Abstract
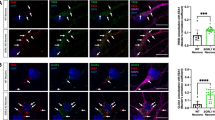
Accumulating evidence indicates that the synaptic activation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) has a neuroprotective effect on neurons. Our previous study demonstrated that APPL1 (adaptor protein containing pleckstrin homology domain, phosphotyrosine-binding domain, and leucine zipper motif) mediates the synaptic activity-dependent activation of PI3K-Akt signaling via coupling this pathway with NMDAR-PSD95 (postsynaptic density protein 95) complexes. However, the molecular mechanism underlying this process is still unknown. In the present study, we investigated the interaction of APPL1 with PSD95 using co-immunocytochemical staining and western blotting. We found that the PDZ2 domain of PSD95 is a binding partner of APPL1. Furthermore, we identified serine 707 of APPL1, a predicted phosphorylation site within the PDZ-binding motif at the C-terminus, as critical for the binding of APPL1 to PSD95, as well as for activation of the Akt signaling pathway during synaptic activity. This suggests that serine 707 of APPL1 is a potential phosphorylation site and may be involved in regulating the neuroprotective Akt signaling pathway that depends on synaptic NMDAR activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deepa SS, Dong LQ. APPL1: role in adiponectin signaling and beyond. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2009, 296: E22–36.
Mitsuuchi Y, Johnson SW, Sonoda G, Tanno S, Golemis EA, Testa JR. Identification of a chromosome 3p14.3-21.1 gene, APPL, encoding an adaptor molecule that interacts with the oncoprotein-serine/threonine kinase AKT2. Oncogene 1999, 18: 4891–4898.
Miaczynska M, Christoforidis S, Giner A, Shevchenko A, Uttenweiler-Joseph S, Habermann B, et al. APPL proteins link Rab5 to nuclear signal transduction via an endosomal compartment. Cell 2004, 116: 445–456.
Lin DC, Quevedo C, Brewer NE, Bell A, Testa JR, Grimes ML, et al. APPL1 associates with TrkA and GIPC1 and is required for nerve growth factor-mediated signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol 2006, 26: 8928–8941.
Mao X, Kikani CK, Riojas RA, Langlais P, Wang L, Ramos FJ, et al. APPL1 binds to adiponectin receptors and mediates adiponectin signalling and function. Nat Cell Biol 2006, 8: 516–523.
Liu J, Yao F, Wu R, Morgan M, Thorburn A, Finley RL Jr, et al. Mediation of the DCC apoptotic signal by DIP13 alpha. J Biol Chem 2002, 277: 26281–26285.
Schenck A, Goto-Silva L, Collinet C, Rhinn M, Giner A, Habermann B, et al. The endosomal protein Appl1 mediates Akt substrate specificity and cell survival in vertebrate development. Cell 2008, 133: 486–497.
Varsano T, Dong MQ, Niesman I, Gacula H, Lou X, Ma T, et al. GIPC is recruited by APPL to peripheral TrkA endosomes and regulates TrkA trafficking and signaling. Mol Cell Biol 2006, 26: 8942–8952.
Cheng KK, Lam KS, Wang Y, Huang Y, Carling D, Wu D, et al. Adiponectin-induced endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation and nitric oxide production are mediated by APPL1 in endothelial cells. Diabetes 2007, 56: 1387–1394.
Majumdar D, Nebhan CA, Hu L, Anderson B, Webb DJ. An APPL1/Akt signaling complex regulates dendritic spine and synapse formation in hippocampal neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 2011, 46: 633–644.
Wang YB, Wang JJ, Wang SH, Liu SS, Cao JY, Li XM, et al. Adaptor protein APPL1 couples synaptic NMDA receptor with neuronal prosurvival phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Neurosci 2012, 32: 11919–11929.
Zhang XM, Lv XY, Tang Y, Zhu LJ, Luo JH. Cysteine residues 87 and 320 in the amino terminal domain of NMDA receptor GluN2A govern its homodimerization but do not influence GluN2A/GluN1 heteromeric assembly. Neurosci Bull 2013, 29: 671–684.
Lu W, Ai H, Peng L, Wang JJ, Zhang B, Liu X, et al. A novel phosphorylation site of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor GluN2B at S1284 is regulated by Cdk5 in neuronal ischemia. Exp Neurol 2015, 271: 251–258.
Lu W, Fang W, Li J, Zhang B, Yang Q, Yan X, et al. Phosphorylation of Tyrosine 1070 at the GluN2B Subunit Is Regulated by Synaptic Activity and Critical for Surface Expression of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) Receptors. J Biol Chem 2015, 290: 22945–22954.
Luo J, Wang Y, Yasuda RP, Dunah AW, Wolfe BB. The majority of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor complexes in adult rat cerebral cortex contain at least three different subunits (NR1/NR2A/NR2B). Mol Pharmacol 1997, 51: 79–86.
Kemp JA, McKernan RM. NMDA receptor pathways as drug targets. Nat Neurosci 2002, 5 Suppl: 1039–1042.
Salter MW, Pitcher GM. Dysregulated Src upregulation of NMDA receptor activity: a common link in chronic pain and schizophrenia. FEBS J 2012, 279: 2–11.
Doucet MV, Harkin A, Dev KK. The PSD-95/nNOS complex: new drugs for depression? Pharmacol Ther 2012, 133: 218–229.
Cao J, Viholainen JI, Dart C, Warwick HK, Leyland ML, Courtney MJ. The PSD95-nNOS interface: a target for inhibition of excitotoxic p38 stress-activated protein kinase activation and cell death. J Cell Biol 2005, 168: 117–126.
Toro C, Deakin JF. NMDA receptor subunit NRI and postsynaptic protein PSD-95 in hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortex in schizophrenia and mood disorder. Schizophr Res 2005, 80: 323–330.
Zhou L, Li F, Xu HB, Luo CX, Wu HY, Zhu MM, et al. Treatment of cerebral ischemia by disrupting ischemia-induced interaction of nNOS with PSD-95. Nat Med 2010, 16: 1439–1443.
Li LL, Ginet V, Liu X, Vergun O, Tuittila M, Mathieu M, et al. The nNOS-p38MAPK pathway is mediated by NOS1AP during neuronal death. J Neurosci 2013, 33: 8185–8201.
Courtney MJ, Li LL, Lai YY. Mechanisms of NOS1AP action on NMDA receptor-nNOS signaling. Front Cell Neurosci 2014, 8: 252.
Maher A, El-Sayed NS, Breitinger HG, Gad MZ. Overexpression of NMDAR2B in an inflammatory model of Alzheimer’s disease: modulation by NOS inhibitors. Brain Res Bull 2014, 109: 109–116.
Gant-Branum RL, Broussard JA, Mahsut A, Webb DJ, McLean JA. Identification of phosphorylation sites within the signaling adaptor APPL1 by mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 2010, 9: 1541–1548.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91232303, 81221003, and 81561168).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Lu, W., Chen, L. et al. Serine 707 of APPL1 is Critical for the Synaptic NMDA Receptor-Mediated Akt Phosphorylation Signaling Pathway. Neurosci. Bull. 32, 323–330 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-016-0042-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-016-0042-9