Abstract
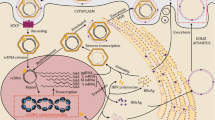
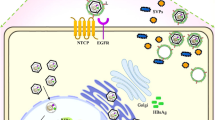
Chronic hepatitis B infection is caused by hepatitis B virus (HBV) and a total cure is yet to be achieved. The viral covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) is the key to establish a persistent infection within hepatocytes. Current antiviral strategies have no effect on the pre-existing cccDNA reservoir. Therefore, the study of the molecular mechanism of cccDNA formation is becoming a major focus of HBV research. This review summarizes the current advances in cccDNA molecular biology and the latest studies on the elimination or inactivation of cccDNA, including three major areas: (1) epigenetic regulation of cccDNA by HBV X protein, (2) immune-mediated degradation, and (3) genome-editing nucleases. All these aspects provide clues on how to finally attain a cure for chronic hepatitis B infection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allweiss L, Dandri M. 2016. Experimental in vitro and in vivo models for the study of human hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol, 64: S17–S31.
Beck J, Nassal M. 2007. Hepatitis B virus replication. World J Gastroenterol, 13: 48–64.
Belloni L, Pollicino T, De Nicola F, Guerrieri F, Raffa G, Fanciulli M, Raimondo G, Levrero M. 2009. Nuclear HBx binds the HBV minichromosome and modifies the epigenetic regulation of cccDNA fuction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106: 19975–19979.
Cai D, Mills C, Yu W, Yan R, Aldrich CE, Saputelli JR, Mason WS, Xu X, Guo JT, Block TM, Cuconati A, Guo H. 2012. Identification of disubstituted sulfonamide compounds as specific inhibitors of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA formation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 56: 4277–4288.
Cui X, McAllister R, Boregowda R, Sohn JA, Cortes Ledesma F, Caldecott KW, Seeger C, Hu J. 2015. Does Tyrosyl DNA Phosphodiesterase-2 Play a Role in Hepatitis B Virus Genome Repair?. PLoS One, 10: e0128401.
Decorsière A, Mueller H, van Breugel PC, Abdul F, Gerossier L, Beran RK, Livingston CM, Niu C, Fletcher SP, Hantz O, Strubin M. 2016. Hepatitis B virus X protein identifies the Smc5/6 complex as a host restriction factor. Nature, 531: 386–389.
Feng H, Hu K. 2009. Structural Characteristics and Molecular Mechanism of Hepatitis B Virus Reverse Transcriptase. Virol Sin, 24: 509–517.
Fu Y, Foden JA, Khayter C, Maeder ML, Reyon D, Joung JK, Sander JD. 2013. High-frequency off-target mutagenesis in-duced by CRISPR-Cas nucleases in human cells. Nat Biotechnol, 31: 822–826.
Gao W, Hu J. 2007. Formation of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA: removal of genome-linked protein. J Virol, 81: 6164–6174.
Guo L, Wang X, Ren L, Zeng M, Wang S, Weng Y, Tang Z, Wang X, Tang Y, Hu H, Li M, Zhang C, Liu C. 2014. HBx affects CUL4-DDB1 function in both positive and negative manners. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 450: 1492–1497.
Guo H, Jiang D, Zhou T, Cuconati A, Block TM, Guo JT. 2007. Characterizat ion of the intracellular deproteinized relaxed c ircular DNA of hepatit is B virus: an intermediate of covalently closed circular DNA formation. J Virol, 81: 12472–12484.
Guo H, Mao R, Block TM, Guo JT. 2010. Production and function of the cytoplasmic deproteinized relaxed circular DNA of hepadnaviruses. J Virol, 84: 387–396.
Guo X, Chen P, Hou X, Xu W, Wang D, Wang TY, Zhang L, Zheng G, Gao ZL, He CY, Zhou B, Chen ZY. 2016. The recombined cccDNA produced using minicircle technology mimicked HBV genome in structure and function closely. Scientific Reports, 6: 25552.
