Abstract
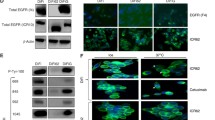
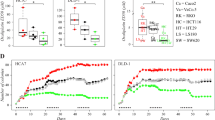
Several monoclonal antibodies and inhibitors targeting signalling pathways are being used in personalised medicine. Anti-EGFR antibodies seem to be effective, however, therapy resistance often occurs in colon carcinoma cases. mTOR inhibitors (mTORIs) could have a potential role in the breakthrough of therapy resistance. The mTOR activity related protein expression patterns and the in vitro effects of EGFR inhibitors (EGFRIs), mTORIs and their combinations were studied in different colon carcinoma cell lines (with different genetic backgrounds). Alamar Blue test and flow cytometry were used to analyse the in vitro proliferation and apoptotic effects of cetuximab, gefitinib, cisplatin, rapamycin, PP242 and NVP-BEZ235. The expressions of mTOR activity related proteins (p-70S6K, p-S6, Rictor, p-mTOR, Raptor) were studied by Western blot, immunocytochemistry and Duolink staining. The EGFRI resistance of the studied colon carcinoma cell lines related to their known mutations were confirmed, neither gefitinib nor cetuximab inhibited the proliferation or induced apoptosis in vitro. Individual differences in Rictor and Raptor expressions were detected by Western blot and immunocytochemistry beside elevated mTOR activity of these different colon carcinoma cell lines. These expression patterns correlated to the mTORIs sensitivity differences, moreover, mTORIs could enhance the effects of EGFRIs and other in vitro treatments. Our results suggest that mTORI combinations could be helpful in both EGFRI and platinum-based therapy of colon carcinomas. Moreover, we suggest determining both mTOR complex activity and mutations in Akt/mTOR signalling pathways for selecting the appropriate mTORIs and patients in potential future combination treatments.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsimberidou D (2015) AM: targeted therapy in cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 76(6):1113–1132
Herzig DO, Tsikitis VL (2015) Molecular markers for colon diagnosis, prognosis and targeted therapy. J Surg Oncol 111(1):96–102
Kalia M (2015) Biomarkers for personalized oncology: recent advances and future challenges. Metabolism 64:S16–S21
Dietel M, Jöhrens K, Laffert MV, Hummel M, Bläker H, Pfitzner BM, Lehmann A, Denkert C, Darb-Esfahani S, Lenze D, Heppner FL, Koch A, Sers C, Klauschen F, Anagnostopoulos I (2015) A 2015 update on predictive molecular pathology and its role in targeted cancer therapy: a review focusing on clinical relevance. Cancer Gene Ther 22(9):417–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2015.39
Chong CR, Jänne PA (2013) The quest to overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat Med 19(11):1389–1400
Khamisipour G, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Jahromi AS, Zandi K, Hojjat-Farsangi M (2016) Mechanisms of tumor cell resistance to the current targeted-therapy agents. Tumour Biol:1–19
Zhao Y, Butler EB, Tan M (2013) Targeting cellular metabolism to improve cancer therapeutics. Cell Death Dis 4(3):e532
Francipane MG, Lagasse E (2014) mTOR pathway in colorectal cancer: an update. Oncotarget 5(1):49–66
Chiarini F, Evangelisti C, McCubrey JA, Martelli AM (2015) Current treatment strategies for inhibiting mTOR in cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci 36(2):124–135
Francipane MG, Lagasse E (2015 Nov 26) Therapeutic potential of mTOR inhibitors for targeting cancer stem cells. Br J Clin Pharmacol 82:1180–1188. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.12844.
