard, M., Hasdai, D., Hatala, R., Mahfoud, F., Masip, J., Muneretto, C., Valgimigli, M., Achenbach, S., & Bax, J. J. (2020). 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. European Heart Journal, 41(3), 407–477.
Pieske, B., Tschope, C., de Boer, R. A., Fraser, A. G., Anker, S. D., Donal, E., Edelmann, F., Fu, M., Guazzi, M., CSP, L., Lancellotti, P., Melenovsky, V., Morris, D. A., Nagel, E., Pieske-Kraigher, E., Ponikowski, P., Solomon, S. D., Vasan, R. S., Rutten, F. H., Voors, A. A., Ruschitzka, F., Paulus, W. J., Seferovic, P., & Filippatos, G. (2019). How to diagnose heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: The HFA-PEFF diagnostic algorithm: A consensus recommendation from the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal, 40(40), 3297–3317.
Reddy, Y. N. V., Carter, R. E., Obokata, M., Redfield, M. M., & Borlaug, B. A. (2018). A simple, evidence-based approach to help guide diagnosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation, 138(9), 861–870.
Hicks, K. A., Mahaffey, K. W., Mehran, R., Nissen, S. E., Wiviott, S. D., Dunn, B., Solomon, S. D., Marler, J. R., Teerlink, J. R., Farb, A., Morrow, D. A., Targum, S. L., Sila, C. A., MTT, H., Jaff, M. R., Joffe, H. V., Cutlip, D. E., Desai, A. S., Lewis, E. F., Gibson, C. M., Landray, M. J., Lincoff, A. M., White, C. J., Brooks, S. S., Rosenfield, K., Domanski, M. J., Lansky, A. J., JJV, M. M., Tcheng, J. E., Steinhubl, S. R., Burton, P., Mauri, L., O’Connor, C. M., Pfeffer, M. A., HMJ, H., Stockbridge, N. L., Chaitman, B. R., & Temple, R. J. (2017). Cardiovascular and stroke endpoint definitions for clinical trials. Circulation 2018, 137(9), 961–972.
Houstis, N. E., Eisman, A. S., Pappagianopoulos, P. P., Wooster, L., Bailey, C. S., Wagner, P. D., & Lewis, G. D. (2018). Exercise intolerance in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Diagnosing and ranking its causes using personalized O2 pathway analysis. Circulation, 137(2), 148–161.
Reddy, Y. N. V., Olson, T. P., Obokata, M., Melenovsky, V., & Borlaug, B. A. (2018). Hemodynamic correlates and diagnostic role of cardiopulmonary exercise testing in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. JACC Heart Fail, 6(8), 665–675.
Tramarin, R., Torbicki, A., Marchandise, B., Laaban, J. P., & Morpurgo, M. (1991). Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of pulmonary artery pressure in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A European multicentre study. Working Group on Noninvasive Evaluation of Pulmonary Artery Pressure. European Office of the World Health Organization, Copenhagen. European Heart Journal, 12(2), 103–111.
Borlaug, B. A., Olson, T. P., Lam, C. S., Flood, K. S., Lerman, A., Johnson, B. D., & Redfield, M. M. (2010). Global cardiovascular reserve dysfunction in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 56(11), 845–854.
Oldham, W. M., Oliveira, R. K. F., Wang, R. S., Opotowsky, A. R., Rubins, D. M., Hainer, J., Wertheim, B. M., Alba, G. A., Choudhary, G., Tornyos, A., MacRae, C. A., Loscalzo, J., Leopold, J. A., Waxman, A. B., Olschewski, H., Kovacs, G., Systrom, D. M., & Maron, B. A. (2018). Network analysis to risk stratify patients with exercise intolerance. Circulation Research, 122(6), 864–876.
Lewis, G. D., Murphy, R. M., Shah, R. V., Pappagianopoulos, P. P., Malhotra, R., Bloch, K. D., Systrom, D. M., & Semigran, M. J. (2011). Pulmonary vascular response patterns during exercise in left ventricular systolic dysfunction predict exercise capacity and outcomes. Circulation. Heart Failure, 4(3), 276–285.