Hayes CN, Chayama K. 2016. HBV culture and infections systems. Hepatol Int, 10: 559–566.
Hong X, Kim ES, Guo H. 2017. Epigenetic Regulation of Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA: Implications for Epigenetic Therapy against Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology. doi: 10.1002/hep.29479.
Keeffe EB, Dieterich DT, Han SH, Jacobson IM, Martin P, Schiff ER, Tobias H. 2008. A treatment algorithm for the management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in the United States: 2008 update. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 6: 1315–1341.
Kitamura K, Wang Z, Chowdhury S, Simadu M, Koura M, Muramatsu M. 2013. Uracil DNA Glycosylase Counteracts APOBEC3G-Induced Hypermutation of Hepatitis B Viral Genomes: Excision Repair of Covalently Closed Circular DNA. PLoS Pathog, 9: e1003361.
Königer C, Wingert I, Marsmann M, Rösler C, Beck J, Nassal M. 2014. Involvement of the host DNA-repair enzyme TDP2 in formation of the covalently closed circular DNA persistence reservoir of hepatitis B viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 111: E4244–E4253.
Ladner SK, Otto MJ, Barker CS, Zaifert K, Wang GH, Guo JT, Seeger C, King RW. 1997. Inducible Expression of Human Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) in Stably Transfected Hepatoblastoma Cells: a Novel System for Screening Potential Inhibitors of HBV Replication. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 41: 1715–1720.
Li F, Cheng L, Murphy CM, Reszka-Blanco NJ, Wu Y, Chi L, Hu J, Su L. 2016. Minicircle HBV cccDNA with a Gaussia luciferase reporter for investigating HBV cccDNA biology and developing cccDNA-targeting drugs. Scientific Reports, 6: 36483.
Lin SR, Yang HC, Kuo YT, Liu CJ, Yang TY, Sung KC, Lin YY, Wang HY, Wang CC, Shen YC, Wu FY, Kao JH, Chen DS, Chen PJ. 2014. The CRISPR/Cas9 system facilitates clearance of the intrahepatic HBV templates in vivo. Molecular therapy Nucleic acids, 3: e186.
Lilley CE, Schwartz RA,Weitzman MD. 2007. Using or abusing: viruses and the cellular DNA damage response. Trends Microbiol, 15: 119–126.
Lin GG, Zhang K, Li JM. 2015. Application of CRISPR/Cas9 Technology to HBV. Int J Mol Sci, 16: 26077–26086.
Liu Y, Li J, Chen J, Li Y, Wang W, Du X, Song W, Zhang W, Lin L, Yuan Z. 2015. Hepatitis B virus polymerase disrupts K63-linked ubiquitination of STING to block innate cytosolic DNAsensing pathways. J Virol, 89: 2287–2300.
Luangsay S, Gruffaz M, Isorce N, Testoni B, Michelet M, Faure-Dupuy S, Maadadi S, Ait-Goughoulte M, Parent R, Rivoire M, Javanbakht H, Lucifora J, Durantel D. 2015. Zoulim F Early inhibition of hepatocyte innate responses by hepatitis B virus. J Hepatol, 63: 1314–1322.
Lucifora J, Protzer U. 2016. Attacking hepatitis B virus cccDNA- The holy grail to hepatitis B cure. J Hepatol, 64: S41–S48.
Lucifora J, Xia Y, Reisinger F, Zhang K, Stadler D, Cheng X, Sprinzl MF, Koppensteiner H, Makowska Z, Volz T, Remouchamps C, Chou WM, Thasler WE, Hüser N, Durantel D, Liang TJ, Münk C, Heim MH, Browning JL, Dejardin E, Dandri M, Schindler M, Heikenwalder M, Protzer U. 2014. Specific and Nonhepatotoxic Degradation of Nuclear Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA. Science, 343: 1221–1228.
Luo X, Huang Y, Chen Y, Tu Z, Hu J, Tavis JE, Huang A, Hu Y. 2016. Association of Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA and Human APOBEC3B in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS One, 11: e0157708.
