Abstract
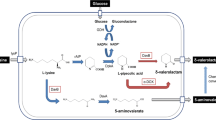
6-Aminocaproic acid and adipic acid are the key value-added chemical precursors in the pharmaceutical, solvent and polyamide industry, including nylon-6, and nylon-6, 6. An enzymatic interconversion of the two precursors can provide a convenient and eco-friendly biosynthetic route to each of the precursors and thus, require analysis of the reaction process. Herein, an in vitro enzymatic method was employed to convert the two precursors while most studies so far have focused on the whole cell bioconversion to investigate the process. 4-Aminobutyrate aminotransferase was utilized to mediate the reactions between 6-aminocaproic acid and the intermediate 6-oxohexanoic acid with the aid of pyridoxal 5’-phosphate and amine donor/acceptor. 6-Oxohexanoate dehydrogenase was utilized for the reaction from 6-oxohexanoic acid to adipic acid with NADP+. A range of reaction conditions were investigated including the type of amine donor, pH conditions, the concentrations of enzyme and amine donor/acceptor. The optimum condition resulted in 78% yield for the reaction from 6-oxohexanoic acid to 6-aminocaproic acid. The yield for the one-pot, two-step enzymatic cascade from 6-aminocaproic acid via 6-oxohexanoate intermediate to adipic acid was 88%, which was higher than the yield for each individual step in the cascade, with 31% and 32%, for the first and second step, respectively. Furthermore, structural analysis on the active site of the 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase docked with a range of amine donors implicates the optimal donor is glutamate in accordance with the experimental data and suggests enzyme engineering possibilities for more readily available donors to facilitate the industrial application of the process.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schaffer S, Haas T (2014) Biocatalytic and fermentative production of α, ω-bifunctional polymer precursors. Org Process Res Dev 18:752–766. https://doi.org/10.1021/op5000418
Mares F, Sheehan D (1978) Kinetics of caprolactam formation from 6-aminocaproic acid, ester, and amide. Ind Eng Chem Process Des Dev 17:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1021/i260065a003
Polen T, Spelberg M, Bott M (2013) Toward biotechnological production of adipic acid and precursors from biorenewables. J Biotechnol 167:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.07.008
Zuidhof KT, de Croon MHJM, Schouten JC (2010) Beckmann rearrangement of cyclohexanone oxime to ε-caprolactam in microreactors. AIChE J 56:1297–1304. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.12051
Srinivasamurthy VST, Böttcher D, Bornscheuer UT (2019) A multi-enzyme cascade reaction for the production of 6-hydroxyhexanoic acid. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci 74:71–76. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2018-0216
Schmidt S, Scherkus C, Muschiol J et al (2015) An enzyme cascade synthesis of ε-caprolactone and its oligomers. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 54:2784–2787. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201410633
Yin DL, Bernhardt P, Morley KL et al (2010) Switching catalysis from hydrolysis to perhydrolysis in pseudomonas fluorescens esterase. Biochemistry 49:1931–1942. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9021268
Rudat J, Brucher BR, Syldatk C (2012) Transaminases for the synthesis of enantiopure beta-amino acids. AMB Express 2:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/2191-0855-2-11
Liu W, Peterson PE, Langston JA et al (2005) Kinetic and crystallographic analysis of active site mutants of Escherichia coli gamma-aminobutyrate aminotransferase. Biochemistry 44:2982–2992. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi048657a
Priestman MA, Shell TA, Sun L et al (2012) Merging of confocal and caging technologies: selective three-color communication with profluorescent reporters. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51:7684–7687. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201202820
Lam S (1990) High performance liquid chromatographic assay of Amicar, epsilon-aminocaproic acid, in plasma and urine after pre-column derivatization with o-phthalaldehyde for fluorescence detection. Biomed Chromatogr 4:175–177. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.1130040414
Lee HS, Na JG, Lee J et al (2019) Structure-based mutational studies of D-3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase for substrate recognition of aliphatic hydroxy acids with a variable length of carbon chain. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 24:605–612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0135-1
Shin JS, Kim BG (2001) Comparison of the omega-transaminases from different microorganisms and application to production of chiral amines. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:1782–1788. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.65.1782
Der Garabedian PA, Lotti AM, Vermeersch JJ (1986) 4-Aminobutyrate: 2-Oxoglutarate aminotransferase from Candida. Purification and properties Eur J Biochem 156:589–596. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09618.x
Iijima K, Kojima N (1986) 4-Aminobutyrate: 2-Oxoglutarate transaminase-containing neurons in the perinuclear zone of the rat supraoptic nucleus. Acta Histochem 79:211–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-1281(86)80085-X
White HL (1979) 4-Aminobutyrate: 2-Oxoglutarate aminotransferase in blood platelets. Science 205:696–698. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.462176
Hwang BY, Cha M, Park HY et al (2011) Aminotransferase-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of benazepril intermediate. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 16:625–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0066-y
Bergmeyer HU, Scheibe P, Wahlefeld AW (1978) Optimization of methods for aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase. Clin Chem 24:58–73. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/24.1.58
Maître M, Ciesielski L, Cash C et al (1975) Purification and studies on some properties of the 4-aminobutyrate: 2-oxoglutarate transaminase from rat brain. Eur J Biochem 52:157–169. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03983.x
Ramírez-Palacios C, Wijma HJ, Thallmair S et al (2021) Computational prediction of ω-transaminase specificity by a combination of docking and molecular dynamics simulations. J Chem Inf Model 61:5569–5580. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00617
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (2022M3J4A1091452) and the Ministry of Education (2021R1I1A3060595).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
No ethical approval and informed consent are required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, HS., Yang, YH., Yeon, Y.J. et al. Enzymatic synthesis of nylon precursors by 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase and 6-oxohexanoate dehydrogenase. Biotechnol Bioproc E 29, 211–218 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-024-00011-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-024-00011-x