Abstract
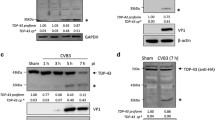
Enterovirus A71 (EV-A71) is one of the etiological pathogens leading to hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD), which can cause severe neurological complications. The neuropathogenesis of EV-A71 infection is not well understood. The mislocalization and aggregation of TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) is the pathological hallmark of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). However, whether TDP-43 was impacted by EV-A71 infection is unknown. This study demonstrated that TDP-43 was cleaved during EV-A71 infection. The cleavage of TDP-43 requires EV-A71 replication rather than the activated caspases due to viral infection. TDP-43 is cleaved by viral protease 3C between the residues 331Q and 332S, while mutated TDP-43 (Q331A) was not cleaved. In addition, mutated 3C which lacks the protease activity failed to induce TDP-43 cleavage. We also found that TDP-43 was translocated from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, and the mislocalization of TDP-43 was induced by viral protease 2A rather than 3C. Taken together, we demonstrated that TDP-43 was cleaved by viral protease and translocated to the cytoplasm during EV-A71 infection, implicating the possible involvement of TDP-43 in the pathogenesis of EV-A71infection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berning BA, Walker AK (2019) The pathobiology of TDP-43 C-terminal fragments in ALS and FTLD. Front Neurosci 13:335
Buratti E, Brindisi A, Giombi M, Tisminetzky S, Ayala YM, Baralle FE (2005) TDP-43 binds heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B through its C-terminal tail: an important region for the inhibition of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator exon 9 splicing. J Biol Chem 280:37572–37584
Cai Q, Yameen M, Liu W, Gao Z, Li Y, Peng X, Cai Y, Wu C, Zheng Q, Li J, Lin T (2013) Conformational plasticity of the 2A proteinase from enterovirus 71. J Virol 87:7348–7356
Caine EA, Moncla LH, Ronderos MD, Friedrich TC, Osorio JE (2016) A single mutation in the VP1 of enterovirus 71 is responsible for increased virulence and neurotropism in adult interferon-deficient mice. J Virol 90:8592–8604
Chang PC, Chen SC, Chen KT (2016) The current status of the disease caused by enterovirus 71 infections: epidemiology, pathogenesis, molecular epidemiology, and vaccine development. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13:890
Chen YF, Hu L, Xu F, Liu CJ, Li J (2019) A case report of a teenager with severe hand, foot, and mouth disease with brainstem encephalitis caused by enterovirus 71. BMC Pediatr 19:59
Colombrita C, Onesto E, Megiorni F, Pizzuti A, Baralle FE, Buratti E, Silani V, Ratti A (2012) TDP-43 and FUS RNA-binding proteins bind distinct sets of cytoplasmic messenger rnas and differently regulate their post-transcriptional fate in motoneuron-like cells. J Biol Chem 287:15635–15647
Donde A, Sun M, Jeong YH, Wen X, Ling J, Lin S, Braunstein K, Nie S, Wang S, Chen L, Wong PC (2020) Upregulation of ATG7 attenuates motor neuron dysfunction associated with depletion of TARDBP/TDP-43. Autophagy 16:672–682
Duan H, Zhu M, Xiong Q, Wang Y, Xu C, Sun J, Wang C, Zhang H, Xu P, Peng Y (2017) Regulation of enterovirus 2A protease-associated viral IRES activities by the cell’s ERK signaling cascade: implicating ERK as an efficiently antiviral target. Antiviral Res 143:13–21
Ertel KJ, Brunner JE, Semler BL (2010) Mechanistic consequences of hnRNP C binding to both RNA termini of poliovirus negative-strand RNA intermediates. J Virol 84:4229–4242
