Abstract
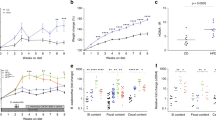
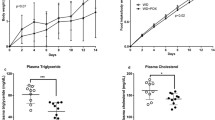
Gut microbiota dysbiosis and consequent dysregulation of the intestinal barrier homeostasis have been implicated in the development of metabolic complications. Korean red ginseng (RG) and its fermented RG (bio-transformed by microorganism, FRG) have been recognized for their prebiotic role in the regulation of intestinal barrier function and inflammation. Thus, we investigated the effects of RG and FRG supplementation on gut barrier integrity and inflammatory profile in association with the compositional change in the gut microbiota of rats fed a high-fat (HF) diet. Male Sprague-Dawley rats (n = 8/group; 6 weeks old) were counterbalanced by initial weight into four groups and fed either a low-fat (LF; 10% kcal as fat), HF (45% kcal as fat), or HF diet supplemented with RG or FRG at 1% (w/w) in diet for 6 weeks. RG and FRG supplementation led to compositional shifts in the gut microbiota characterized by Eubacterium by RG and Akkermansia genus by FRG, which have been associated with improved obese phenotype and glucose homeostasis. These changes were associated with improvements in gut barrier integrity, consequently protecting from HF-induced local (colon, liver) and systemic inflammation. RG and FRG supplementation also ameliorated lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by inhibiting its downstream pathway. Taken together, these data show that RG and FRG supplementation can improve the gut barrier function and local and systemic inflammation in HF-fed rats in association with compositional changes of the gut microbiota, supporting the promising application of RG and FRG for the regulation of gut barrier integrity and inflammatory profile under a metabolic challenge.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qin, J., R. Li, J. Raes, M. Arumugam, K. S. Burgdorf, C. Manichanh, T. Nielsen, N. Pons, F. Levenez, T. Yamada, D. R. Mende, J. Li, J. Xu, S. Li, D. Li, J. Cao, B. Wang, H. Liang, H. Zheng, Y. Xie, J. Tap, P. Lepage, M. Bertalan, J. M. Batto, T. Hansen, D. Le Paslier, A. Linneberg, H. B. Nielsen, E. Pelletier, P. Renault, T. Sicheritz-Ponten, K. Turner, H. Zhu, C. Yu, S. Li, M. Jian, Y. Zhou, Y. Li, X. Zhang, S. Li, N. Qin, H. Yang, J. Wang, S. Brunak, J. Doré, F. Guarner, K. Kristiansen, O. Pedersen, J. Parkhill, J. Weissenbach, MetaHIT Consortium, P. Bork, S. D. Ehrlich, and J. Wang (2010) A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 464: 59–65.
Lee, S. H. and C. B. de La Serre (2015) Gut microbiome-brain communications regulate host physiology and behavior. J. Nutrit. Health Food Sci. 3: 1–12.
Romaní-Pérez, M., A. Agusti, and Y. Sanz (2017) Innovation in microbiome-based strategies for promoting metabolic health. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 20: 484–491.
Carding, S., K. Verbeke, D. T. Vipond, B. M. Corfe, and L. J. Owen (2015) Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota in disease. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 26: 26191.
de La Serre, C. B., C. L. Ellis, J. Lee, A. L. Hartman, J. C. Rutledge, and H. E. Raybould (2010) Propensity to high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats is associated with changes in the gut microbiota and gut inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 299: G440–G448.
Cani, P. D., J. Amar, M. A. Iglesias, M. Poggi, C. Knauf, D. Bastelica, A. M. Neyrinck, F. Fava, K. M. Tuohy, C. Chabo, A. Waget, E. Delmée, B. Cousin, T. Sulpice, B. Chamontin, J. Ferrières, J. F. Tanti, G. R. Gibson, L. Casteilla, N. M. Delzenne, M. C. Alessi, and R. Burcelin (2007) Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 56: 1761–1772.
de La Serre, C. B., G. de Lartigue, and H. E. Raybould (2015) Chronic exposure to low dose bacterial lipopolysaccharide inhibits leptin signaling in vagal afferent neurons. Physiol. Behav. 139: 188–194.
Lee, S., K. I. Keirsey, R. Kirkland, Z. I. Grunewald, J. G. Fischer, and C. B. de La Serre (2018) Blueberry supplementation influences the gut microbiota, inflammation, and insulin resistance in high-fat-diet-fed rats. J. Nutr. 148: 209–219.
