Abstract
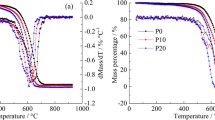
To evaluate the Influence of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers (PODE) on particulate matter (PM) chemical features, PM samples emitted from diesel fuel and PODE/diesel blends at volume ratios of 10 %, 20 %, and 30 % (P10, P20, and P30) were characterized using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic (FT-IR). Results showed that adding PODE in diesel fuel could increase the proportions of the lower carbon-atom-number components and the contents of oxygen-containing compounds in the soluble organic fractions extracted from PM samples. The ratio of oxygen to carbon (O/C), the functional groups, and the nanostructure of dry soot obtained from XPS showed that the O/C rose as the PODE volume ratio increased. The graphitization degree of dry soot decreased in the order: diesel fuel > P10 > P30 > P20. The relative content of hydroxyl functional groups exhibited the same trend, while the relative content of carbonyl functional groups exhibited an opposite trend with the graphitization degree. Moreover, according to FT-IR, both the branching degree and the relative content of hydrocarbon functional groups of aliphatics are influenced by the graphitization degree of dry soot. A turning point at P20 observed by analysis results above indicated that the chemical characteristics of PM could be affected not only by fuel properties but also by the process of fuel combustion and PM formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alptekin, E. (2017). Evaluation of ethanol and isopropanol as additives with diesel fuel in a CRDI diesel engine. Fuel, 205, 161–172.
Bagheri, M. and Baar, R. (2018). Simultaneous application of exhaust gas recirculation and non-constant injection rates to reduce NOx and soot emissions in diesel engines. Emission Control Science and Technology 4, 1, 4–14.
Bermudez, V., Luján, J. M., Ruiz, S., Campos, D. and Linares, W. G. (2015). New European Driving Cycle assessment by means of particle size distributions in a light-duty diesel engine fuelled with different fuel formulations. Fuel, 140, 649–659.
Bui, T. T., Balasubramanian, D., Hoang, A. T., Konur, O., Nguyen, D. C. and Tran, V. N. (2021). Characteristics of PM and soot emissions of internal combustion engines running on biomass-derived DMF biofuel: A review. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 1–22.
Burger, J., Siegert, M., Ströfer, E. and Hasse, H. (2010). Poly (oxymethylene) dimethyl ethers as components of tailored diesel fuel: Properties, synthesis and purification concepts. Fuel 89, 11, 3315–3319.
Cain, J. P., Gassman, P. L., Wang, H. and Laskin, A. (2010). Micro-FTIR study of soot chemical composition—evidence of aliphatic hydrocarbons on nascent soot surfaces. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 12, 20, 5206–5218.
Cao, D. N., Hoang, A. T., Luu, H. Q., Bui, V. G. and Tran, T. T. H. (2020). Effects of injection pressure on the NOx and PM emission control of diesel engine: A review under the aspect of PCCI combustion condition. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 1–18.
Ding, T., Shen, Z. and Zhang, J. (2016). Research progress on synthesis and application of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress 35, 3, 758–765.
Gao, W., Liu, J., Sun, P., Yang, C. and Fang, J. (2019). Gaseous emissions and particle microstructure characteristics of PODE/diesel blend fuel. Int. J. Automotive Technology 20, 3, 607–617.
Iannuzzi, S. E., Barro, C., Boulouchos, K. and Burger, J. (2017). POMDME-diesel blends: Evaluation of performance and exhaust emissions in a single cylinder heavy-duty diesel engine. Fuel, 203, 57–67.
Ibarra, J., Munoz, E. and Moliner, R. (1996). FTIR study of the evolution of coal structure during the coalification process. Organic Geochemistry 24, 6–7, 725–735.
Jamrozik, A., Tutak, W., Pyrc, M., Gruca, M. and Kočiško, M. (2018). Study on co-combustion of diesel fuel with oxygenated alcohols in a compression ignition dual-fuel engine. Fuel, 221, 329–345.
Kalghatgi, G. T., Risberg, P. and Ångström, H. (2007). Partially pre-mixed auto-ignition of gasoline to attain low smoke and low NOx at high load in a compression ignition engine and comparison with a diesel fuel. SAE Paper No. 2007-01-10006.
Liu, H., Wang, Z., Wang, J., He, X., Zheng, Y., Tang, Q. and Wang, J. (2015). Performance, combustion and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers (PODE3–4)/diesel blends. Energy, 88, 793–800.