Feng Q, Langereis MA, Lork M, Nguyen M, Hato SV, Lanke K, Emdad L, Bhoopathi P, Fisher PB, Lloyd RE, van Kuppeveld FJ (2014) Enterovirus 2Apro targets MDA5 and MAVS in infected cells. J Virol 88:3369–3378
Feng M, Guo S, Fan S, Zeng X, Zhang Y, Liao Y, Wang J, Zhao T, Wang L, Che Y, Wang J, Ma N, Liu L, Yue L, Li Q (2016) The preferential infection of astrocytes by enterovirus 71 plays a key role in the viral neurogenic pathogenesis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 6:192
Fiesel FC, Weber SS, Supper J, Zell A, Kahle PJ (2012) TDP-43 regulates global translational yield by splicing of exon junction complex component SKAR. Nucleic Acids Res 40:2668–2682
Freibaum BD, Chitta RK, High AA, Taylor JP (2010) Global analysis of TDP-43 interacting proteins reveals strong association with RNA splicing and translation machinery. J Proteome Res 9:1104–1120
Fung G, Shi J, Deng H, Hou J, Wang C, Hong A, Zhang J, Jia W, Luo H (2015) Cytoplasmic translocation, aggregation, and cleavage of TDP-43 by enteroviral proteases modulate viral pathogenesis. Cell Death Differ 22:2087–2097
Gao J, Wang L, Yan T, Perry G, Wang X (2019) TDP-43 proteinopathy and mitochondrial abnormalities in neurodegeneration. Mol Cell Neurosci 100:103396
Gerhauser I, Hansmann F, Ciurkiewicz M, Loscher W, Beineke A (2019) Facets of theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus-induced diseases: an update. Int J Mol Sci 20:448
Guo Z, Zhong X, Lin L, Wu S, Wang T, Chen Y, Zhai X, Wang Y, Wu H, Tong L, Han Y, Pan B, Peng Y, Si X, Zhang F, Zhao W, Zhong Z (2014) A 3C(pro)-dependent bioluminescence imaging assay for in vivo evaluation of anti-enterovirus 71 agents. Antiviral Res 101:82–92
Hart MP, Gitler AD (2012) ALS-associated ataxin 2 polyq expansions enhance stress-induced caspase 3 activation and increase TDP-43 pathological modifications. J Neurosci 32:9133–9142
Holmes CW, Koo SS, Osman H, Wilson S, Xerry J, Gallimore CI, Allen DJ, Tang JW (2016) Predominance of enterovirus B and echovirus 30 as cause of viral meningitis in a UK population. J Clin Virol 81:90–93
Huang CC, Liu CC, Chang YC, Chen CY, Wang ST, Yeh TF (1999) Neurologic complications in children with enterovirus 71 infection. N Engl J Med 341:936–942
Huang Q, Wang Y, Si C, Zhao D, Wang Y, Duan Y (2017) Interleukin-35 modulates the imbalance between regulatory T cells and T helper 17 cells in enterovirus 71-induced hand, foot, and mouth disease. J Interferon Cytokine Res 37:522–530
Hung HC, Chen TC, Fang MY, Yen KJ, Shih SR, Hsu JT, Tseng CP (2010) Inhibition of enterovirus 71 replication and the viral 3d polymerase by aurintricarboxylic acid. J Antimicrob Chemother 65:676–683
Ju Y, Tan Z, Huang H, Chen M, Tan Y, Zhang C, Wang J, Wang H, Chen M (2020) Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of coxsackievirus a6- and enterovirus 71-associated clinical stage 2 and 3 severe hand, foot, and mouth disease in Guangxi, Southern China, 2017. J Infect 80:121–142
Lee KY (2016) Enterovirus 71 infection and neurological complications. Korean J Pediatr 59:395–401
Lei X, Liu X, Ma Y, Sun Z, Yang Y, Jin Q, He B, Wang J (2010) The 3C protein of enterovirus 71 inhibits retinoid acid-inducible gene I-mediated interferon regulatory factor 3 activation and type I interferon responses. J Virol 84:8051–8061
Lei X, Sun Z, Liu X, Jin Q, He B, Wang J (2011) Cleavage of the adaptor protein TRIF by enterovirus 71 3C inhibits antiviral responses mediated by toll-like receptor 3. J Virol 85:8811–8818
Lei X, Zhang Z, Xiao X, Qi J, He B, Wang J (2017) Enterovirus 71 inhibits pyroptosis through cleavage of gasdermin D. J Virol 91:e01069
Levengood JD, Tolbert M, Li ML, Tolbert BS (2013) High-affinity interaction of hnRNP A1 with conserved RNA structural elements is required for translation and replication of enterovirus 71. RNA Biol 10:1136–1145
