Abstract
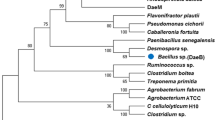
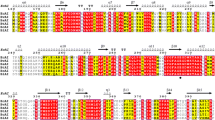
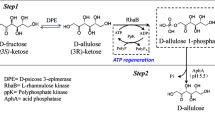
We found a putative dolichol phosphate mannose synthases (DPMS) from Bacillus sp., which exhibited the highest specific activity toward d-allulose, one of a functional rare sugars and also known as d-psicose, and identified it as d-allulose 3-epimerase (Basp_DAEase). The gene of Basp_DAEase from Bacillus sp. was cloned to the expression vector (pET-28a(+)) and then expressed as a recombinant enzyme in the Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). The recombinant enzyme was purified homogeneously on the SDS-PAGE with 34 kDa by 6XHis-tagging affinity chromatography and it was found to exist in dimer form as its activity form by Sephacryl S 200 HR 16/60 gelfiltration chromatography. The reaction conditions for a recombinant Basp_DAEase were optimized to produce d-allulose from d-fructose. The epimerization activity of Basp_DAEase toward d-fructose was maximum at pH 7.5 and 40°C with 1 mM Co2+. The half-lives of Basp_DAEase at 35°C, 40°C, 45°C, 50°C, and 55°C were 45.8, 4.18, 1.24, 0.46, and 0.17 h, respectively. At pH 7.5, 40°C, and 1mM Co2+, 215 g/L of d-allulose was produced from 700 g/L of d-fructose by 20 U/mL of Basp_DAEase after 50 min of enzyme reaction with a conversion yield of 31% and productivity of 258 g/L/h. This is the highest productivity of d-allulose from d-fructose reported to date. From this result, it is strongly suggested that Basp_DAEase has high potential application value in the industrial d-allulose production from d-fructose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang, S., W. Xiao, X. Zhu, P. Yang, Z. Zheng, S. Lu, S. Jiang, G. Zhang, and J. Liu (2020) Review on d-allulose: in vivo metabolism, catalytic mechanism, engineering strain construction, bio-production technology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8: 26.
Matsuo, T. and K. Izumori (2009) d-psicose inhibits intestinal alpha-glucosidase and suppresses the glycemic response after ingestion of carbohydrates in rats. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 45: 202–206.
Hossain, M. A., S. Kitagaki, D. Nakano, A. Nishiyama, Y. Funamoto, T. Matsunaga, I. Tsukamoto, F. Yamaguchi, K. Kamitori, Y. Dong, Y. Hirata, K. Murao, Y. Toyoda, and M. Tokuda (2011) Rare sugar d-psicose improves insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in type 2 diabetes Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 405: 7–12.
Iida, T., T. Yamada, N. Hayashi, K. Okuma, K. Izumori, R. Ishii, and T. Matsuo (2013) Reduction of abdominal fat accumulation in rats by 8-week ingestion of a newly developed sweetener made from high fructose corn syrup. Food Chem. 138: 781–785.
Zhang, W., T. Zhang, B. Jiang, and W. Mu (2017) Enzymatic approaches to rare sugar production. Biotechnol. Adv. 35: 267–274.
He, W., B. Jiang, W. Mu, and T. Zhang (2016) Production of d-allulose with d-psicose 3-epimerase expressed and displayed on the surface of Bacillus subtilis spores. J. Agric. Food Chem. 64: 7201–7207.
Park, C. S., T. Kim, S. H. Hong, K. C. Shin, K. R. Kim, and D. K. Oh (2016) d-allulose production from d-fructose by permeabilized recombinant cells of Corynebacterium glutamicum cells expressing D-allulose 3-epimerase Flavonifractor plautii. PLoS One. 11: e0160044.
Zhang, J., C. Xu, X. Chen, X. Ruan, Y. Zhang, H. Xu, Y. Guo, J. Xu, P. Lv, and Z. Wang (2020) Engineered Bacillus subtilis harbouring gene of d-tagatose 3-epimerase for the bioconversion of d-fructose into d-psicose through fermentation. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 136: 109531.
Itoh, H., H. Okaya, A. R. Khan, S. Tajima, S. Hayakawa, and K. Izumori (1994) Purification and characterization of d-tagatose 3-epimerase from Pseudomonas sp. ST-24. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 58: 2168–2171.
Yoshida, H., M. Yamada, T. Nishitani, G. Takada, K. Izumori, and S. Kamitori (2007) Crystal structures of d-tagatose 3-epimerase from Pseudomonas cichorii and its complexes with d-tagatose and d-fructose. J. Mol. Biol. 374: 443–453.
Zhang, L., W. Mu, B. Jiang, and T. Zhang (2009) Characterization of d-tagatose-3-epimerase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides that converts d-fructose into d-psicose. Biotechnol. Lett. 31: 857–862.
Li, S., Z. Chen, W. Zhang, C. Guang, and W. Mu (2019) Characterization of a d-tagatose 3-epimerase from Caballeronia fortuita and its application in rare sugar production. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 138: 536–545.