Liu, H., Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Wang, J. and Shuai, S. (2017). Study on combustion and emission characteristics of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers/diesel blends in light-duty and heavy-duty diesel engines. Applied Energy, 185, 1393–1402.
Liu, J., Liu, Z., Wang, L., Wang, P., Sun, P., Ma, H. and Wu, P. (2021). Effects of PODE/diesel blends on particulate matter emission and particle oxidation characteristics of a common-rail diesel engine. Fuel Processing Technology, 212, 106634.
Liu, J., Wang, H., Li, Y., Zheng, Z., Xue, Z., Shang, H. and Yao, M. (2016). Effects of diesel/PODE (polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers) blends on combustion and emission characteristics in a heavy duty diesel engine. Fuel, 177, 206–216.
Liu, J., Yang, J., Sun, P., Gao, W., Yang, C. and Fang, J. (2019). Compound combustion and pollutant emissions characteristics of a common-rail engine with ethanol homogeneous charge and polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers injection. Applied Energy, 239, 1154–1162.
Meng, X., Hu, E., Yoo, K. H., Boehman, A. L. and Huang, Z. (2019). Experimental and numerical study on autoignition characteristics of the polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether/diesel blends. Energy & Fuels 33, 3, 2538–2546.
Mustafi, N. N., Raine, R. R. and James, B. (2010). Characterization of exhaust particulates from a dual fuel engine by TGA, XPS, and Raman techniques. Aerosol Science and Technology 44, 11, 954–963.
Pan, M., Wu, C., Qian, W., Wang, Y., Huang, H., Zhou, X. and Wei, J. (2022). Impact of dimethoxymethane-diesel fuel blends on the exhaust soot’s evolutionary behavior. Fuel, 309, 122221.
Pellegrini, L., Marchionna, M., Patrini, R., Beatrice, C., Del Giacomo, N. and Guido, C. (2012). Combustion behaviour and emission performance of neat and blended polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers in a light-duty diesel engine. SAE World Cong. & Exhibition, Detroit, Michigan, USA.
Pellegrini, L., Marchionna, M., Patrini, R. and Florio, S. (2013). Emission performance of neat and blended polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers in an old light-duty diesel car. SAE Paper No. 2013-01-1035.
Pirjola, L., Rönkkö, T., Saukko, E., Parviainen, H., Malinen, A., Alanen, J. and Saveljeff, H. (2017). Exhaust emissions of non-road mobile machine: Real-world and laboratory studies with diesel and HVO fuels. Fuel, 202, 154–164.
Qu, L. (2017). Study on the formation and characteristics of particles with biodiesel blend fuels in the exhaust gas atmosphere. Ph.D. Dissertation. Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China.
Ren, S., Wang, Z., Li, B., Liu, H. and Wang, J. (2019). Development of a reduced polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers (PODEn) mechanism for engine applications. Fuel, 238, 208–224.
Roy, M. M., Calder, J., Wang, W., Mangad, A. and Diniz, F. C. M. (2016). Cold start idle emissions from a modern Tier-4 turbo-charged diesel engine fueled with diesel-biodiesel, diesel-biodiesel-ethanol, and diesel-biodiesel-diethyl ether blends. Applied Energy, 180, 52–65.
Savic, N., Rahman, M. M., Miljevic, B., Saathoff, H., Naumann, K. H., Leisner, T., Riches, J., Gupta, B., Motta, N., and Ristovski, Z. D. (2016). Influence of biodiesel fuel composition on the morphology and microstructure of particles emitted from diesel engines. Carbon, 104, 179–189.
Shah, A. N., Ge, Y., Tan, J., Liu, Z., He, C. and Zeng, T. (2012). Characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon emissions from diesel engine retrofitted with selective catalytic reduction and continuously regenerating trap. J. Environmental Sciences 24, 8, 1449–1456.
Shi, Y., Cai, Y., Li, X., Ji, L., Chen, Y. and Wang, W. (2019). Evolution of diesel particulate physicochemical properties using nonthermal plasma. Fuel, 253, 1292–1299.
Smith, M., Scudiero, L., Espinal, J., McEwen, J. S. and Garcia-Perez, M. (2016). Improving the deconvolution and interpretation of XPS spectra from chars by ab initio calculations. Carbon, 110, 155–171.
Suhaimi, H., Adam, A., Mrwan, A. G., Abdullah, Z., Othman, M. F., Kamaruzzaman, M. K. and Hagos, F. Y. (2018). Analysis of combustion characteristics, engine performances and emissions of long-chain alcohol-diesel fuel blends. Fuel, 220, 682–691.
