Abstract
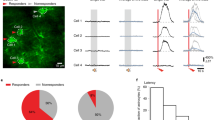
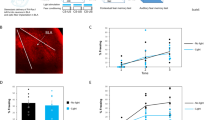
The importance of astrocytes in behavior control is increasingly appreciated, but little is known about the effects of their dynamic activity in regulating learning and memory. In the present study, we constructed AAVs of photoactivatable and photoinactivatable Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1) under the mGFAP promoter, which enabled the manipulation of Rac1 activity in astrocytes by optical stimulation in free-moving mice. We found that both up-regulation and down-regulation of astrocytic Rac1 activity in the basolateral amygdala (BLA) attenuated memory acquisition in a fear conditioning mouse model. Meanwhile, neuronal activation in the BLA induced by memory acquisition was inhibited under both the up- and down-regulation of astrocytic Rac1 activity during training. In terms of the impact on fear memory retrieval, we found both up- and down-regulation of BLA astrocytic Rac1 activity impaired memory retrieval of fear conditioning and memory retrieval-induced neuronal activation. Notably, the effect of astrocytic Rac1 on memory retrieval was reversible. Our results demonstrate that the normal activity of astrocytic Rac1 is necessary for the activation of neurons and memory formation. Both activation and inactivation of astrocytic Rac1 activity in the BLA reduced the excitability of neurons, and thereby impaired fear memory acquisition and retrieval.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen NJ, Barres BA. Neuroscience: Glia - more than just brain glue. Nature 2009, 457: 675–677.
Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci 2006, 7: 41–53.
Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG. Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci 1999, 22: 208–215.
Allen NJ, Eroglu C. Cell biology of astrocyte-synapse interactions. Neuron 2017, 96: 697–708.
Lopez-Bayghen E, Ortega A. Glial glutamate transporters: new actors in brain signaling. IUBMB Life 2011, 63: 816–823.
Pascual O, Casper KB, Kubera C, Zhang J, Revilla-Sanchez R, Sul JY. Astrocytic purinergic signaling coordinates synaptic networks. Science 2005, 310: 113–116.
Araque A, Carmignoto G, Haydon PG, Oliet SH, Robitaille R, Volterra A. Gliotransmitters travel in time and space. Neuron 2014, 81: 728–739.
Savtchouk I, Volterra A. Gliotransmission: beyond black-and-white. J Neurosci 2018, 38: 14–25.
Qin C, Zhou LQ, Ma XT, Hu ZW, Yang S, Chen M, et al. Dual functions of microglia in ischemic stroke. Neurosci Bull 2019, 35: 921–933.
Rose CR, Karus C. Two sides of the same coin: sodium homeostasis and signaling in astrocytes under physiological and pathophysiological conditions. Glia 2013, 61: 1191–1205.
Kim JJ, Jung MW. Neural circuits and mechanisms involved in Pavlovian fear conditioning: a critical review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2006, 30: 188–202.
Malleret G, Alarcon JM, Martel G, Takizawa S, Vronskaya S, Yin D, et al. Bidirectional regulation of hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity and its influence on opposing forms of memory. J Neurosci 2010, 30: 3813–3825.
Maren S. Synaptic mechanisms of associative memory in the amygdala. Neuron 2005, 47: 783–786.
Rodrigues SM, Schafe GE, LeDoux JE. Molecular mechanisms underlying emotional learning and memory in the lateral amygdala. Neuron 2004, 44: 75–91.
Takeuchi T, Duszkiewicz AJ, Morris RG. The synaptic plasticity and memory hypothesis: encoding, storage and persistence. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2014, 369: 20130288.
Alberini CM, Cruz E, Descalzi G, Bessieres B, Gao V. Astrocyte glycogen and lactate: New insights into learning and memory mechanisms. Glia 2018, 66: 1244–1262.
Logan S, Pharaoh GA, Marlin MC, Masser DR, Matsuzaki S, Wronowski B, et al. Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling regulates working memory, mitochondrial metabolism, and amyloid-beta uptake in astrocytes. Mol Metab 2018, 9: 141–155.
Zhang X, Shen X, Dong J, Liu WC, Song M, Sun Y, et al. Inhibition of reactive astrocytes with fluorocitrate ameliorates learning and memory impairment through upregulating CRTC1 and synaptophysin in ischemic stroke rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2019, 39: 1151–1163.
Jaffe AB, Hall A. Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2005, 21: 247–269.
Racchetti G, D’Alessandro R, Meldolesi J. Astrocyte stellation, a process dependent on Rac1 is sustained by the regulated exocytosis of enlargeosomes. Glia 2012, 60: 465–475.
Liao Z, Tao Y, Guo X, Cheng D, Wang F, Liu X, et al. Fear conditioning downregulates Rac1 activity in the basolateral amygdala astrocytes to facilitate the formation of fear memory. Front Mol Neurosci 2017, 10: 396.
Martinez LA, Klann E, Tejada-Simon MV. Translocation and activation of Rac in the hippocampus during associative contextual fear learning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2007, 88: 104–113.
Wu YI, Frey D, Lungu OI, Jaehrig A, Schlichting I, Kuhlman B, et al. A genetically encoded photoactivatable Rac controls the motility of living cells. Nature 2009, 461: 104–108.
