Abstract
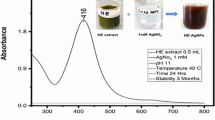
Nowadays, the fabrication and characterization of plant extract-based gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) as well as their anticancer activities have gained significant attention. Acorus calamus is a typical Chinese medicinal herb that has been utilized since a period of thousand years for treating rheumatism, asthma, tracheitis, etc. In the current study, the reaction parameters are optimized for managing the size of NPs as categorized by the high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. Various characterization methods such as X-ray diffraction, UV-visible spectroscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy were carried out to confirm the fabrication of AuNPs mediated by the leaf extract of A. calamus. Further, the neuroprotective potential of fabricated AuNPs was studied by evaluating the cholinesterase inhibitory activity and antioxidant potential. The nanogold aqueous extracts exhibited the highest antioxidant and anti-acetyl cholinesterase activity, confirming that AuNPs can cross the blood-brain barrier and raise the level of acetyl cholinesterase, at the same time reduces the oxidative stress levels. The obtained results concluded their important potential for development of anti-Alzheimer drug having antioxidant and anticholinesterase activity against oxidative stress.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Gour A, Jain NK (2019) Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:844–851. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1577878
Gardea-Torresdey JL, Gomez E, Peralta-Videa JR et al (2003) Alfalfa sprouts: a natural source for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Langmuir 19:1357–1361. https://doi.org/10.1021/la020835i
Huang J, Li Q, Sun D et al (2007) Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by novel sundried Cinnamomum camphora leaf. Nanotechnology 18:105104. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/10/105104
Leela A, Vivekanandan M (2008) Tapping the unexploited plant resources for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Afr J Biotechnol 7:3162–3165. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB08.425
Li S, Shen Y, Xie A et al (2007) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Capsicum annuum L. extract. Green Chem 9:852–858. https://doi.org/10.1039/B615357G
Shankar SS, Rai A, Ahmad A et al (2004) Rapid synthesis of au, Ag, and bimetallic au core-Ag shell nanoparticles using neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf broth. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:496–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.03.003
Song JY, Kim BS (2009) Rapid biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant leaf extracts. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 32:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-008-0224-6
Mani A, Lakshmi S, Gopal V (2012) Bio-mimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of its free radical scavenging activity. Int J Biol Pharm Res 3:631–633
Aparna Mani KM, Seethalakshmi S, Gopal V (2015) Evaluation of in-vitro anti-inflammatory activity of silver nanoparticles synthesised using Piper nigrum extract. J Nanomed Nanotechnol 6:268. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7439.1000268
Shawkey AM, Rabeh MA, Abdulall A et al (2013) Green nanotechnology: anticancer activity of silver nanoparticles using Citrullus colocynthis aqueous extracts. Int J Adv Life Sci Technol 13:60–70
Chandra Mohan S, Sasikala K, Anand T et al (2014) Green synthesis, antimicrobial and antioxidant effects of silver nanoparticles using Canthium coromandelicum leaves extract. Res J Microbiol 9:142–150. https://doi.org/10.3923/jm.2014.142.150
Rajenran R, Ganesan N, Balu SK et al (2015) Green synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial and cytotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles using Origanum heracleoticum L. leaf extract. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 7:288–293
Nazem A, Mansoori GA (2011) Nanotechnology for Alzheimer’s disease detection and treatment. Insciences J 1:169–193. https://doi.org/10.5640/insc.0104169
Nazıroğlu M, Muhamad S, Pecze L (2017) Nanoparticles as potential clinical therapeutic agents in Alzheimer’s disease: focus on selenium nanoparticles. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 10:773–782. https://doi.org/10.1080/17512433.2017.1324781
Saraiva C, Praça C, Ferreira R et al (2016) Nanoparticle-mediated brain drug delivery: overcoming blood–brain barrier to treat neurodegenerative diseases. J Control Release 235:34–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.05.044
Hajipour MJ, Santoso MR, Rezaee F et al (2017) Advances in Alzheimer’s diagnosis and therapy: the implications of nanotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 35:937–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2017.06.002
Zheng X, Zhang C, Guo Q et al (2017) Dual-functional nanoparticles for precise drug delivery to Alzheimer’s disease lesions: targeting mechanisms, pharmacodynamics and safety. Int J Pharm 525:237–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.04.033
Carradori D, Balducci C, Re F et al (2018) Antibody-functionalized polymer nanoparticle leading to memory recovery in Alzheimer’s disease-like transgenic mouse model. Nanomedicine 14:609–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2017.12.006
Loureiro JA, Gomes B, Fricker G et al (2016) Cellular uptake of PLGA nanoparticles targeted with anti-amyloid and anti-transferrin receptor antibodies for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 145:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.04.041
Yulizar Y, Utari T, Ariyanta HA et al (2017) Green method for synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Polyscias scutellaria leaf extract under UV light and their catalytic activity to reduce methylene blue. J Nanomater 2017:3079636. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3079636
Makarov VV, Love AJ, Sinitsyna OV et al (2014) Green nanotechnologies: synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Naturae 6:35–44. https://doi.org/10.32607/20758251-2014-6-1-35-44
Sadeghi B, Mohammadzadeh M, Babakhani B (2015) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Stevia rebaudiana leaf extracts: characterization and their stability. J Photochem Photobiol B 148:101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.03.025
Maddinedi SB, Mandal BK, Anna KK (2017) Environment friendly approach for size controllable synthesis of biocompatible silver nanoparticles using diastase. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 49:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2016.11.019
Maddinedi SB, Mandal BK, Anna KK (2017) Tyrosine assisted size controlled synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their catalytic, in-vitro cytotoxicity evaluation. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 51:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.02.020
Maddinedi SB, Mandal BK, Maddili SK (2017) Biofabrication of size controllable silver nanoparticles—A green approach. J Photochem Photobiol B 167:236–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.01.003
Mohan Kumar K, Mandal BK, Kiran Kumar HA et al (2013) Green synthesis of size controllable gold nanoparticles. Spectrochim Acta Mol Biomol Spectrosc 116:539–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.07.077
Ragab D, Abdallah DM, El-Abhar HS (2014) Cilostazol renoprotective effect: modulation of PPAR-γ, NGAL, KIM-1 and IL-18 underlies its novel effect in a model of ischemia-reperfusion. PLoS ONE 9:e95313. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095313
Satoh K (1978) Serum lipid peroxide in cerebrovascular disorders determined by a new colorimetric method. Clin Chim Acta 90:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(78)90081-5
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Galle P, Berry GP, Duckett S (1980) Electron microprobe ultrastructural localization of aluminum in rat brain. Acta Neuropathol 49:245–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00707114
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HP: Experimental works for materials preparation, manuscript writing. SZ: Manuscript writing, interpretation of data, data analysis. QC: Biological experiments, statistical analysis. ZH: Manuscript writing, interpretation of data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All the animal experiments were performed with the approval from Research Centre ethics committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Shaoyang University and experiments were performed according to their guidelines.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, H., Zhang, S., Chai, Q. et al. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Acorus calamus leaf extract and study on their anti-alzheimer potential. Biotechnol Bioproc E 29, 157–163 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-024-00010-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-024-00010-y