Abstract
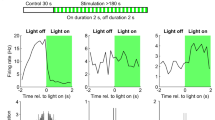
Neuronal oscillations are fundamental to hippocampal function. It has been shown that GABAergic interneurons make an important contribution to hippocampal oscillations, but the underlying mechanism is not well understood. Here, using whole-cell recording in the complete hippocampal formation isolated from rats at postnatal days 14–18, we showed that GABAA receptor-mediated activity enhanced the generation of slow CA1 oscillations. In vitro, slow oscillations (0.5–1.5 Hz) were generated in CA1 neurons, and they consisted primarily of excitatory rather than inhibitory membrane-potential changes. These oscillations were greatly reduced by blocking GABAA receptor-mediated activity with bicuculline and were enhanced by increasing such activity with midazolam, suggesting that interneurons are required for oscillation generation. Consistently, CA1 fast-spiking interneurons were found to generate action potentials usually preceding those in CA1 pyramidal cells. These findings indicate a GABAA receptor-based mechanism for the generation of the slow CA1 oscillation in the hippocampus.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axmacher N, Mormann F, Fernandez G, Elger CE, Fell J. Memory formation by neuronal synchronization. Brain Res Rev 2006, 52: 170–182.
Bissiere S, Zelikowsky M, Ponnusamy R, Jacobs NS, Blair HT, Fanselow MS. Electrical synapses control hippocampal contributions to fear learning and memory. Science 2011, 331: 87–91.
Wang DV, Yau H-J, Broker CJ, Tsou J-H, Bonci A, Ikemoto S. Mesopontine median raphe regulates hippocampal ripple oscillation and memory consolidation. Nat Neurosci 2015, 18: 728–735.
Marshall L, Helgadottir H, Moelle M, Born J. Boosting slow oscillations during sleep potentiates memory. Nature 2006, 444: 610–613.
Ku Y, Bodner M, Zhou YD. Prefrontal cortex and sensory cortices during working memory: quantity and quality. Neurosci Bull 2015, 31: 175–182.
Csicsvari J, Hirase H, Czurko A, Mamiya A, Buzsaki G. Oscillatory coupling of hippocampal pyramidal cells and interneurons in the behaving rat. J Neurosci 1999, 19: 274–287.
Freund TF, Buzsaki G. Interneurons of the hippocampus. Hippocampus 1996, 6: 347–470.
Cobb SR, Buhl EH, Halasy K, Paulsen O, Somogyi P. Synchronization of neuronal activity in hippocampus by individual GABAergic interneurons. Nature 1995, 378: 75–78.
Klausberger T, Somogyi P. Neuronal diversity and temporal dynamics: The unity of hippocampal circuit operations. Science 2008, 321: 53–57.
Fukuda T, Kosaka T. Gap junctions linking the dendritic network of GABAergic interneurons in the hippocampus. J Neuorsci 2000, 20: 1519–1528.
Tamas G, Buhl EH, Lorincz A, Somogyi P. Proximally targeted GABAergic synapses and gap junctions synchronize cortical interneurons. Nat Neurosci 2000, 3: 366–371.
Mann EO, Paulsen O. Role of GABAergic inhibition in hippocampal network oscillations. Trends Neurosci 2007, 30: 343–349.
Allen K, Monyer H. Interneuron control of hippocampal oscillations. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2015, 31: 81–87.
Roux L, Buzsaki G. Tasks for inhibitory interneurons in intact brain circuits. Neuropharmacology 2015, 88: 10–23.
Bonifazi P, Goldin M, Picardo MA, Jorquera I, Cattani A, Bianconi G, et al. GABAergic hub neurons orchestrate synchrony in developing hippocampal networks. Science 2009, 326: 1419–1424.
Quilichini PP, Le Van Quyen M, Ivanov A, Turner DA, Carabalona A, Gozlan H, et al. Hub GABA neurons mediate gamma-frequency oscillations at ictal-like event onset in the immature hippocampus. Neuron 2012, 74: 57–64.
