Abstract
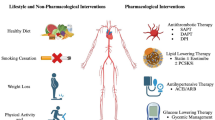
Patients with critical limb ischemia (CLI) represent the highest risk patients with peripheral artery disease (PAD), with high rates of death, amputation, and other cardiovascular events. Previously, nonsurgical options for patients with CLI were limited. However, advances in endovascular techniques such as angiosome-based revascularization and technologies such as drug-eluting balloon and stent platforms have dramatically improved the therapeutic outlook. Additionally, advances in stem cell-based therapy and angiogenic factors show promise as adjuvant medical therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J. L., Halperin, J. L., Albert, N. M., Bozkurt, B., Brindis, R. G., Curtis, L. H., et al. (2013). Management of patients with peripheral artery disease (compilation of 2005 and 2011 ACCF/AHA guideline recommendations): a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation, 127(13), 1425–1443. Epub 2013/03/05.
Taylor, G. I., & Palmer, J. H. (1987). The vascular territories (angiosomes) of the body: experimental study and clinical applications. British Journal of Plastic Surgery, 40(2), 113–141. Epub 1987/03/01.
Morris, S. F., & Taylor, G. I. (1993). Predicting the survival of experimental skin flaps with a knowledge of the vascular architecture. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 92(7), 1352–1361. Epub 1993/12/01.
Attinger, C., Cooper, P., Blume, P., & Bulan, E. (2001). The safest surgical incisions and amputations applying the angiosome principles and using the Doppler to assess the arterial-arterial connections of the foot and ankle. Foot and Ankle Clinics, 6(4), 745–799. Epub 2002/07/24.
Lejay A, Georg Y, Tartaglia E, Gaertner S, Geny B, Thaveau F, et al. Long-term outcomes of direct and indirect below-the-knee open revascularization based on the angiosome concept in diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia. Annals Vascular Surgery. Epub 2013/12/18.
Kabra, A., Suresh, K. R., Vivekanand, V., Vishnu, M., Sumanth, R., & Nekkanti, M. (2013). Outcomes of angiosome and non-angiosome targeted revascularization in critical lower limb ischemia. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 57(1), 44–49. Epub 2012/10/13.
Iida, O., Soga, Y., Hirano, K., Kawasaki, D., Suzuki, K., Miyashita, Y., et al. (2012). Long-term results of direct and indirect endovascular revascularization based on the angiosome concept in patients with critical limb ischemia presenting with isolated below-the-knee lesions. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 55(2), 363–70 e5. Epub 2011/11/05.
Soderstrom, M., Alback, A., Biancari, F., Lappalainen, K., Lepantalo, M., & Venermo, M. (2013). Angiosome-targeted infrapopliteal endovascular revascularization for treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 57(2), 427–435. Epub 2012/12/12.
Duda, S. H., Bosiers, M., Lammer, J., Scheinert, D., Zeller, T., Oliva, V., et al. (2006). Drug-eluting and bare nitinol stents for the treatment of atherosclerotic lesions in the superficial femoral artery: long-term results from the SIROCCO trial. Journal of Endovascular Therapy, 13(6), 701–710. Epub 2006/12/13.
Lammer, J., Bosiers, M., Zeller, T., Schillinger, M., Boone, E., Zaugg, M. J., et al. (2011). First clinical trial of nitinol self-expanding everolimus-eluting stent implantation for peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 54(2), 394–401. Epub 2011/06/11.
Dake, M. D., Ansel, G. M., Jaff, M. R., Ohki, T., Saxon, R. R., Smouse, H. B., et al. (2011). Paclitaxel-eluting stents show superiority to balloon angioplasty and bare metal stents in femoropopliteal disease: twelve-month Zilver PTX randomized study results. Circulation. Cardiovascular Interventions, 4(5), 495–504. Epub 2011/09/29.
Dake, M. D., Ansel, G. M., Jaff, M. R., Ohki, T., Saxon, R. R., Smouse, H. B., et al. (2013). Sustained safety and effectiveness of paclitaxel-eluting stents for femoropopliteal lesions: 2-year follow-up from the Zilver PTX randomized and single-arm clinical studies. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 61(24), 2417–2427. Epub 2013/04/16.
Zeller, T., Dake, M. D., Tepe, G., Brechtel, K., Noory, E., Beschorner, U., et al. (2013). Treatment of femoropopliteal in-stent restenosis with paclitaxel-eluting stents. JACC. Cardiovascular Interventions, 6(3), 274–281. Epub 2013/03/23.