Li B, Yue Y, Zhang Y, Yuan Z, Li P, Song N, Lin W, Liu Y, Gu L, Meng H (2017) A novel enterovirus 71 (ev71) virulence determinant: the 69th residue of 3C protease modulates pathogenicity. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:26
Li J, Gao F, Hao SB, Cheng D, Zhang WQ, Lin B, Zhao L, Yu XJ, Wang ZY, Wen HL (2017) Contribution of 3CD region to the virulence of enterovirus 71. Biomed Environ Sci 30:767–771
Masaki K, Sonobe Y, Ghadge G, Pytel P, Roos RP (2019) TDP-43 proteinopathy in theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus infection. PLoS Pathog 15:e1007574
McCluskey LF, Elman LB, Martinez-Lage M, Van Deerlin V, Yuan W, Clay D, Siderowf A, Trojanowski JQ (2009) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-plus syndrome with TAR DNA-binding protein-43 pathology. Arch Neurol 66:121–124
Park N, Schweers NJ, Gustin KE (2015) Selective removal of FG repeat domains from the nuclear pore complex by enterovirus 2A(pro). J Virol 89:11069–11079
Riku Y, Watanabe H, Yoshida M, Tatsumi S, Mimuro M, Iwasaki Y, Katsuno M, Iguchi Y, Masuda M, Senda J, Ishigaki S, Udagawa T, Sobue G (2014) Lower motor neuron involvement in TAR DNA-binding protein of 43 kDa-related frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. JAMA Neurol 71:172–179
Riku Y, Watanabe H, Yoshida M, Mimuro M, Iwasaki Y, Masuda M, Ishigaki S, Katsuno M, Sobue G (2016) Marked involvement of the striatal efferent system in TAR DNA-binding protein 43 kDa-related frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 75:801–811
Rohn TT (2009) Cytoplasmic inclusions of TDP-43 in neurodegenerative diseases: a potential role for caspases. Histol Histopathol 24:1081–1086
Romano M, Buratti E, Romano G, Klima R, Del Bel Belluz L, Stuani C, Baralle F, Feiguin F (2014) Evolutionarily conserved heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) A/B proteins functionally interact with human and drosophila TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43). J Biol Chem 289:7121–7130
Shimonaka S, Nonaka T, Suzuki G, Hisanaga S, Hasegawa M (2016) Templated aggregation of TAR DNA-binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43) by seeding with TDP-43 peptide fibrils. J Biol Chem 291:8896–8907
Sun D, Chen S, Cheng A, Wang M (2016) Roles of the picornaviral 3C proteinase in the viral life cycle and host cells. Viruses 8:82
Takahashi S, Liao Q, Van Boeckel TP, Xing W, Sun J, Hsiao VY, Metcalf CJ, Chang Z, Liu F, Zhang J, Wu JT, Cowling BJ, Leung GM, Farrar JJ, van Doorn HR, Grenfell BT, Yu H (2016) Hand, foot, and mouth disease in china: modeling epidemic dynamics of enterovirus serotypes and implications for vaccination. PLoS Med 13:e1001958
Teoh HL, Mohammad SS, Britton PN, Kandula T, Lorentzos MS, Booy R, Jones CA, Rawlinson W, Ramachandran V, Rodriguez ML, Andrews PI, Dale RC, Farrar MA, Sampaio H (2016) Clinical characteristics and functional motor outcomes of enterovirus 71 neurological disease in children. JAMA Neurol 73:300–307
Tolbert M, Morgan CE, Pollum M, Crespo-Hernandez CE, Li ML, Brewer G, Tolbert BS (2017) HnRNP A1 alters the structure of a conserved enterovirus IRES domain to stimulate viral translation. J Mol Biol 429:2841–2858
Tudor EL, Galtrey CM, Perkinton MS, Lau KF, De Vos KJ, Mitchell JC, Ackerley S, Hortobagyi T, Vamos E, Leigh PN, Klasen C, McLoughlin DM, Shaw CE, Miller CC (2010) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mutant vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein-B transgenic mice develop TAR-DNA-binding protein-43 pathology. Neuroscience 167:774–785
Ule J (2008) Ribonucleoprotein complexes in neurologic diseases. Curr Opin Neurobiol 18:516–523