Sukjit, E., Herreros, J. M., Dearn, K. D., García-Contreras, R. and Tsolakis, A. (2012). The effect of the addition of individual methyl esters on the combustion and emissions of ethanol and butanol-diesel blends. Energy 42, 1, 364–374.
Sun, R., Chen, Z. and Li, K. (2013). Proportion optimization of ethanol-diesel fuel and engine performance test. Trans. Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering 29, 9, 55–63.
Tan, Y. R., Botero, M. L., Sheng, Y., Dreyer, J. A., Xu, R., Yang, W. and Kraft, M. (2018). Sooting characteristics of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether blends with diesel in a diffusion flame. Fuel, 224, 499–506.
Tian, J., Cai, Y., Shi, Y., Cui, Y. and Fan, R. (2019). Effect of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers/diesel blends on fuel properties and particulate matter oxidation activity of a light-duty diesel engine. Int. J. Automotive Technology 20, 2, 277–288.
Wang, H. W., Zhou, L. B., Jiang, D. M. and Huang, Z. H. (2000). Study on the performance and emissions of a compression ignition engine fuelled with dimethyl ether. Proc. Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: J. Automobile Engineering 214, 1, 101–106.
Wang, L., Song, C., Song, J., Lv, G., Pang, H. and Zhang, W. (2013). Aliphatic C–H and oxygenated surface functional groups of diesel in-cylinder soot: Characterizations and impact on soot oxidation behavior. Proc. Combustion Institute 34, 2, 3099–3106.
Wang, X., Wang, Y., Guo, F., Wang, D. and Bai, Y. (2020). Physicochemical characteristics of particulate matter emitted by diesel blending with various aromatics. Fuel, 275, 117928.
Weng, J. Q., Shen, Y. G., Zhang, X. L. and Fan, Y. L. (2008). The corrosion wear of biodiesel on diesel engine and its mechanism analysis. Lubrication Engineering 33, 8, 54–57.
Weng, S. (2010). Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. 2nd edn. Chemical Industry Press. Beijing, China.
Xie, M., Ma, Z. J., Wang, Q. H., Liu, J. C. and Liu, S. H. (2017). Investigation of engine combustion and emission performance fuelled with neat PODE and PODE/diesel blend. J. Xi’an Jiaotong University 51, 3, 32–37.
Yu, Y., Gang, L., Song, C., Song, J., Hao, B., Li, B. and Sun, H. (2016). Impact of oxidation reaction temperature on surface functional groups transformation of diesel particles. J. Combustion Science and Technology 22, 1, 37–44.
Zhang, P., He, J., Chen, H., Zhao, X. and Geng, L. (2020). Improved combustion and emission characteristics of ethylene glycol/diesel dual-fuel engine by port injection timing and direct injection timing. Fuel Processing Technology, 199, 106289.
Zhang, W. (2009). Effect of dimethyl carbonate on emission characteristics of diesel engines. Chemical Engineering (China) 37, 8, 59–62.
Zhang, W., Wei, X., Kin, D. and Zhu, Y. (2016). Experimental study on the influence of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers (PODE) on ultrafine particle emission of a compression ignition engine. J. Automotive Safety and Energy 7, 3, 330–336.
Zhang, X., Wu, P., Jiang, Z., Gao, X., Liu, T. and Hu, Y. (2015). Thermodynamic analysis on synthesis of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers. Chemical Engineering (China) 43, 4, 39–44.
Zhao, Y., Xu, Z., Chen, H., Fu, Y. and Shen, J. (2013). Mechanism of chain propagation for the synthesis of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers. J. Energy Chemistry 22, 6, 833–836.w
Zhou, X. (2017). Study on emission characteristics of particulate matter emitted from diesel engine fueled with blending biodiesel. M. S. thesis. Jiangsu University. Zhenjiang, China.
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by doctor of entrepreneurship and innovation in Jiangsu Province (JSSCBS20211280), Natural Science Research of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (18KJB470006), Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province (GDZB-128), Zhenjiang Key R&D Program-Social Development (SH2020006), and the Science Research Project of Xuzhou University of Technology (XKY2019217).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, X., Tian, J., Liu, S. et al. Particulate Matter Chemical Characteristics from a Light-Duty Diesel Engine Fueled with PODE/Diesel Blends. Int.J Automot. Technol. 24, 669–679 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-023-0056-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-023-0056-z