Abstract
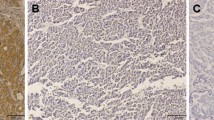
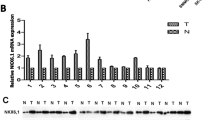
As a co-receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), Neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) plays an important role in angiogenesis and malignant progression of many human cancers. However, the role of NRP-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is not well understood. The study aimed to detected the expression of Neuropilin-1 in HCC and investigate the association between its expression and the clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of HCC. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), Western blot, Immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry (IHC) analyses were performed to characterize the expression of NRP-1 in HCC cell lines and tissues. The association of NRP-1 expression with the clinicopathological characteristics and the prognosis was subsequently assessed. qRT-PCR and Western blot assays revealed that the expression of NRP-1 in HCC was significantly increased relative to that of normal live cells and tissues (P < 0.05,and <0.001, respectively). In addition, high expression of NRP-1 was significantly associated with intrahepatic metastasis (P = 0.036), Edmondson grade (P = 0.007), TNM classification (P = 0.0031), and portal vein invasion (P = 0.004). Furthermore, the HCC patients with high NRP-1 expression had shorter overall survival (OS), and recurrence-free survival (RFS), whereas, patients with low NRP-1 expression had better OS and RFS (P = 0.0035, and 0.0048, respectively). These data indicate that NRP-1 expression may play an important role in the progression of HCC, and that high NRP-1 expression suggests unfavorable clinicopathological characteristics and survival in HCC patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2013) Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 63(1):11–30
Qu LS, Liu JX, Liu TT, Shen XZ, Chen TY, Ni ZP, Lu CH (2014) Association of hepatitis B virus pres- deletions with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in qidong, China. PLoS One 9(5):e98257
Fong ZV, Tanabe KK (2014) The clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States, Europe, and Asia: a comprehensive and evidence-based comparison and review. Cancer 120(18):2824–2830
Wong RJ, Devaki P, Nguyen L, Cheung R, Nguyen MH (2014) Ethnic disparities and liver transplantation rates in hepatocellular carcinoma patients in the recent era: results from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results registry. Liver Transpl 20(5):528–535
Marrero JA, El-Serag HB (2011) Alpha-fetoprotein should be included in the hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance guidelines of the American association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 53(3):1060–1061 author reply 1061-1062
He Z, Tessier-Lavigne M (1997) Neuropilin is a receptor for the axonal chemorepellent semaphorin III. Cell 90(4):739–751
Oh H, Takagi H, Otani A, Koyama S, Kemmochi S, Uemura A, Honda Y (2002) Selective induction of neuropilin-1 by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): a mechanism contributing to VEGF -induced angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(1):383–388
Xu Y, Li P, Zhang X, Wang J, Gu D, Wang Y (2013) Prognostic implication of neuropilin-1 up- regulation in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Diagn Pathol 8:155
Cheng W, Fu D, Wei ZF, Xu F, Xu XF, Liu YH, et al. (2014) NRP-1 expression in bladder cancer and its implications for tumor progression. Tumour Biol 36(6):6089–6094
Pan Q, Chanthery Y, Liang WC, Stawicki S, Mak J, Rathore N, et al. (2007) Blocking neuropilin-1 function has an additive effect with anti-VEGF to inhibit tumor growth. Cancer Cell 11(1):53–67
Bergé M, Allanic D, Bonnin P, de Montrion C, Richard J, Suc M, et al. (2011) Neuropilin-1 is upre- gulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and contributes to tumour growth and vascular remodelling. J Hepatol 55(4):866–875
Chen L, Miao W, Tang X, Zhang H, Wang S, Luo F, Yan J (2013) The expression and significan- ce of neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) on glioma cell lines and glioma tissues. J Biomed Nanotechnol 9(4):559–563
Li X, Luo F, Wang S, Ni E, Tang X, Lv H, et al. (2011) Monoclonal antibody against NRP-1 b1b2. Hybridoma (Larchmt) 30(4):369–373
Varotti G, Ramacciato G, Ercolani G, Grazi GL, Vetrone G, et al. (2005) Comparison between the fifth and sixth editions of the AJCC/UICC TNM staging systems for hepatocellular carcinoma: multicentric study on 393 cirrhotic resected patients. Eur J Surg Oncol 31(7):760–767
Kamiya T, Kawakami T, Abe Y, Nishi M, Onoda N, Miyazaki N, et al. (2006) The preserved expre- ssion of neuropilin (NRP) 1 contributes to a better prognosis in colon cancer. Oncol Rep 15(2):369–373
Su X, Chen Q, Chen W, Chen T, Li W, Li Y, et al. (2014) Mycoepoxydiene inhibits activation of BV2 microglia stimulated by lipopolysaccharide through suppressing NF-κB, ERK 1/2 and toll-like receptor pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 19(1):88–93
Li W, Li M, Su X, Qin L, Miao M, Yu C, et al. (2014) Mycoepoxydiene induces apoptosis and inhibits TPA-induced invasion in human cholangiocarcinoma cells via blocking NF-κB pathway. Bio- Chimie 101:183–191
Gu X, Fu M, Ge Z, Zhan F, Ding Y, Ni H, et al. (2014) High expression of MAGE-A9 correlates with unfavorable survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. 4:6625
Herzog Y, Kalcheim C, Kahane N, Reshef R, Neufeld G (2001) Differential expression of neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 in arteries and veins. Mech Dev 109(1):115–119
Zhu H, Cai H, Tang M, Tang J (2014) Neuropilin-1 is overexpressed in osteosarcoma and contributes to tumor progression and poor prognosis. Clin Transl Oncol 16(8):732–738
Zhuang PY, Wang JD, Tang ZH, Zhou XP, Yang Y, Quan ZW, et al. (2014) Peritumoral neuropilin- 1 and VEGF receptor-2 expression increases time to recurrence in hepatocellularcarcinoma patients undergoing curative hepatectomy. Oncotarget 5(22):11121–11121
Acknowledgments
Dr. X. Su was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (81071182) and the Program for Training Young Talents of Fujian Health (2014-ZQN-ZD-35). Dr. J. Yan was supported by grants from NSFC (81172970) and Natural Science Foundation of Fujian (2013 J01384,2013Y0080).
Authors’ Contributions
YZ, XS and JY conceived and designed experiments and interpreted data. YZ and XD performed experiments. YZ, PL, YJ, CM, QF, WW, FS, and HT completed patient follow-ups and data collection. YZ and XS wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Liu, P., Jiang, Y. et al. High Expression of Neuropilin-1 Associates with Unfavorable Clinicopathological Features in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 22, 367–375 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-015-0003-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-015-0003-z