Sticz T, Molnár A, Márk Á, Hajdu M, Nagy N, Gy V, Micsik T, Kopper L, Sebestyén A (2016) mTOR activity and its prognostic significance in human colorectal carcinoma depending on C1 and C2 complex related protein expression. Clin Pathol 70:410–416. https://doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2016-203913
Huang Z, Wu Y, Zhou X, Qian J, Zhu W, Shu Y, Liu P (2015) Clinical efficacy of mTOR inhibitors in solid tumors: a systematic review. Future Oncol 11(11):1687–1699. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon.15.70
Lamming DW (2016) Inhibition of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR)-rapamycin and beyond. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 6(5). https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a025924
Ahmed D, Eide PW, Eilertsen IA, Danielsen SA, Eknæs M, Hektoen M, Lind GE, Lothe RA (2013 Sep 16) Epigenetic and genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines. Oncogene 2:e71. https://doi.org/10.1038/oncsis.2013.35
Roohi A, Hojjat-Farsangi M (2016) Recent advances in targeting mTOR signaling pathway using small molecule inhibitors. J Drug Target 3:1–13 PubMedPMID: 27632356
Spindler KL, Sorensen MM, Pallisgaard N, Andersen RF, Havelund BM, Ploen J, Lassen U, Jakobsen AK (2013) Phase II trial of temsirolimus alone and in combination with irinotecan for KRAS mutant metastatic colorectal cancer: outcome and results of KRAS mutational analysis in plasma. Acta Oncol 52(5):963–970
Harada K, Miyake H, Kumano M, Fujisawa M (2013 [Epub ahead of print]) Acquired resistance to temsirolimus in human renal cell carcinoma cells is mediated by the constitutive activation of signal transduction pathways through mTORC2. Br J Cancer 109:2389–2395
Sebestyén A, Márk Á, Hajdu M, Nagy N, Molnár A, Végső G, Barna G, Kopper L (2015) Rapamycin can restore the negative regulatory function of transforming growth factor beta 1 in high grade lymphomas. Cytokine 73(2):219–224
Márk Á, Hajdu M, Váradi Z, Sticz TB, Nagy N, Csomor J, Berczi L, Varga V, Csóka M, Kopper L, Sebestyén A (2013) Characteristic mTOR activity in Hodgkin-lymphomas offers a potential therapeutic target in high risk disease--a combined tissue microarray, in vitro and in vivo study. BMC Cancer 13:250. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-13-250
Gao F, Huang C, Zhang Y, Sun R, Zhang Y, Wang H, Zhang S (2016) Combination targeted therapy of VEGFR inhibitor, sorafenib, with an mTOR inhibitor, sirolimus induced a remakable response of rapid progressive Uterine PEComa. Cancer Biol Ther 17(6):595–598
Martin R, Desponds C, Eren RO, Quadroni M, Thome M, Fasel N (2016) Caspase-mediated cleavage of raptor participates in the inactivation of mTORC1 during cell death. Cell Death Discov 2:16024. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddiscovery.2016.24.eCollection
Weigelt B, Warne PH, Downward J (2011) PIK3CA mutation, but not PTEN loss of function, determines the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to mTOR inhibitor drugs. Oncogene 30(29):3222–3233
Wang Z, Martin D, Molinolo AA, Patel V, Iglesias-Bartolome R, Degese MS, Vitale-Cross L, Chen Q, Gutkind JS (2014) mTOR co-targeting in cetuximab resistance in head and neck cancers harboring PIK3CA and RAS mutations. J Natl Cancer Inst 106(9). https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/dju215
Li B, Gao S, Wei F, Bellail AC, Hao C, Liu T (2012) Simultaneous targeting of EGFR and mTOR inhibits the growth of colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep 28(1):15–20
Leisching GR, Loos B, Botha MH, Engelbrecht AM (2015) The role of mTOR during cisplatin treatment in an in vitro and ex vivo model of cervical cancer. Toxicology 335:72–78
Liu J, Zhang L, Zhang X, Xing X (2015) Rapamycin enhanced the antitumor efficacy of oxaliplatin in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells A2780cis both in vitro and in vivo. J Chemother 27(6):358–364. https://doi.org/10.1179/1973947815Y.0000000021