Bosiers, M., Scheinert, D., Peeters, P., Torsello, G., Zeller, T., Deloose, K., et al. (2012). Randomized comparison of everolimus-eluting versus bare-metal stents in patients with critical limb ischemia and infrapopliteal arterial occlusive disease. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 55(2), 390–398. Epub 2011/12/16.
Scheinert, D., Katsanos, K., Zeller, T., Koppensteiner, R., Commeau, P., Bosiers, M., et al. (2012). A prospective randomized multicenter comparison of balloon angioplasty and infrapopliteal stenting with the sirolimus-eluting stent in patients with ischemic peripheral arterial disease: 1-year results from the ACHILLES trial. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 60(22), 2290–2295. Epub 2012/12/01.
Fusaro, M., Cassese, S., Ndrepepa, G., Tepe, G., King, L., Ott, I., et al. (2013). Drug-eluting stents for revascularization of infrapopliteal arteries: updated meta-analysis of randomized trials. JACC. Cardiovascular Interventions, 6(12), 1284–1293. Epub 2013/12/21.
Tepe, G., Zeller, T., Albrecht, T., Heller, S., Schwarzwalder, U., Beregi, J. P., et al. (2008). Local delivery of paclitaxel to inhibit restenosis during angioplasty of the leg. New England Journal of Medicine, 358(7), 689–699. Epub 2008/02/15.
Cassese, S., Byrne, R. A., Ott, I., Ndrepepa, G., Nerad, M., Kastrati, A., et al. (2012). Paclitaxel-coated versus uncoated balloon angioplasty reduces target lesion revascularization in patients with femoropopliteal arterial disease: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Circulation. Cardiovascular Interventions, 5(4), 582–589. Epub 2012/08/02.
Liistro, F., Grotti, S., Porto, I., Angioli, P., Ricci, L., Ducci, K., et al. (2013). Drug-eluting balloon in peripheral intervention for the superficial femoral artery: the DEBATE-SFA Randomized Trial (drug eluting balloon in peripheral intervention for the superficial femoral artery). JACC. Cardiovascular Interventions, 6(12), 1295–1302. Epub 2013/11/19.
Liistro, F., Porto, I., Angioli, P., Grotti, S., Ricci, L., Ducci, K., et al. (2013). Drug-eluting balloon in peripheral intervention for below the knee angioplasty evaluation (DEBATE-BTK): a randomized trial in diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia. Circulation, 128(6), 615–621. Epub 2013/06/26.
As reported on Endovascular Today website on December 4, 2013 http://evtodaycom/2013/12/04/medtronic-recalls-inpact-amphirion-deb-for-btk-disease-based-on-trial-results Accessed 1/16/14.
Owens, CD., Gasper, WJ., Walker, JP., Alley, HF., Conte, MS., Grenon, SM. (2014). Safety and feasibility of adjunctive dexamethasone infusion into the adventitia of the femoropopliteal artery following endovascular revascularization. Journal of Vascular Surgergy 2014. Epub 2014/01/16.
Adam, D. J., Beard, J. D., Cleveland, T., Bell, J., Bradbury, A. W., Forbes, J. F., et al. (2005). Bypass versus angioplasty in severe ischaemia of the leg (BASIL): multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet, 366(9501), 1925–1934. Epub 2005/12/06.
Vogel, T. R., Dombrovskiy, V. Y., Galinanes, E. L., & Kruse, R. L. (2013). Preoperative statins and limb salvage after lower extremity revascularization in the medicare population. Circulation. Cardiovascular Interventions, 6(6), 694–700. Epub 2013/12/05.
Gulcan, E., Gulcan, A., Erbilen, E., & Toker, S. (2007). Statins may be useful in diabetic foot ulceration treatment and prevention. Medical Hypotheses, 69(6), 1313–1315. Epub 2007/05/15.
El-Azab, M. F., Hazem, R. M., & Moustafa, Y. M. (2012). Role of simvastatin and/or antioxidant vitamins in therapeutic angiogenesis in experimental diabetic hindlimb ischemia: effects on capillary density, angiogenesis markers, and oxidative stress. European Journal of Pharmacology, 690(1–3), 31–41. Epub 2012/06/19.