Lee, S., M. Goodson, W. Vang, K. Kalanetra, D. Barile, and H. Raybould (2020) 2′-fiicosyllactose supplementation improves gut-brain signaling and diet-induced obese phenotype and changes the gut microbiota in high fat-fed mice. Nutrients 12: 1003.
Jeong, S., M. Park, M. Kang, Y.-J. Park, M. Lee, C. You, U. Hwang, Y. Song, H. Park, S. Lee, and H. Suh (2021) Supplementation of non-fermented and fermented red ginseng improves obese phenotypes, lipid and inflammatory profiles, and antioxidant defense system in high fat-fed rats. J. Food Nutr. Res. (Newark) 9: 154–162.
Lee, S., R. Kirkland, Z. I. Grunewald, Q. Sun, L. Wicker, and C. B. de La Serre (2019) Beneficial effects of non-encapsulated or encapsulated probiotic supplementation on microbiota composition, intestinal barrier functions, inflammatory profiles, and glucose tolerance in high fat fed rats. Nutrients 11: 1975.
Coon, J. T. and E. Ernst (2002) Panax ginseng: a systematic review of adverse effects and drug interactions. Drug Saf. 25: 323–344.
Kim, J.-H. (2012) Cardiovascular diseases and Panax ginseng: a review on molecular mechanisms and medical applications. J. Ginseng Res. 36: 16–26.
Hasegawa, H. (2004) Proof of the mysterious efficacy of ginseng: basic and clinical trials: metabolic activation of ginsenoside: deglycosylation by intestinal bacteria and esterification with fatty acid. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 95: 153–157.
Guo, M., S. Ding, C. Zhao, X. Gu, X. He, K. Huang, Y. Luo, Z. Liang, H. Tian, and W. Xu (2015) Red Ginseng and Semen Coicis can improve the structure of gut microbiota and relieve the symptoms of ulcerative colitis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 162: 7–13.
Jeon, H., H.-Y. Kim, C.-H. Bae, Y. Lee, and S. Kim (2020) Korean red ginseng regulates intestinal tight junction and inflammation in the colon of a Parkinson’s disease mouse model. J. Med. Food 23: 1231–1237.
Ahn, H., B.-C. Han, J. Kim, S. G. Kang, P.-H. Kim, K. H. Jang, S. H. So, S.-H. Lee, and G.-S. Lee (2019) Nonsaponin fraction of Korean Red Ginseng attenuates cytokine production via inhibition of TLR4 expression. J. Ginseng Res. 43: 291–299.
Truong, V.-L., M. J. Bak, and W.-S. Jeong (2019) Chemopreventive activity of red ginseng oil in a mouse model of azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium-induced inflammation-associated colon carcinogenesis. J. Med. Food 22: 578–586.
Jang, S.-H., J. Park, S.-H. Kim, K.-M. Choi, E.-S. Ko, J.-D. Cha, Y.-R. Lee, H. Jang, and Y.-S. Jang (2017) Oral administration of red ginseng powder fermented with probiotic alleviates the severity of dextran-sulfate sodium-induced colitis in a mouse model. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 15: 192–201.
Fan, J., S. Liu, Z. Ai, Y. Chen, Y. Wang, Y. Li, X. Li, S. Xiao, and Y. Wang (2021) Fermented ginseng attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses by activating the TLR4/MAPK signaling pathway and remediating gut barrier. Food Funct. 12: 852–861.
Bae, E.-A., Y.-I. Yoo, I.-A. Lee, M. J. Han, and D.-H. Kim (2008) The anti-inflammmatory effect of fermented red ginseng in experimental colitic mice. Food Agric. Immunol. 19: 313–323.
Livak, K. J. and T. D. Schmittgen (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25: 402–408.
Caporaso, J. G., C. L. Lauber, W. A. Walters, D. Berg-Lyons, J. Huntley, N. Fierer, S. M. Owens, J. Betley, L. Fraser, M. Bauer, N. Gormley, J. A. Gilbert, G. Smith, and R. Knight (2012) Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 6: 1621–1624.
Arndt, D., J. Xia, Y. Liu, Y. Zhou, A. C. Guo, J. A. Cruz, I. Sinelnikov, K. Budwill, C. L. Nesbø, and D. S. Wishart (2012) METAGENassist: a comprehensive web server for comparative metagenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 40(Web Server issue): W88–W95.