Murphy CM, Xu Y, Li F, Nio K, Reszka-Blanco N, Li X, Wu Y, Yu Y, Xiong Y, Su L. 2016. Hepatitis B Virus X protein promotes degradation of SMC5/6 to enhance HBV replication. Cell Rep, 16: 2846–2854.
Nassal M. 2015. HBV cccDNA: viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut, 64: 1972–1984.
Ni Y, Lempp FA, Mehrle S, Nkongolo S, Kaufman C, Fälth M, Stindt J, Königer C, Nassal M, Kubitz R, Sültmann H, Urban S. 2014. Hepatitis B and D viruses exploit sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide for species-specific entry into hepatocytes. Gastroenterology, 146: 1070–1083.
Niu C, Livingston CM, Li L, Beran RK, Daffis S, Ramakrishnan D, Burdette D, Peiser L, Salas E, Ramos H, Yu M, Cheng G, Strubin M, Delaney Iv WE, Fletcher SP. 2017. The Smc5/6 Complex Restricts HBV when Localized to ND10 without Inducing an Innate Immune Response and Is Counteracted by the HBV X Protein Shortly after Infection. PLoS One, 12: e0169648.
Ogi T, Lehmann AR. 2006. The Y-family DNA polymerase kappa (pol kappa) functions in mammalian nucleotide-excision repair. Nat Cell Biol, 8: 640–642.
Ogi T, Limsirichaikul S, Overmeer RM, Volker M, Takenaka K, Cloney R, Nakazawa Y, Niimi A, Miki Y, Jaspers NG, Mullenders LH, Yamashita S, Fousteri MI, Lehmann AR. 2010. Three DNA polymerases, recruited by different mechanisms, carry out NER repair synthesis in human cells. Mol Cell, 37: 714–727.
Palumbo GA, Scisciani C, Pediconi N, Lupacchini L, Alfalate D, Guerrieri F, Calvo L, Salerno D, Di Cocco S, Levrero M, Belloni L. 2015. IL6 inhibits HBV transcription by targeting the epigenetic control of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. PLoS One, 10: e0142599.
Pommier Y, Huang SY, Gao R, Das BB, Murai J, Marchand C. 2014. Tyrosyl-DNA-phosphodiesterases (TDP1 and TDP2). DNA Repair (Amst), 19: 114–129.
Qi Y, Gao Z, Xu G, Peng B, Liu C, Yan H, Yao Q, Sun G, Liu Y, Tang D, Song Z, He W, Sun Y, Guo JT, Li W. 2016. DNA Polymerase ? Is a Key Cellular Factor for the Formation of Covalently Closed Circular DNA of Hepatitis B Virus. PLoS Pathog, 12: e1005893.
Qi Z, Li G, Hu H, Yang C, Zhang X, Leng Q, Xie Y, Yu D, Zhang X, Gao Y, Lan K, Deng Q. 2014. Recombinant covalently closed circular hepatitis B virus DNA induces prolonged viral Persistence in Immunocompetent Mice. J Virol, 88: 8045–8056.
Ramanan V, Shlomai A, Cox DB, Schwartz RE, Michailidis E, Bhatta A, Scott DA, Zhang F, Rice CM, Bhatia SN. 2015. CRISPR/Cas9 cleavage of viral DNA efficiently suppresses hepatitis B virus. Sci Rep, 5: 10833.
Revill P, Locarnini S. 2016. Antiviral strategies to eliminate hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA). Curr Opin Pharmacol, 30: 144–150.
Rivière L, Gerossier L, Ducroux A, Dion S, Deng Q, Michel ML, Buendia MA, Hantz O, Neuveut C. 2015. HBX relieves chromatin- mediated transcriptional repression of hepatitis B viral cccDNA involving SETDB1 histone methyltransferase. J Hepatol, 63: 1093–1102.
Schubeler D. 2015. Function and information content of DNA methylation. Nature, 517: 321–326.
Schreiner S, Nassal M. 2017. A Role for the Host DNA Damage Response in Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA Formation—and Beyond?. Viruses, 9: 125.