Picardo MA, Guigue P, Bonifazi P, Batista-Brito R, Allene C, Ribas A, et al. Pioneer GABA cells comprise a subpopulation of hub neurons in the developing hippocampus. Neuron 2011, 71: 695–709.
Korotkova T, Fuchs EC, Ponomarenko A, von Engelhardt J, Monyer H. NMDA receptor ablation on parvalbumin-positive interneurons impairs hippocampal synchrony, spatial representations, and working memory. Neuron 2010, 68: 557–569.
Fuchs EC, Zivkovic AR, Cunningham MO, Middleton S, LeBeau FEN, Bannerman DM, et al. Recruitment of parvalbumin-positive interneurons determines hippocampal function and associated behavior. Neuron 2007, 53: 591–604.
Wulff P, Ponomarenko AA, Bartos M, Korotkova TM, Fuchs EC, Baehner F, et al. Hippocampal theta rhythm and its coupling with gamma oscillations require fast inhibition onto parvalbumin-positive interneurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106: 3561–3566.
Caputi A, Fuchs EC, Allen K, Le Magueresse C, Monyer H. Selective reduction of AMPA currents onto hippocampal interneurons impairs network Oscillatory Activity. PLoS One 2012, 7: e37318.
Royer S, Zemelman BV, Losonczy A, Kim J, Chance F, Magee JC, et al. Control of timing, rate and bursts of hippocampal place cells by dendritic and somatic inhibition. Nat Neurosci 2012, 15: 769–775.
Stark E, Eichler R, Roux L, Fujisawa S, Rotstein HG, Buzsaki G. Inhibition-induced theta resonance in cortical circuits. Neuron 2013, 80: 1263–1276.
Stark E, Roux L, Eichler R, Senzai Y, Royer S, Buzsaki G. Pyramidal cell-interneuron interactions underlie hippocampal ripple oscillations. Neuron 2014, 83: 467–480.
Goutagny R, Jackson J, Williams S. Self-generated theta oscillations in the hippocampus. Nat Neurosci 2009, 12: 1491–1493.
Wang Z, Xu NL, Wu CP, Duan S, Poo MM. Bidirectional changes in spatial dendritic integration accompanying long-term synaptic modifications. Neuron 2003, 37: 463–472.
Ben-Ari Y, Tseeb V, Raggozzino D, Khazipov R, Gaiarsa JL. gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA): a fast excitatory transmitter which may regulate the development of hippocampal neurones in early postnatal life. Prog Brain Res 1994, 102: 261–273.
Lujan R, Shigemoto R, Lopez-Bendito G. Glutamate and GABA receptor signalling in the developing brain. Neuroscience 2005, 130: 567–580.
Fregnac Y. Dynamics of functional connectivity in visual cortical networks: an overview. J Physiol Paris 1996, 90: 113–139.
Roudi Y, Dunn B, Hertz J. Multi-neuronal activity and functional connectivity in cell assemblies. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2015, 32: 38–44.
Chavas J, Marty A. Coexistence of excitatory and inhibitory GABA synapses in the cerebellar interneuron network. J Neurosci 2003, 23: 2019–2031.
Gulledge AT, Stuart GJ. Excitatory actions of GABA in the cortex. Neuron 2003, 37: 299–309.
Cossart R, Bernard C, Ben-Ari Y. Multiple facets of GABAergic neurons and synapses: multiple fates of GABA signalling in epilepsies. Trends Neurosci 2005, 28: 108–115.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91132711; 30970960; 31471078), a Key Scientific Project of the Shanghai Science and Technology Commission, China (15JC1400102), and the Shanghai Pu-Jiang Program, China (08PJ14044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yuan Xu and Lidan Wang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Wang, L., Liu, Yz. et al. GABAergic Interneurons are Required for Generation of Slow CA1 Oscillation in Rat Hippocampus. Neurosci. Bull. 32, 363–373 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-016-0049-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-016-0049-2