Segata, N., J. Izard, L. Waldron, D. Gevers, L. Miropolsky, W. S. Garrett, and C. Huttenhower (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 12: R60.
Udayappan, S., L. Manneras-Holm, A. Chaplin-Scott, C. Belzer, H. Herrema, G. M. Dallinga-Thie, S. H. Duncan, E. S. G. Stroes, A. K. Groen, H. J. Flint, F. Backhed, W. M. de Vos, and M. Nieuwdorp (2016) Oral treatment with Eubacterium hallii improves insulin sensitivity in db/db mice. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2: 16009.
Liu, S., P. Qin, and J. Wang (2019) High-fat diet alters the intestinal microbiota in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice. Microorganisms 7: 176.
Lee, S., M. L. Goodson, W. Vang, J. Rutkowsky, K. Kalanetra, M. Bhattacharya, D. Barile, and H. E. Raybould (2021) Human milk oligosaccharide 2’-fucosyllactose supplementation improves gut barrier function and signaling in the vagal afferent pathway in mice. Food Funct. 12: 8507–8521.
Kanauchi, O., M. Fukuda, Y. Matsumoto, S. Ishii, T. Ozawa, M. Shimizu, K. Mitsuyama, and A. Andoh (2006) Eubacterium limosum ameliorates experimental colitis and metabolite of microbe attenuates colonic inflammatory action with increase of mucosal integrity. World J. Gastroenterol. 12: 1071–1077.
Xu, Y., N. Wang, H.-Y. Tan, S. Li, C. Zhang, and Y. Feng (2020) Function of Akkermansia muciniphila in obesity: interactions with lipid metabolism, immune response and gut systems. Front. Microbiol. 11: 219.
Chelakkot, C., J. Ghim, and S. H. Ryu (2018) Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 50: 1–9.
Dun, Y., M. Liu, J. Chen, D. Peng, H. Zhao, Z. Zhou, T. Wang, C. Liu, Y. Guo, C. Zhang, and D. Yuan (2018) Regulatory effects of saponins from Panax japonicus on colonic epithelial tight junctions in aging rats. J. Ginseng Res. 42: 50–56.
Zenewicz, L. A., G. D. Yancopoulos, D. M. Valenzuela, A. J. Murphy, S. Stevens, and R. A. Flavell (2008) Innate and adaptive interleukin-22 protects mice from inflammatory bowel disease. Immunity 29: 947–957.
Sabihi, M., M. Böttcher, P. Pelczar, and S. Huber (2020) Microbiota-dependent effects of IL-22. Cells 9: 2205.
Zenewicz, L. A. and R. A. Flavell (2011) Recent advances in IL-22 biology. Int. Immunol. 23: 159–163.
Ceccarelli, S., N. Panera, M. Mina, D. Gnani, C. De Stefanis, A. Crudele, C. Rychlicki, S. Petrini, G. Bruscalupi, L. Agostinelli, L. Stronati, S. Cucchiara, G. Musso, C. Furlanello, G. Svegliati-Baroni, V. Nobili, and A. Alisi (2015) LPS-induced TNF-α factor mediates pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrogenic pattern in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Oncotarget 6: 41434–41452.
Larrosa, M., M. Azorín-Ortuño, M. J. Yañez-Gascón, M. T. García-Conesa, F. Tomás-Barberán, and J. C. Espín (2011) Lack of effect of oral administration of resveratrol in LPS-induced systemic inflammation. Eur. J. Nutr. 50: 673–680.
Khan, H. U., K. Aamir, P. R. Jusuf, G. Sethi, S. P. Sisinthy, R. Ghildyal, and A. Arya (2021) Lauric acid ameliorates lipopoly-saccharide (LPS)-induced liver inflammation by mediating TLR4/MyD88 pathway in Sprague Dawley (SD) rats. Life Sci. 265: 118750.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Sun Moon University Research Grant of 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, and investigation, S.E., H.S., S.L., H.S. and S.J.; Data curation, S.E., S.L.; Writing — original draft preparation, S.E.; Writing — review & editing, S.E., H.S., S.L., H.S., and S.J.; Supervision, S.L., H.S., and S.J.; Funding acquisition, S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Animals were maintained and handled in accordance with protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Sun Moon University (approval no.: SM-2020-01-02, approval date: 2 January 2020).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eun, S., Seo, H., Suh, Hj. et al. Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Inflammation Profile in High Fat-fed Rats. Biotechnol Bioproc E 28, 74–82 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-022-0379-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-022-0379-z