Schwartz RE, Fleming HE, Khetani SR, Bhatia SN. 2014. Pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells. Biotechnol Adv, 32: 504–513.
Seeger C, Sohn JA. 2016. Complete Spectrum of CRISPR/Cas9- induced Mutations on HBV cccDNA. Mol Ther, 24: 1258–1266.
Seeger C, Sohn JA. 2014. Targeting hepatitis B virus cccDNA using CRISPR/Cas9. Mol Ther Nucl Acids, 3: e216.
Shimura S, Watashi K, Fukano K, Peel M, Sluder A, Kawai F, Iwamoto M, Tsukuda S, Takeuchi JS, Miyake T, Sugiyama M, Ogasawara Y, Park SY, Tanaka Y, Kusuhara H, Mizokami M, Sureau C, Wakita T. 2017. Cyclosporin derivatives inhibit hepatitis B virus entry without interfering with NTCP transporter activity. J Hepatol, 66: 685–692.
Si-Tayeb K, Noto FK, Nagaoka M, Li J, Battle MA, Duris C, North PE, Dalton S, Duncan SA. 2010. Highly efficient generation of human hepatocyte-like cells from induced pluripotent stem cells. Hepatology, 51: 297–305.
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. 2006. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell, 126: 663–676.
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S. 2007. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell, 131: 861–872.
Touboul T, Hannan NR, Corbineau S, Martinez A, Martinet C, Branchereau S, Mainot S, Strick-Marchand H, Pedersen R, Di Santo J, Weber A, Vallier L. 2010. Generation of functional hepatocytes from human embryonic stem cells under chemically defined conditions that recapitulate liver development. Hepatology, 51: 1754–1765.
Vivekanandan P, Daniel HDJ, Kannangai R, Martinez-Murillo F, Torbenson M. 2010. Hepatitis B virus replication induces methylation of both host and viral DNA. J. Virol, 84: 4321–4329.
Wieland SF. 2015. The chimpanzee model for hepatitis B virus infection. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 5. pii: a021469.
Wood RD., Mitchell M., Sgouros J., Lindahl T 2001. Human DNA repair genes. Science, 291: 1284–1289.
Yan H, Zhong G, Xu G, He W, Jing Z, Gao Z, Huang Y, Qi Y, Peng B, Wang H, Fu L, Song M, Chen P, Gao W, Ren B, Sun Y, Cai T, Feng X, Sui J, Li W. 2012. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. Elife, 1: e00049.
Yan Z, Zeng J, Yu Y, Xiang K, Hu H, Zhou X, Gu L, Wang L, Zhao J, Young JA, Gao L. 2017. HBV circle: A novel tool to investigate hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA. J Hepatol, pii: S0168-8278(17)30072-7.
Yang D, Zuo C, Wang X, Meng X, Xue B, Liu N, Yu R, Qin Y, Gao Y, Wang Q, Hu J, Wang L, Zhou Z, Liu B, Tan D, Guan Y, Zhu H. 2014. Complete replication of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus in a newly developed hepatoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 111: E1264–E1273.
Yang L, Lu M. 2017. Small molecule inhibitors of hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid assembly: a new approach to treat chronic HBV infection. Curr Med Chem, doi: 10.2174/09298673246661 70704121800.
Zhen S, Hua L, Liu YH, Gao LC, Fu J, Wan DY, Dong LH, Song HF, Gao X. 2015. Harnessing the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated Cas9 system to disrupt the hepatitis B virus. Gene Ther, 22: 404–412.
Zoulim F, Locarnini S. 2009. Hepatitis B virus resistance to nucleos(t)ide analogues. Gastroenterology, 137: 1593–1608.e1-2.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Key Project of Hubei Province Natural Science Foundation (2014CFA075), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31400153) and the Applied Basic Research Program (2015060101010033), Wuhan, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, M., Hu, K. Recent advances in the study of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA. Virol. Sin. 32, 454–464 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-017-4009-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-017-4009-4