Costello BA, Borad MJ, Qi Y, Kim GP, Northfelt DW, Erlichman C, Alberts SR (2014) Phase I trial of everolimus, gemcitabine and cisplatin in patients with solid tumors. Investig New Drugs 32(4):710–716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0096-3
Im-Aram A, Farrand L, Bae SM, Song G, Song YS, Han JY, Tsang BK (2013) The mTORC2 component Rictor contributes to cisplatin resistance in human ovarian Cancer cells. PLoS One 8(9):e75455
Kim A, Lee JE, Lee SS, Kim C, Lee SJ, Jang WS, Park S (2013) Coexistent mutations of KRAS and PIK3CA affect the efficacy of NVP-BEZ235, a dual PI3K/MTOR inhibitor, in regulating the PI3K/MTOR pathway in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 133:984–996
Yang F, Qian XJ, Qin W, Deng R, Wu XQ, Qin J, Feng GK, Zhu XF (2013) Dual phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 has a therapeutic potential and sensitizes cisplatin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One 8(3):e59879
Hecht JR, Reid TR, Garrett CR, Beck JT, Davidson SJ, Mackenzie MJ, Brandt U, Rizvi S, Sharma S (2015) Phase I study of everolimus, cetuximab and irinotecan as second-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 35(3):1567–1573
Severyn B, Nguyen T, Altman MD, Li L, Nagashima K, Naumov GN, Sathyanarayanan S, Cook E, Morris E, Ferrer M, Arthur B, Benita Y, Watters J, Loboda A, Hermes J, Gilliland DG, Cleary MA, Carroll PM, Strack P, Tudor M, Andersen JN (2016) Development of a high-throughput gene expression screen for modulators of RAS-MAPK signaling in a mutant RAS cellular context. J Biomol Screen 21(9):989–997. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087057116658646
Pohl M, Schmiegel W (2016) Therapeutic strategies in diseases of the digestive tract- 2015 and beyond targeted therapies in Colon Cancer today and tomorrow. Dig Dis 34(5):574–579. https://doi.org/10.1159/000445267
Kim ST, Kim SY, Klempner SJ, Yoon J, Kim N, Ahn S, Bang H, Kim KM, Park W, Park SH, Park JO, Park YS, Lim HY, Lee SH, Park K, Kang WK, Lee J (2016) Rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR (RICTOR) amplification defines a subset of advanced gastric Cancer and is sensitive to AZD2014-mediated mTORC1/2 inhibition. Ann Oncol:mdw669. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw669
McCoach CE, Bivona TG, Blakely CM, Doebele RC (2016) Neoadjuvant oncogene-targeted therapy in early stage non-small-cell lung Cancer as a strategy to improve clinical outcome and identify early mechanisms of resistance. Clin Lung Cancer 17(5):466–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2016.05.025
Chen DH, Zhang XS (2015) Targeted therapy: resistance and re-sensitization. Chin J Cancer 34(11):496–501
Acknowledgements
The project was supported by OTKA project (K84262) and Semmelweis University Scientific and Innovation Founds (STIA-KF-17); and by Bolyai fellowship (590/2015 - Hungarian Academy of Sciences) of the corresponding author (A. Sebestyén). The related research works of Z.Hujber and T. Dankó were also supported by New National Excellence Programs (ÚNKP-17-3; ÚNKP-17-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights:
- Activity of mTOR complexes in colon carcinoma cells correlates to mTORI sensitivity
- mTORIs promote anti-tumour effects of EGFRIs in therapy resistant colon carcinomas
- Additional markers and agents related to mTOR activity for personalised treatments
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sticz, T., Molnár, A., Dankó, T. et al. The Effects of Different mTOR Inhibitors in EGFR Inhibitor Resistant Colon Carcinoma Cells. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 25, 1379–1386 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-018-0434-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-018-0434-4