Guazzi, M., Naeije, R., Arena, R., Corra, U., Ghio, S., Forfia, P., Rossi, A., Cahalin, L. P., Bandera, F., & Temporelli, P. (2015). Echocardiography of right ventriculoarterial coupling combined with cardiopulmonary exercise testing to predict outcome in heart failure. Chest, 148(1), 226–234.
Lewis, G. D., Bossone, E., Naeije, R., Grunig, E., Saggar, R., Lancellotti, P., Ghio, S., Varga, J., Rajagopalan, S., Oudiz, R., & Rubenfire, M. (2013). Pulmonary vascular hemodynamic response to exercise in cardiopulmonary diseases. Circulation, 128(13), 1470–1479.
Ho, J. E., Zern, E. K., Lau, E. S., Wooster, L., Bailey, C. S., Cunningham, T., Eisman, A. S., Hardin, K. M., Farrell, R., Sbarbaro, J. A., Schoenike, M. W., Houstis, N. E., Baggish, A. L., Shah, R. V., Nayor, M., Malhotra, R., & Lewis, G. D. (2020). Exercise pulmonary hypertension predicts clinical outcomes in patients with dyspnea on effort. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 75(1), 17–26.
Fayyaz, A. U., Edwards, W. D., Maleszewski, J. J., Konik, E. A., DuBrock, H. M., Borlaug, B. A., Frantz, R. P., Jenkins, S. M., & Redfield, M. M. (2018). Global pulmonary vascular remodeling in pulmonary hypertension associated with heart failure and preserved or reduced ejection fraction. Circulation, 137(17), 1796–1810.
Claessen, G., La, G. A., Voigt, J. U., Dymarkowski, S., Schnell, F., Petit, T., Willems, R., Claus, P., Delcroix, M., & Heidbuchel, H. (2016). Accuracy of echocardiography to evaluate pulmonary vascular and RV function during exercise. JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging, 9(5), 532–543.
Guazzi, M., & Naeije, R. (2017). Pulmonary hypertension in heart failure: Pathophysiology, pathobiology, and emerging clinical perspectives. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 69(13), 1718–1734.
Shim, C. Y., Kim, S. A., Choi, D., Yang, W. I., Kim, J. M., Moon, S. H., Lee, H. J., Park, S., Choi, E. Y., Chung, N., & Ha, J. W. (2011). Clinical outcomes of exercise-induced pulmonary hypertension in subjects with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction: Implication of an increase in left ventricular filling pressure during exercise. Heart, 97(17), 1417–1424.
Borlaug, B. A., Kane, G. C., Melenovsky, V., & Olson, T. P. (2016). Abnormal right ventricular-pulmonary artery coupling with exercise in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. European Heart Journal, 37(43), 3293–3302.
Yoshida, Y., Nakanishi, K., Daimon, M., Ishiwata, J., Sawada, N., Hirokawa, M., Kaneko, H., Nakao, T., Mizuno, Y., Morita, H., Di Tullio, M. R., Homma, S., & Komuro, I. (2019). Alteration of cardiac performance and serum B-type natriuretic peptide level in healthy aging. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 74(14), 1789–1800.
Reddy, Y. N. V., Obokata, M., Egbe, A., Yang, J. H., Pislaru, S., Lin, G., Carter, R., & Borlaug, B. A. (2019). Left atrial strain and compliance in the diagnostic evaluation of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. European Journal of Heart Failure, 21(7), 891–900.
Deferm, S., Martens, P., Verbrugge, F. H., Bertrand, P. B., Dauw, J., Verhaert, D., Dupont, M., Vandervoort, P. M., & Mullens, W. (2020). LA Mechanics in decompensated heart failure: Insights from strain echocardiography with invasive hemodynamics. JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Associate Editor Jozine ter Maaten oversaw the review of this article
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 309 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martens, P., Herbots, L., Timmermans, P. et al. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing with Echocardiography to Identify Mechanisms of Unexplained Dyspnea. J. of Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 15, 116–130 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-021-10142-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-021-10142-8