Zhu, Z., C. Li, X. Liu, D. Gao, X. Wang, M. Tanokura, H. M. Qin, and F. Lu (2019) Biochemical characterization and biocatalytic application of a novel d-tagatose 3-epimerase from Sinorhizobium sp. RSC Adv. 9: 2919–2927.
Kim, H. J., E. K. Hyun, Y. S. Kim, Y. J. Lee, and D. K. Oh (2006) Characterization of an Agrobacterium tumefaciensd-psicose 3-epimerase that converts d-fructose to d-psicose. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72: 981–985.
Mu, W., F. Chu, Q. Xing, S. Yu, L. Zhou, and B. Jiang (2011) Cloning, expression, and characterization of a d-psicose 3-epimerase from Clostridium cellulolyticum H10. J. Agric. Food Chem. 59: 7785–7792.
Zhu, Y., Y. Men, W. Bai, X. Li, L. Zhang, Y. Sun, and Y. Ma (2012) Overexpression of d-psicose 3-epimerase from Ruminococcus sp. in Escherichia coli and its potential application in d-psicose production. Biotechnol. Lett. 34: 1901–1906.
Zhang, W., D. Fang, Q. Xing, L. Zhou, B. Jiang, and W. Mu (2013) Characterization of a novel metal-dependent d-psicose 3-epimerase from Clostridium scindens 35704. PLoS One. 8: e62987.
Mu, W., W. Zhang, D. Fang, L. Zhou, B. Jiang, and T. Zhang (2013) Characterization of a d-psicose-producing enzyme, d-psicose 3-epimerase, from Clostridium sp. Biotechnol. Lett. 35: 1481–1486.
Zhang, W., D. Fang, T. Zhang, L. Zhou, B. Jiang, and W. Mu (2013) Characterization of a metal-dependent d-psicose 3-epimerase from a novel strain, Desmospora sp. 8437. J. Agric. Food Chem. 61: 11468–11476.
Jia, M., W. Mu, F. Chu, X. Zhang, B. Jiang, L. L. Zhou, and T. Zhang (2014) A d-psicose 3-epimerase with neutral pH optimum from Clostridium bolteae for d-psicose production: cloning, expression, purification, and characterization. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98: 717–725.
Zhang, W., H. Li, T. Zhang, B. Jiang, L. Zhou, and W. Mu (2015) Characterization of a d-psicose 3-epimerase from Dorea sp. CAG317 with an acidic pH optimum and a high specific activity. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 120: 68–74.
Zhang, W., T. Zhang, B. Jiang, and W. Mu (2016) Biochemical characterization of a d-psicose 3-epimerase from Treponema primitia ZAS-1 and its application on enzymatic production of d-psicose. J. Sci. Food Agric. 96: 49–56.
Yoshihara, A., T. Kozakai, T. Shintani, R. Matsutani, K. Ohtani, T. Iida, K. Akimitsu, K. Izumori, and P. K. Gullapalli (2017) Purification and characterization of d-allulose 3-epimerase derived from Arthrobacter globiformis M30, a GRAS microorganism. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 123: 170–176.
Tseng, W. C., C. N. Chen, C. T. Hsu, H. C. Lee, H. Y. Fang, M. J. Wang, Y. H. Wu, and T. Y. Fang (2018) Characterization of a recombinant d-allulose 3-epimerase from Agrobacterium sp. ATCC 31749 and identification of an important interfacial residue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 112: 767–774.
Yang, J., C. Tian, T. Zhang, C. Ren, Y. Zhu, Y. Zeng, Y. Men, Y. Sun, and Y. Ma (2019) Development of food-grade expression system for d-allulose 3-epimerase preparation with tandem isoenzyme genes in Corynebacterium glutamicum and its application in conversion of cane molasses to d-allulose. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 116: 745–756.
Zhu, Z., D. Gao, C. Li, Y. Chen, M. Zhu, X. Liu, M. Tanokura, H. M. Qin, and F. Lu (2019) Redesign of a novel d-allulose 3-epimerase from Staphylococcus aureus for thermostability and efficient biocatalytic production of d-allulose. Microb. Cell Fact. 18: 59.
Patel, S. N., G. Kaushal, and S. P. Singh (2020) A novel d-allulose 3-epimerase gene from the metagenome of a thermal aquatic habitat and d-allulose production by Bacillus subtilis whole-cell catalysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 86: e02605–19.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2019R1F1A1059906) and R&D Program for Forest Science Technology (Project No. 2020197A00-2022-BA01) provided by the Korea Forest Service (Korea Forestry Promotion Institute).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no competing financial interests. Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, MJ., Kwon, E.R., Kim, S.J. et al. d-Allulose Production from d-fructose by Putative Dolichol Phosphate Mannose Synthase from Bacillus sp. with Potential d-allulose 3-epimrase Activity. Biotechnol Bioproc E 26, 976–984 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-021-0007-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-021-0007-3