Zhou Y, Zhu H, Liu Z, Chen X, Su X, Ma C, et al. A ventral CA1 to nucleus accumbens core engram circuit mediates conditioned place preference for cocaine. Nat Neurosci 2019, 22: 1986–1999.
Couto A, Mack NA, Favia L, Georgiou M. An apicobasal gradient of Rac activity determines protrusion form and position. Nat Commun 2017, 8: 15385.
Fan XC, Fu S, Liu FY, Cui S, Yi M, Wan Y. Hypersensitivity of prelimbic cortex neurons contributes to aggravated nociceptive responses in rats with experience of chronic inflammatory pain. Front Mol Neurosci 2018, 11: 85.
Daneman R, Prat A. The blood-brain barrier. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2015, 7: a020412.
Verkhratsky A, Nedergaard M. Physiology of astroglia. Physiol Rev 2018, 98: 239–389.
Ioannou MS, Jackson J, Sheu SH, Chang CL, Weigel AV, Liu H, et al. Neuron-astrocyte metabolic coupling protects against activity-induced fatty acid toxicity. Cell 2019, 177(1522–1535): e1514.
Chung WS, Allen NJ, Eroglu C. Astrocytes control synapse formation, function, and elimination. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2015, 7: a020370.
Breslin K, Wade JJ, Wong-Lin K, Harkin J, Flanagan B, Van Zalinge H, et al. Potassium and sodium microdomains in thin astroglial processes: A computational model study. PLoS Comput Biol 2018, 14: e1006151.
Rose CR, Ziemens D, Untiet V, Fahlke C. Molecular and cellular physiology of sodium-dependent glutamate transporters. Brain Res Bull 2018, 136: 3–16.
Martin-Fernandez M, Jamison S, Robin LM, Zhao Z, Martin ED, Aguilar J, et al. Synapse-specific astrocyte gating of amygdala-related behavior. Nat Neurosci 2017, 20: 1540–1548.
Adamsky A, Kol A, Kreisel T, Doron A, Ozeri-Engelhard N, Melcer T, et al. Astrocytic activation generates de novo neuronal potentiation and memory enhancement. Cell 2018, 174(59–71): e14.
Bechtholt-Gompf AJ, Walther HV, Adams MA, Carlezon WA Jr, Ongur D, Cohen BM. Blockade of astrocytic glutamate uptake in rats induces signs of anhedonia and impaired spatial memory. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35: 2049–2059.
Suzuki A, Stern SA, Bozdagi O, Huntley GW, Walker RH, Magistretti PJ, et al. Astrocyte-neuron lactate transport is required for long-term memory formation. Cell 2011, 144: 810–823.
Pannasch U, Freche D, Dallerac G, Ghezali G, Escartin C, Ezan P, et al. Connexin 30 sets synaptic strength by controlling astroglial synapse invasion. Nat Neurosci 2014, 17: 549–558.
Poskanzer KE, Yuste R. Astrocytes regulate cortical state switching in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016, 113: E2675-2684.
Panatier A, Theodosis DT, Mothet JP, Touquet B, Pollegioni L, Poulain DA, et al. Glia-derived D-serine controls NMDA receptor activity and synaptic memory. Cell 2006, 125: 775–784.
Papouin T, Dunphy JM, Tolman M, Dineley KT, Haydon PG. Septal Cholinergic neuromodulation tunes the astrocyte-dependent gating of hippocampal NMDA receptors to wakefulness. Neuron 2017, 94(840–854): e847.
Newey SE, Velamoor V, Govek EE, Van Aelst L. Rho GTPases, dendritic structure, and mental retardation. J Neurobiol 2005, 64: 58–74.
Gordon-Weeks PR, Fournier AE. Neuronal cytoskeleton in synaptic plasticity and regeneration. J Neurochem 2014, 129: 206–212.
Tashiro A, Minden A, Yuste R. Regulation of dendritic spine morphology by the rho family of small GTPases: antagonistic roles of Rac and Rho. Cereb Cortex 2000, 10: 927–938.
Tashiro A, Yuste R. Regulation of dendritic spine motility and stability by Rac1 and Rho kinase: evidence for two forms of spine motility. Mol Cell Neurosci 2004, 26: 429–440.
Fan L, Lu Y, Shen X, Shao H, Suo L, Wu Q. Alpha protocadherins and Pyk2 kinase regulate cortical neuron migration and cytoskeletal dynamics via Rac1 GTPase and WAVE complex in mice. Elife 2018, 7: e35242.
Vaghi V, Pennucci R, Talpo F, Corbetta S, Montinaro V, Barone C, et al. Rac1 and rac3 GTPases control synergistically the development of cortical and hippocampal GABAergic interneurons. Cereb Cortex 2014, 24: 1247–1258.
Posada-Duque RA, Lopez-Tobon A, Piedrahita D, Gonzalez-Billault C, Cardona-Gomez GP. p35 and Rac1 underlie the neuroprotection and cognitive improvement induced by CDK5 silencing. J Neurochem 2015, 134: 354–370.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (BX20180070 and 2019M661347), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31930046 and 31771176).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors claim that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, XC., Ma, CN., Song, JC. et al. Rac1 Signaling in Amygdala Astrocytes Regulates Fear Memory Acquisition and Retrieval. Neurosci. Bull. 37, 947–958 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-021-00677-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-021-00677-w