Abstract
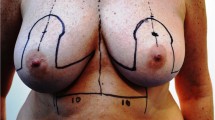
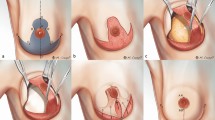
Breast hypertrophy causes medical problems ranging from back and neck pain to dermatitis creating a demand for breast reduction surgery along with aesthetic and psychological reasons. Free-nipple-graft breast reduction surgery is a safeguard procedure for patients who are at risk for nipple necrosis with pedicled techniques but has a disadvantage of resultant flat breasts with poor projection. Study included twenty-three postmenopausal women who underwent breast reduction with inferior pedicled dermaglandular flap and free-nipple-grafting, between September 2015 and January 2020. A rectangular 8 × 10 cm inferior-pedicled dermaglandular flap was dissected and anchored to the thoracic wall for better projection and upper pole fullness. All patients had at least one comorbidity. Visual analog scale was evaluated at 1–3 months. Mean age of the patients was 54.08 SD 4.65 years, and mean body mass index (BMI) was 33.56 SD 2.53. Mean follow-up period was 10.56 SD 5.6 months. Mean SN-N distance was 37.45 SD 3.77 and 38.86 SD 3.91 cm for right and left breasts, respectively. Mean resection weight was 1373 SD 440 g. Wound dehiscence was seen in 3 patients (13.0%) and treated medically. No other complications, including total nipple areolar complex (NAC) loss, were seen. Mean visual analog scale score for patient satisfaction was 7.7. All patients were satisfied with their final breast shapes. Utilizing inferior dermaglandular pedicled flap technique with free-nipple-graft breast reduction mammaplasty provides better nipple projection and a more aesthetically pleasing breast shape and contour. It helps achieve an effortless preoperative planning and a straightforward procedure with high patient satisfaction in postmenopausal obese women.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brühlmann Y, Tschopp H (1998) Breast reduction improves symptoms of macromastia and has a long-lasting effect. Ann Plast Surg 41(3):240–245
Schnur PL, Schnur DP, Petty PM, Hanson TJ, Weaver AL (1997) Reduction mammaplasty: An outcome study. Plast Reconstr Surg 100(4):875–883
Gorgu M, Ayhan M, Aytug Z, Aksungur E, Demirdover C (2007) Maximizing breast projection with combined free nipple graft reduction mammaplasty and back-folded dermaglandular inferior pedicle. Breast J 13(3):226–232
Firat C, Gurlek A, Erbatur S, Aytekin AH (2012) An autoprosthesis technique for better breast projection in free nipple graft reduction mammaplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg 36(6):1340–1346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9984-0
Surgeons ASoP (2018) 2018 National plastic surgery statistics. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2018/plastic-surgery-statistics-full-report-2018.pdf. Accessed 7 June 2020
Davis GM, Ringler SL, Short K, Sherrick D, Bengtson BP (1995) Reduction mammaplasty: long-term efficacy, morbidity, and patient satisfaction. Plast Reconstr Surg 96(5):1106–1110
Nelson JA, Fischer JP, Chung CU, West A, Tuggle CT, Serletti JM, Kovach SJ (2014) Obesity and early complications following reduction mammaplasty: an analysis of 4545 patients from the 2005–2011 NSQIP datasets. J Plast Surg Hand Surg 48(5):334–339
Jensen JA, Lin JH, Kapoor N, Giuliano AE (2012) Surgical delay of the nipple–areolar complex: a powerful technique to maximize nipple viability following nipple-sparing mastectomy. Ann Surg Oncol 19(10):3171–3176
Kelahmetoglu O, Firinciogullari R, Yagmur C, Yildiz K, Guneren E (2017) Combination of Würinger’s horizontal septum and inferior pedicle techniques to increase nipple-areolar complex viability during breast reduction surgery. Aesthetic Plast Surg 41(6):1311–1317
Karacaoglu E, Zienowicz RJ (2017) Septum-inferior-medial (SIM)-based pedicle: a safe pedicle with well-preserved nipple sensation for reduction in gigantomastia. Aesthetic Plast Surg 41(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-016-0763-1
Portincasa A, Ciancio F, Cagiano L, Innocenti A, Parisi D (2017) Septum-enhanced mammaplasty in inferocentral pedicled breast reduction for macromastia and gigantomastia patients. Aesthetic Plast Surg 41(5):1037–1044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0868-1
Gerzenshtein J, Oswald T, McCluskey P, Caplan J, Angel MF (2005) Avoiding free nipple grafting with the inferior pedicle technique. Ann Plast Surg 55(3):245–249. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sap.0000174363.04135.b9
Freeman M, Carney M, Matatov T, Vemula R, Babycos C (2015) Leech (Hirudo medicinalis) therapy for the treatment of nipple-areolar complex congestion following breast reduction. Eplasty 15:ic45
Jackson IT, Bayramicli M, Gupta M, Yavuzer R (1999) Importance of the pedicle length measurement in reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 104(2):398–400. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199908000-00012
Blomqvist L (1996) Reduction mammaplasty: analysis of patients’ weight, resection weights, and late complications. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 30(3):207–210. https://doi.org/10.3109/02844319609062816
Mello AA, Domingos NA, Miyazaki MC (2010) Improvement in quality of life and self-esteem after breast reduction surgery. Aesthetic Plast Surg 34(1):59–64
Woodman R, Radzyminski S (2009) Women’s perception of life following breast reduction: A phenomenological study. Plast Surg Nurs 29(1):39–46
Ahmed OA, Kolhe PS (2000) Comparison of nipple and areolar sensation after breast reduction by free nipple graft and inferior pedicle techniques. Br J Plast Surg 53(2):126–129
Sterodimas A, Pineda EF, Meirelles V, Pitanguy I (2008) Maximizing nipple graft survival after performing free nipple-areolar complex reduction mammaplasty. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61(8):971–972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2008.04.004
Graf R, Biggs TM, Steely RL (2000) Breast shape: a technique for better upper pole fullness. Aesthetic Plast Surg 24(5):348–352
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelahmetoglu, O., Camli, M.F., Unal, M. et al. Simplifying Free Nipple Graft Mammoplasty in Postmenopausal Obese Patients using Inferior Dermaglandular Flap. Indian J Surg 84 (Suppl 3), 627–632 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-021-02992-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-021-02992-y