Abstract
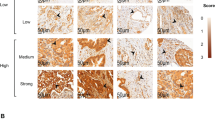
The aim of this study was to investigate the expression of Delta-like ligand 4(DLL4) and Endoglin(CD105) labeled microvessel density(MVD) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and evaluate their correlation with major clinicopathologic features and patients’ survival. Forty-two pancreatic cancer and 20 normal pancreatic tissues were included in the study. Immunohistochemical staining was employed to assess the expression level of DLL4 both in tumor cells and stromal vascular endothelial cells, as well as CD105 which was used to determine MVD. The relationships of DLL4 and CD105 expression with clinicopathologic parameters and clinical outcome were evaluated. Both DLL4 and CD105-labeled microvessel were observed highly immunostained in PDAC cases, and high expression of DLL4 was positively correlated with MVD. Moreover, the high expression of DLL4 was significantly associated with histological grade, node stage and TNM stage in not only the cancer cells but also stroma; while high expression of CD105 was associated with histological grade, TNM stage, node stage and distant metastasis. In univariant analysis, patients with high expression of DLL4 and CD105 tended to significantly poorer overall survival. Both DLL4 and CD105 were overexpressed in a large proportion of patients with PDAC. The expression of DLL4 was positively correlated with CD105-labeled MVD, indicating DLL4 may involved in angiogenesis. In addition, high DLL4 and CD105 expression correlated with the poor clinical outcome and overall survival in patients with PDAC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarkar FH, Banerjee S, Li Y (2007) Pancreatic cancer: pathogenesis, prevention and treatment. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 224(3):326–336
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM et al (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90
Folkman J (1995) Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med 1(1):27–31
Svagzdys S, Lesauskaite V, Pavalkis D et al (2009) Microvessel density as a new prognostic marker after radiotherapy in rectal cancer. BMC Cancer 9:95
Uzzan B, Nicolas P, Cucherat M et al (2004) Microvessel density as a prognostic factor in womenwith breast cancer: a systematic reviewof the literature and meta-analysis. Cancer Res 64(9):2941–2955
Zhao HC, Qin R, Chen XX et al (2006) Microvessel density is a prognostic marker of human gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 12(47):7598–7603
Han H, Silverman JF, Santucci TS et al (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in stage I non-small cell lung cancer correlates with neoangiogenesis and a poor prognosis. Ann Surg Oncol 8(1):72–79
Barău A, Ruiz-Sauri A, Valencia G et al (2013) High microvessel density in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is associated with high grade. Virchows Arch 462:541–546
van der Zee JA, van Eijck CH, Hop WC et al (2011) Angiogenesis: a prognostic determinant in pancreatic cancer? Eur J Cancer 47(17):2576–2584
Kuiper P, Hawinkels LJAC, de Jonge-Muller ESM et al (2011) Angiogenic markers endoglin and vascular endothelial growth factor in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. World J Gastroenterol 17(2):219–225
Zhou W, Wang G, Guo S (2013) Regulation of angiogenesis via Notch signaling in breast cancer and cancer stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1836(2):304–320
Liu Z, Fan F, Wang A et al (2014) Dll4-Notch signaling in regulation of tumor angiogenesis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140(4):525–536
Chen HT, Cai QC, Zheng JM et al (2012) High expression of delta-like ligand 4 predicts poor prognosis after curative resection for pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 19(Suppl 3):S464–S474
Jubb AM, Soilleux EJ, Turley H et al (2010) Expression of vascular notch ligand delta-like 4 and inflammatory markers in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 176(4):2019–2028
Linder S, Blåsjö M, von Rosen A et al (2001) Pattern of distribution and prognostic value of angiogenesis in pancreatic duct carcinoma:a semiquantitative immunohistochemical study of 45 patients. Pancreas 22(3):240–247
Mullendore ME, Koorstra JB, Li YM et al (2009) Ligand-dependent Notch signaling is involved in tumor initiation and tumor maintenance in pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15(7):2291–2301
Ishigami S, Arigami T, Uenosono Y et al (2013) Clinical implications of DLL4 expression in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 32:46
Donnem T, Andersen S, Al-Shibli K et al (2010) Prognostic impact of Notch ligands and receptors in non-small cell lung cancer: coexpression of Notch-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor-A predicts poor survival. Cancer 116:5676–5685
Kofler NM, Shawber CJ, Kangsamaksin T et al (2011) Notch signaling in developmental and tumor angiogenesis. Genes Cancer 2(12):1106–1116
Oishi H, Sunamura M, Egawa S et al (2010) Blockade of Delta-like ligand 4 signaling inhibits both growth and angiogenesis of pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 39(6):897–903
Sheldon H, Heikamp E, Turley H et al (2010) New mechanism for Notch signaling to endothelium at a distance by Delta-like 4 incorporation into exosomes. Blood 116(13):2385–2394
Jacobsen TL, Brennan K, Arias AM et al (1998) Cis-interactions between Delta and Notch modulate neurogenic signalling in Drosophila. Development 125(22):4531–4540
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (87783893) and Research Funds of National Health And Family Planning Commission (wkj2013-2-018).
Conflict of Interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Yu, L., Ding, G. et al. Overexpressions of DLL4 and CD105 are Associated with Poor Prognosis of Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 21, 1141–1147 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-015-9937-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-015-9937-4