Undas, A., Celinska-Lowenhoff, M., Stepien, E., Nizankowski, R., Tracz, W., & Szczeklik, A. (2006). Effects of simvastatin on angiogenic growth factors released at the site of microvascular injury. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 95(6), 1045–1047. Epub 2006/05/30.
Liu, Y., Wei, J., Hu, S., & Hu, L. (2012). Beneficial effects of statins on endothelial progenitor cells. American Journal of the Medical Sciences, 344(3), 220–226. Epub 2012/04/06.
Stone, N. J., Robinson, J., Lichtenstein, A. H., Merz, C. N., Blum, C. B., Eckel, R. H., et al. (2013). ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation, 2013. Epub 2013/11/14.
Creutzig, A., Lehmacher, W., & Elze, M. (2004). Meta-analysis of randomised controlled prostaglandin E1 studies in peripheral arterial occlusive disease stages III and IV. VASA, 33(3), 137–144. Epub 2004/10/06.
Ruffolo, A. J., Romano, M., & Ciapponi, A. (2010). Prostanoids for critical limb ischaemia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 1, CD006544. Epub 2010/01/22.
Smith, F. B., Bradbury, A., & Fowkes, G. (2012 Jul 11). Intravenous naftidrofuryl for critical limb ischaemia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 7, CD002070. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002070.pub2.
Tallis, R. C., Illis, L. S., Sedgwick, E. M., Hardwidge, C., & Garfield, J. S. (1983). Spinal cord stimulation in peripheral vascular disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 46(6), 478–484. Epub 1983/06/01.
Ubbink, D. T., & Vermeulen, H. (2013). Spinal cord stimulation for non-reconstructable chronic critical leg ischaemia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2, CD004001. Epub 2013/03/02.
Labropoulos, N., Leon, L. R., Jr., Bhatti, A., Melton, S., Kang, S. S., Mansour, A. M., et al. (2005). Hemodynamic effects of intermittent pneumatic compression in patients with critical limb ischemia. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 42(4), 710–716. Epub 2005/10/26.
Montori, V. M., Kavros, S. J., Walsh, E. E., & Rooke, T. W. (2002). Intermittent compression pump for nonhealing wounds in patients with limb ischemia. The Mayo Clinic experience (1998–2000). International Angiology, 21(4), 360–366.
Kavros, S. J., Delis, K. T., Turner, N. S., Voll, A. E., Liedl, D. A., Gloviczki, P., et al. (2008). Improving limb salvage in critical ischemia with intermittent pneumatic compression: a controlled study with 18-month follow-up. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 47(3), 543–549. Epub 2008/02/26.
Isner, J. M., Pieczek, A., Schainfeld, R., Blair, R., Haley, L., Asahara, T., et al. (1996). Clinical evidence of angiogenesis after arterial gene transfer of phVEGF165 in patient with ischaemic limb. Lancet, 348(9024), 370–374. Epub 1996/08/10.
Kim, H. J., Jang, S. Y., Park, J. I., Byun, J., Kim, D. I., Do, Y. S., et al. (2004). Vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenic gene therapy in patients with peripheral artery disease. Experimental & Molecular Medicine, 36(4), 336–344. Epub 2004/09/15.
Shyu, K. G., Chang, H., Wang, B. W., & Kuan, P. (2003). Intramuscular vascular endothelial growth factor gene therapy in patients with chronic critical leg ischemia. American Journal of Medicine, 114(2), 85–92. Epub 2003/02/15.
Kusumanto, Y. H., van Weel, V., Mulder, N. H., Smit, A. J., van den Dungen, J. J., Hooymans, J. M., et al. (2006). Treatment with intramuscular vascular endothelial growth factor gene compared with placebo for patients with diabetes mellitus and critical limb ischemia: a double-blind randomized trial. Human Gene Therapy, 17(6), 683–691. Epub 2006/06/17.
Comerota, A. J., Throm, R. C., Miller, K. A., Henry, T., Chronos, N., Laird, J., et al. (2002). Naked plasmid DNA encoding fibroblast growth factor type 1 for the treatment of end-stage unreconstructible lower extremity ischemia: preliminary results of a phase I trial. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 35(5), 930–936. Epub 2002/05/22.
Nikol, S., Baumgartner, I., Van Belle, E., Diehm, C., Visona, A., Capogrossi, M. C., et al. (2008). Therapeutic angiogenesis with intramuscular NV1FGF improves amputation-free survival in patients with critical limb ischemia. Molecular Therapy, 16(5), 972–978. Epub 2008/04/05.