Wang B, Xi X, Lei X, Zhang X, Cui S, Wang J, Jin Q, Zhao Z (2013) Enterovirus 71 protease 2Apro targets MAVS to inhibit anti-viral type I interferon responses. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003231
Wang C, Sun M, Yuan X, Ji L, Jin Y, Cardona CJ, Xing Z (2017) Enterovirus 71 suppresses interferon responses by blocking janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling through inducing karyopherin-alpha1 degradation. J Biol Chem 292:10262–10274
Wang T, Wang B, Huang H, Zhang C, Zhu Y, Pei B, Cheng C, Sun L, Wang J, Jin Q, Zhao Z (2017) Enterovirus 71 protease 2Apro and 3Cpro differentially inhibit the cellular endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway via distinct mechanisms, and enterovirus 71 hijacks ERAD component p97 to promote its replication. PLoS Pathog 13:e1006674
Watters K, Palmenberg AC (2011) Differential processing of nuclear pore complex proteins by rhinovirus 2A proteases from different species and serotypes. J Virol 85:10874–10883
Watters K, Inankur B, Gardiner JC, Warrick J, Sherer NM, Yin J, Palmenberg AC (2017) Differential disruption of nucleocytoplasmic trafficking pathways by rhinovirus 2A proteases. J Virol 91:e02472
Wobst HJ, Delsing L, Brandon NJ, Moss SJ (2017) Truncation of the TAR DNA-binding protein 43 is not a prerequisite for cytoplasmic relocalization, and is suppressed by caspase inhibition and by introduction of the a90v sequence variant. PLoS ONE 12:e0177181
Wong J, Si X, Angeles A, Zhang J, Shi J, Fung G, Jagdeo J, Wang T, Zhong Z, Jan E, Luo H (2013) Cytoplasmic redistribution and cleavage of AUF1 during coxsackievirus infection enhance the stability of its viral genome. FASEB J 27:2777–2787
Wu S, Wang Y, Lin L, Si X, Wang T, Zhong X, Tong L, Luan Y, Chen Y, Li X, Zhang F, Zhao W, Zhong Z (2014) Protease 2A induces stress granule formation during coxsackievirus b3 and enterovirus 71 infections. Virol J 11:192
Zhang YJ, Xu YF, Dickey CA, Buratti E, Baralle F, Bailey R, Pickering-Brown S, Dickson D, Petrucelli L (2007) Progranulin mediates caspase-dependent cleavage of TAR DNA binding protein-43. J Neurosci 27:10530–10534
Zhao T, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Feng M, Fan S, Wang L, Liu L, Wang X, Wang Q, Zhang X, Wang J, Liao Y, He Z, Lu S, Yang H, Li Q (2017) Dynamic interaction of enterovirus 71 and dendritic cells in infected neonatal rhesus macaques. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:171
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Foundation of China (81672007 and 81971920 to Wenran Zhao, 81871652 to Zhaohua Zhong, and 81772188 to Yan Wang) and Health and Family Planning Commission of Heilongjiang Province (2017-158 to Xiaoman Wo). We are grateful to the help of Dr. Ying Wu (School of Life Sciences, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China) in viewing the images of fluorescence microscope.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WZ and ZZ conceived the experiments, analyzed the data. WZ wrote the manuscript. XW, YY, and YX performed the majority of the laboratory work. Yao Wang and YC prepared and performed the immunofluorescence visualization. SZ and Yan Wang prepared of plasmids. LL and XZ prepared Enterovirus A71 for this study.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There is no conflicting interest in this work.
Animal and Human Rights Statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wo, X., Yuan, Y., Xu, Y. et al. TAR DNA-Binding Protein 43 is Cleaved by the Protease 3C of Enterovirus A71. Virol. Sin. 36, 95–103 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-020-00262-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-020-00262-x