Belch, J., Hiatt, W. R., Baumgartner, I., Driver, I. V., Nikol, S., Norgren, L., et al. (2011). Effect of fibroblast growth factor NV1FGF on amputation and death: a randomised placebo-controlled trial of gene therapy in critical limb ischaemia. Lancet, 377(9781), 1929–1937. Epub 2011/05/31.
Makino, H., Aoki, M., Hashiya, N., Yamasaki, K., Azuma, J., Sawa, Y., et al. (2012). Long-term follow-up evaluation of results from clinical trial using hepatocyte growth factor gene to treat severe peripheral arterial disease. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 32(10), 2503–2509. Epub 2012/08/21.
Powell, R. J., Simons, M., Mendelsohn, F. O., Daniel, G., Henry, T. D., Koga, M., et al. (2008). Results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled study to assess the safety of intramuscular injection of hepatocyte growth factor plasmid to improve limb perfusion in patients with critical limb ischemia. Circulation, 118(1), 58–65. Epub 2008/06/19.
Powell, R. J., Goodney, P., Mendelsohn, F. O., Moen, E. K., & Annex, B. H. (2010). Safety and efficacy of patient specific intramuscular injection of HGF plasmid gene therapy on limb perfusion and wound healing in patients with ischemic lower extremity ulceration: results of the HGF-0205 trial. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 52(6), 1525–1530. Epub 2010/12/15.
Rajagopalan, S., Olin, J., Deitcher, S., Pieczek, A., Laird, J., Grossman, P. M., et al. (2007). Use of a constitutively active hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha transgene as a therapeutic strategy in no-option critical limb ischemia patients: phase I dose-escalation experience. Circulation, 115(10), 1234–1243. Epub 2007/02/21.
Kawamoto, A., Katayama, M., Handa, N., Kinoshita, M., Takano, H., Horii, M., et al. (2009). Intramuscular transplantation of G-CSF-mobilized CD34(+) cells in patients with critical limb ischemia: a phase I/IIa, multicenter, single-blinded, dose-escalation clinical trial. Stem Cells, 27(11), 2857–2864. Epub 2009/08/28.
Burt, R. K., Testori, A., Oyama, Y., Rodriguez, H. E., Yaung, K., Villa, M., Bucha, J. M., Milanetti, F., Sheehan, J., Rajamannan, N., & Pearce, W. H. (2010). Autologous peripheral blood CD133+ cell implantation for limb salvage in patients with critical limb ischemia. Bone Marrow Transplantation, 45(1), 111–116.
Walter, D. H., Krankenberg, H., Balzer, J. O., Kalka, C., Baumgartner, I., Schluter, M., et al. (2011). Intraarterial administration of bone marrow mononuclear cells in patients with critical limb ischemia: a randomized-start, placebo-controlled pilot trial (PROVASA). Circulation. Cardiovascular Interventions, 4(1), 26–37. Epub 2011/01/06.
Powell, R. J., Marston, W. A., Berceli, S. A., Guzman, R., Henry, T. D., Longcore, A. T., Stern, T. P., Watling, S., & Bartel, R. L. (2012). Cellular therapy with Ixmyelocel-T to treat critical limb ischemia: the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled RESTORE-CLI trial. Molecular Therapy, 20(6), 1280–1286. doi:10.1038/mt.2012.52. Epub 2011/06/21.
Murphy, M. P., Lawson, J. H., Rapp, B. M., Dalsing, M. C., Klein, J., Wilson, M. G., et al. (2011). Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy is safe and promotes amputation-free survival in patients with critical limb ischemia. Journal of Vascular Surgery, 53(6), 1565–74 e1. Epub 2011/04/26.
Lasala, G. P., Silva, J. A., Gardner, P. A., & Minguell, J. J. (2010). Combination stem cell therapy for the treatment of severe limb ischemia: safety and efficacy analysis. Angiology, 61(6), 551–556. Epub 2010/05/26.
Lasala, G. P., Silva, J. A., & Minguell, J. J. (2012). Therapeutic angiogenesis in patients with severe limb ischemia by transplantation of a combination stem cell product. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 144(2), 377–382. Epub 2011/11/15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Angela Taylor oversaw the review of this article
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, K.P., Sharma, A.M. Critical Limb Ischemia: Current Approach and Future Directions. J. of Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 7, 437–445 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-014-9562-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-014-9562-8